US Navy Essex-class aircraft carriers: USS Wasp (CV-18), USS Hancock (CV-19), USS Bennington (CV-20), USS Boxer (CV-21), USS Bon Homme Richard (CV-31), USS Leyte (CV-32), USS Kearsarge (CV-33)
The Essex class is a retired class of aircraft carriers of the United States Navy. The 20th century’s most numerous class of capital ship, the class consisted of 24 vessels which came in “short-hull” and “long-hull” versions. Thirty-two ships were ordered, but as the Second World War wound down, six were canceled before construction and two were canceled after construction had begun. Fourteen saw combat during the Second World War. None was lost to enemy action although several sustained crippling damage due to aerial attacks. Essex-class carriers were the backbone of the U.S. Navy from mid-1943 and, with the three Midway-class carriers added just after the war, continued to be the heart of U.S. naval strength until supercarriers joined the fleet starting in the 1950s. Several of the carriers were rebuilt to handle heavier and faster aircraft of the early jet age and saw service in the Vietnam War, with Lexington decommissioned as a training carrier in 1991. Of the 24 ships in the class, four – Yorktown, Hornet, Lexington, and Intrepid – have been preserved as museum ships. (Wikipedia)
USS Wasp (CV-18)
USS Wasp (CV-18). Commissioned 24 Nov 1943. Originally named Oriskany, she was renamed in honour of the previous Wasp, which was sunk in 1942. The second Wasp earned eight battle stars. The ship was decommissioned and recommissioned as an attack carrier and then an anti-submarine carrier. Finally, Wasp operated in the Atlantic, Mediterranean, and Caribbean, and retrieved astronauts from a number of Gemini missions. She was retired in 1972 and sold for scrap in 1973.

(USN Photo)
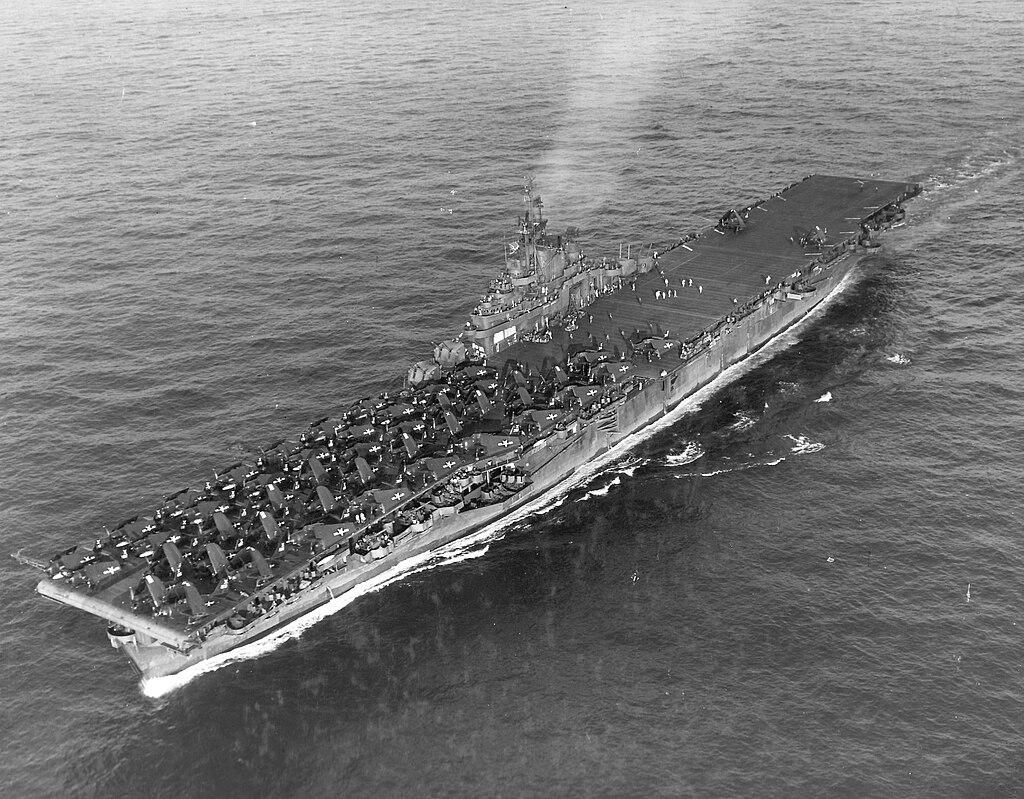
USS Wasp (CV-18) at sea in the Western Pacific on 6 August 1945. Note the scoreboard painted on the carrier’s island. On deck are various aircraft of Carrier Air Group 86 (CVG-86).

(USN Photo)
USS Wasp (CV-18) at the Boston Navy Yard on 14 March 1944. Wasp is painted in Measure 33, Design 10A camouflage.
USS Hancock (CV-19)
USS Hancock (CV-19). Commissioned April 1944. She joined Adm.ral W. F. Halsey’s 3rd Fleet. Her aircraft conducted strikes on enemy airfields and shipping in the Philippines. After the war, she underwent repairs and conversions, continuing its service in the Korean War and the Vietnam War. The ship received four battle stars from its time in the Second World War and the Navy Unit Commendation. She was sold for scrap in 1976.

(USN Photo)
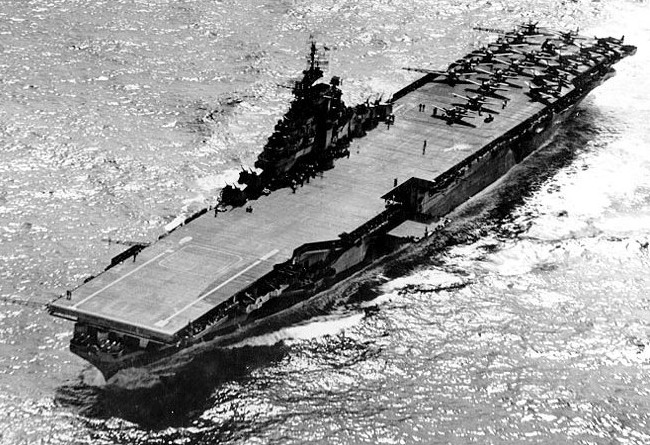
USS Hancock (CV-19) underway on 15 December 1944, during operations in the Philippines area.

(USN Photo)
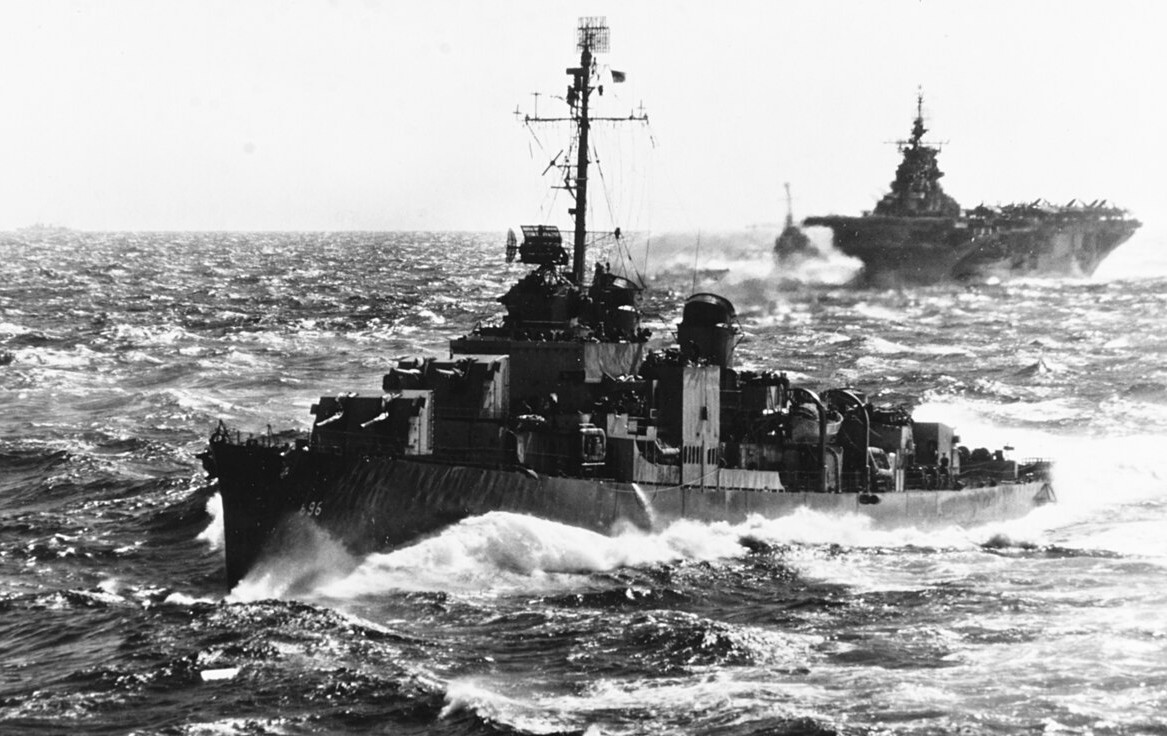
USS English (DD-696) and the aircraft carrier USS Hancock (CV-19) underway in the South China Sea, circa in January 1945. The photo was taken from the battleship USS New Jersey (BB-62).

(USN Photo)
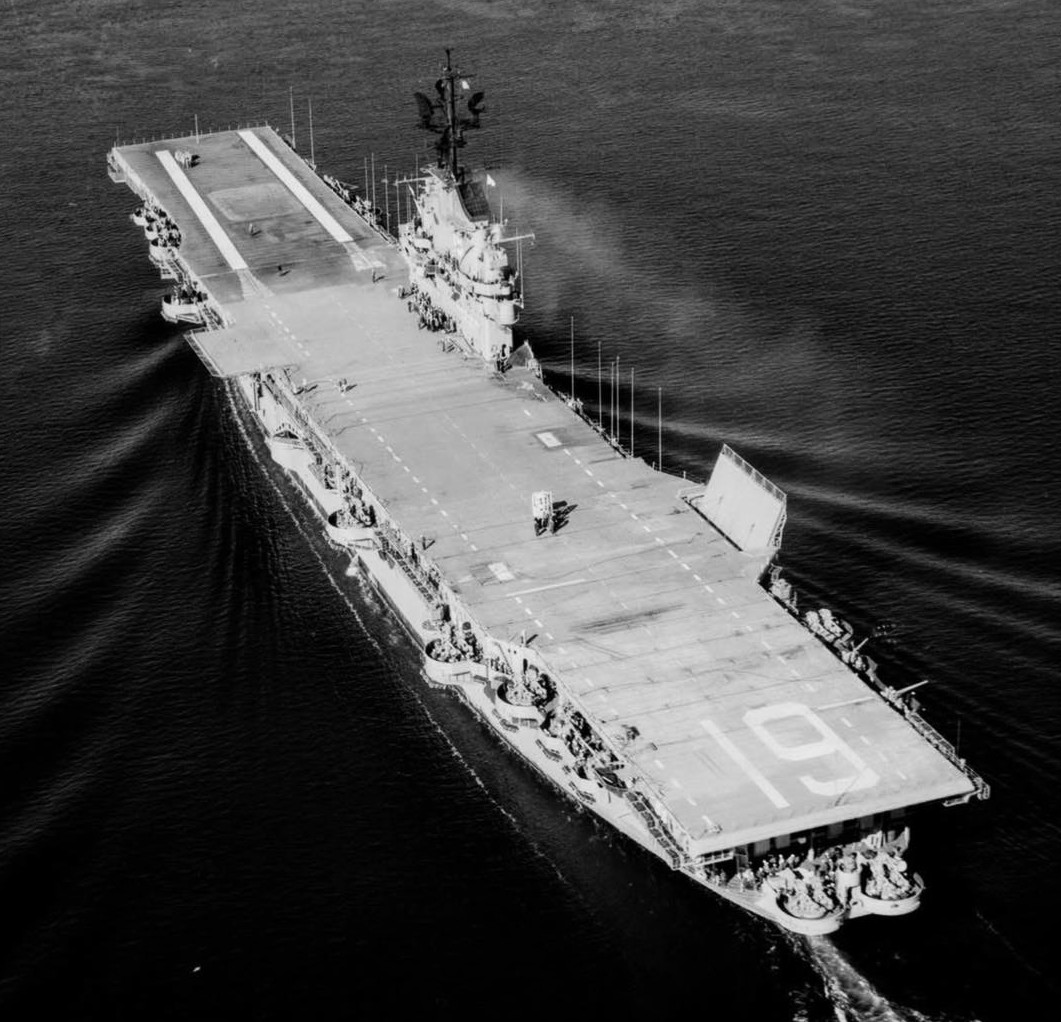
USS Hancock CVA-19 Puget Sound Washington March 1954.
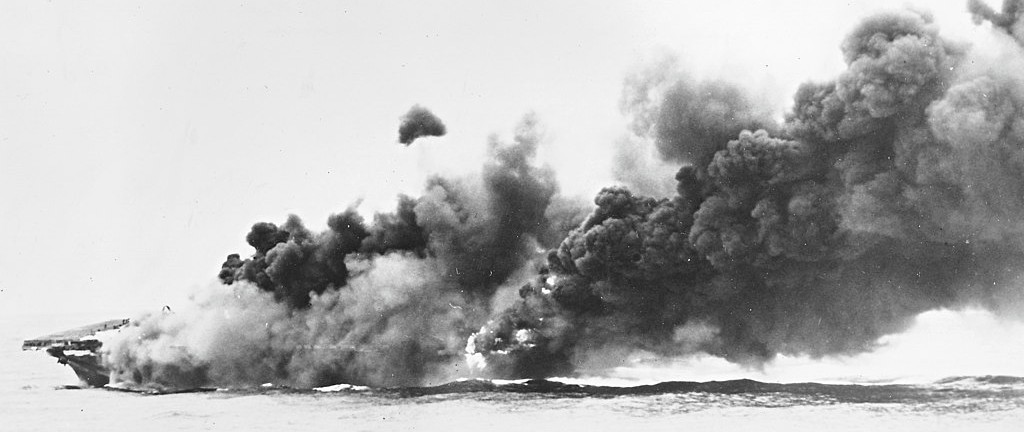

(USN Photo)
USS Hancock (CV-19) on fire after being hit by a kamikaze off Okinawa, 7 April 1945.
USS Bennington (CV-20)
USS Bennington (CVS-20). Commissioned 6 Aug 1944. She served toward the end of the war, participating in the invasion of Okinawa. Following the war, Bennington supported occupation forces in Japan. After recommissioning in 1952, Bennington deployed to the Far East and actively participated in the Vietnam War. After being decommissioned in 1970, the ship was placed in the Pacific Reserve Fleet before being stricken from the Naval Vessel Register in 1989.

(USN Photo)
USS Bennington (CV-20) underway during her shakedown, in the western Atlantic or Caribbean area, 20 October 1944. She is painted in camouflage Measure 32, Design 17A-1.
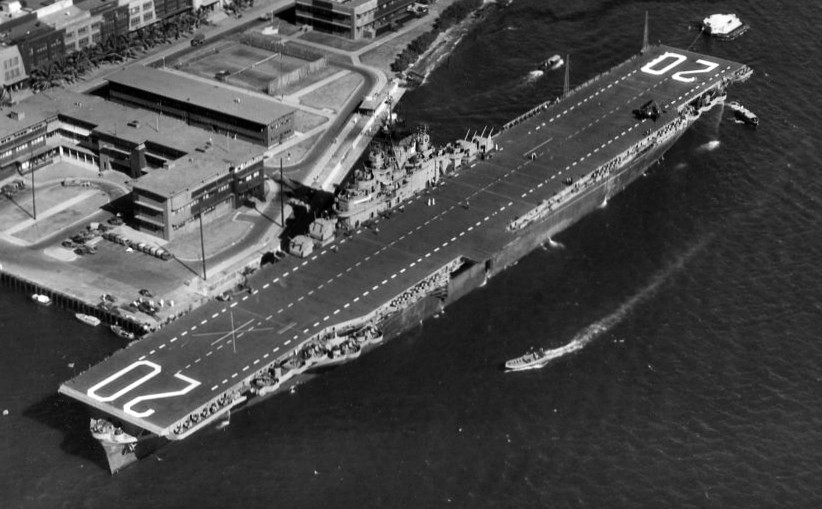

(USN Photo)
USS Bennington (CV-20) at Pearl Harbor, in January 1946. Note post-war high-visibility deck markings and the oil drifting aft of Bennington, most probably coming from the USS Arizona (BB-39), sunk five years earlier.
USS Boxer (CV-21)
USS Boxer (CV/CVA/CVS-21, LPH-4). Commissioned 15 April 1945. She was the fifth ship to be named for HMS Boxer. She was launched on 14 December 1944 and christened by the daughter of a US Senator from Louisiana. Commissioned too late to see any combat in the Second World War, Boxer spent much of her career in the Pacific Ocean, seeing 10 tours in the western Pacific. (Wikipedia)
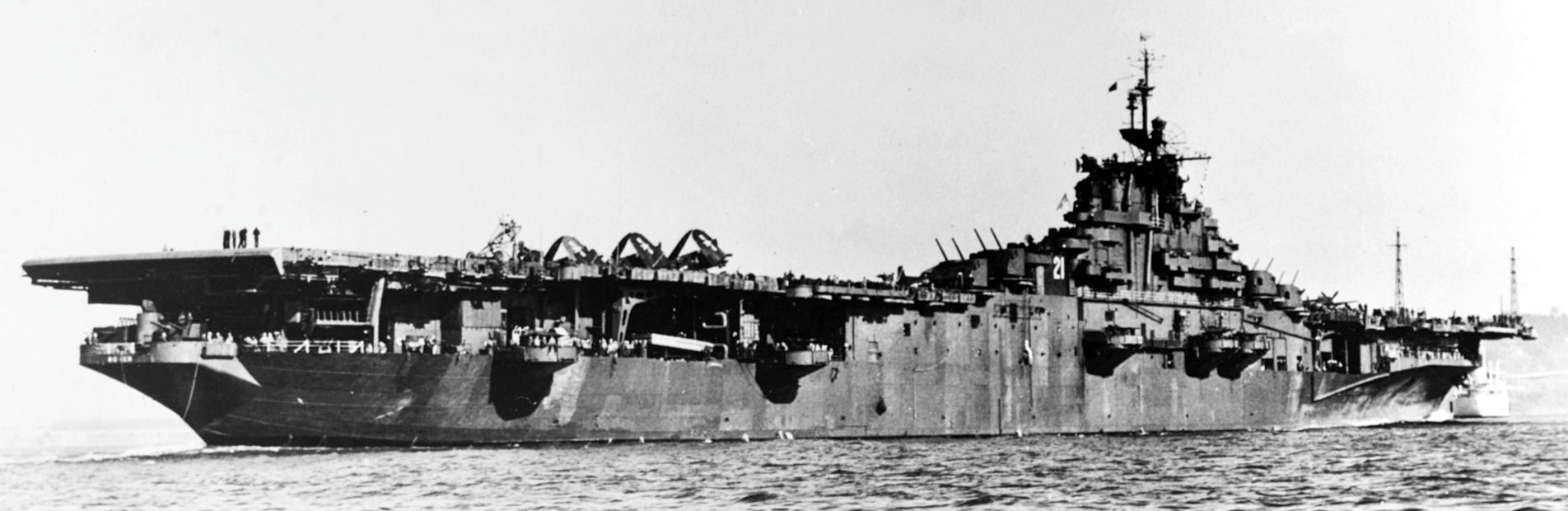
(USN Photo)
USS Boxer (CV-21) shortly after the end of the Second World War. She is painted in wartime Camouflage Measure 21 but has her hull number painted on the island.
USS Bon Homme Richard (CV-31)
USS Bon Homme Richard (CV-31). Commissioned 26 Nov 1944. She was an active participant in both the Second World War and the Korean War. After joining the Pacific Fleet, the carrier participated in attacks on Okinawa and launched strikes against Japan. Following the war, the ship transported service members home during Operation Magic Carpet. After being recommissioned in 1951, it conducted operations off Korea and engaged in heavy strikes against North Korean targets. Reclassified as an attack aircraft carrier, the Bon Homme Richard underwent modernization and continued serving with the Pacific Fleet. The ship was decommissioned in 1971 and scrapped in 1992.
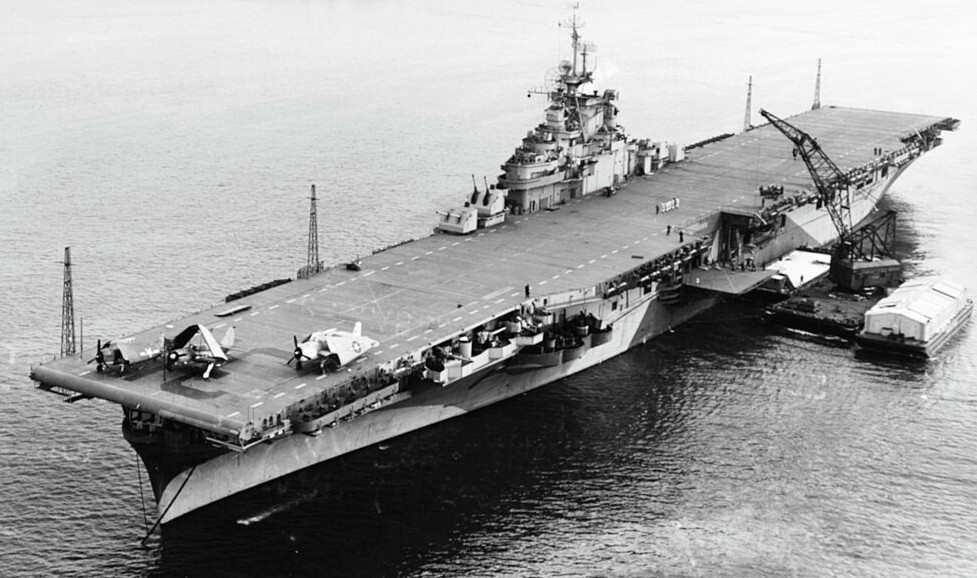

(USN Photo)
USS Bon Homme Richard (CV-31) anchored in New York harbor (USA), with supply barges alongside, on 9 January 1945.
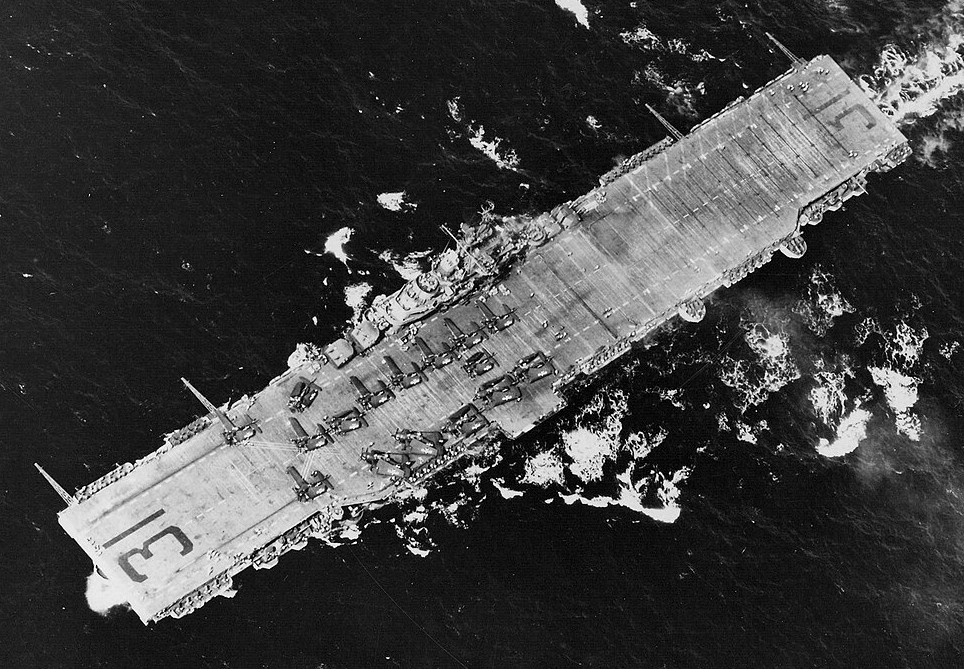

(USN Photo)
USS Bon Homme Richard (CV-31) at sea in the Central Pacific, in May 1945. On deck are aircraft of Night Carrier Air Group 91 (CVG(N)-91).
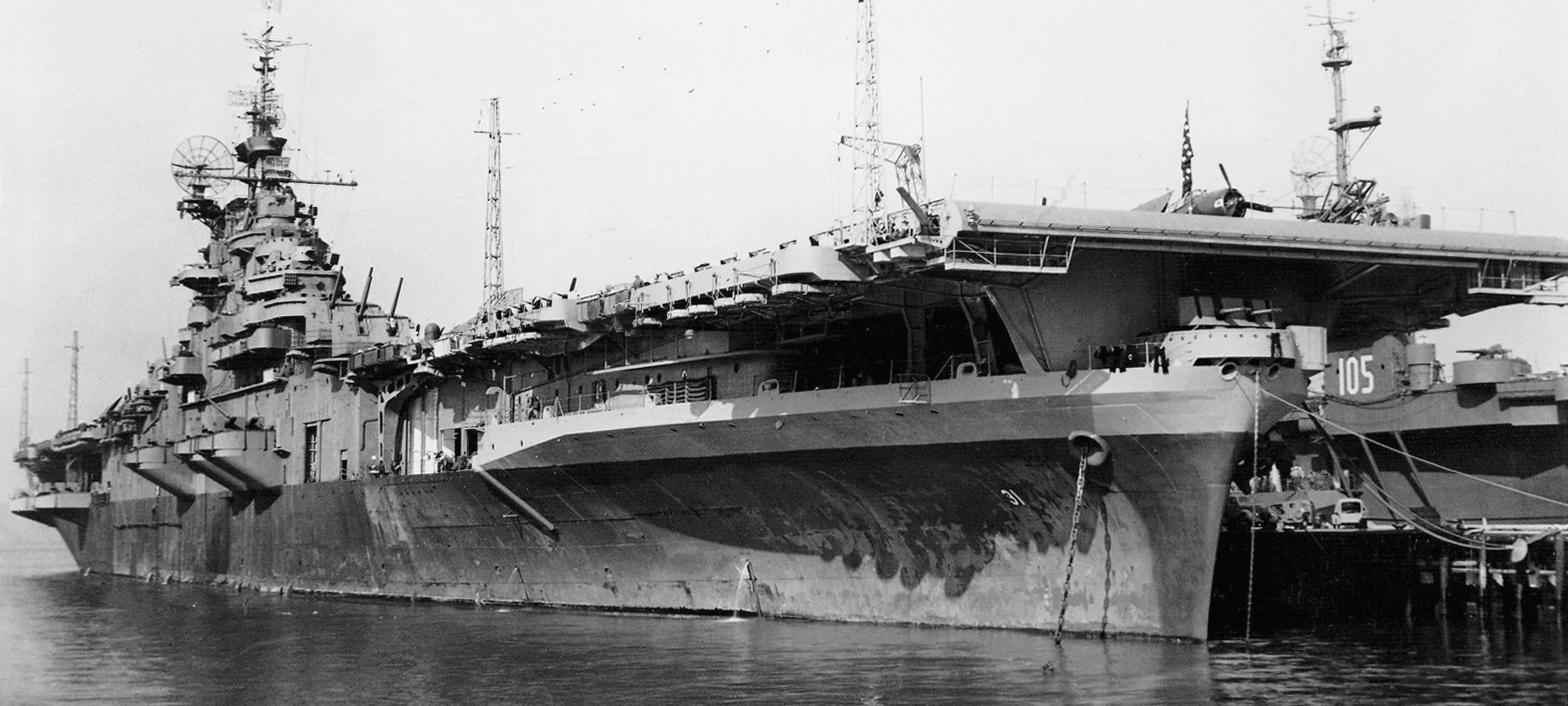

(USN Photo)
USS Bon Homme Richard (CV-31) at Naval Air Station Alameda, California (USA), on 27 October 1945. BHR wears measure 22 camouflage. Note the escort carrier USS Commencement Bay (CVE-105) in the background.
USS Leyte (CV/CVA/CVS-32, AVT-10)
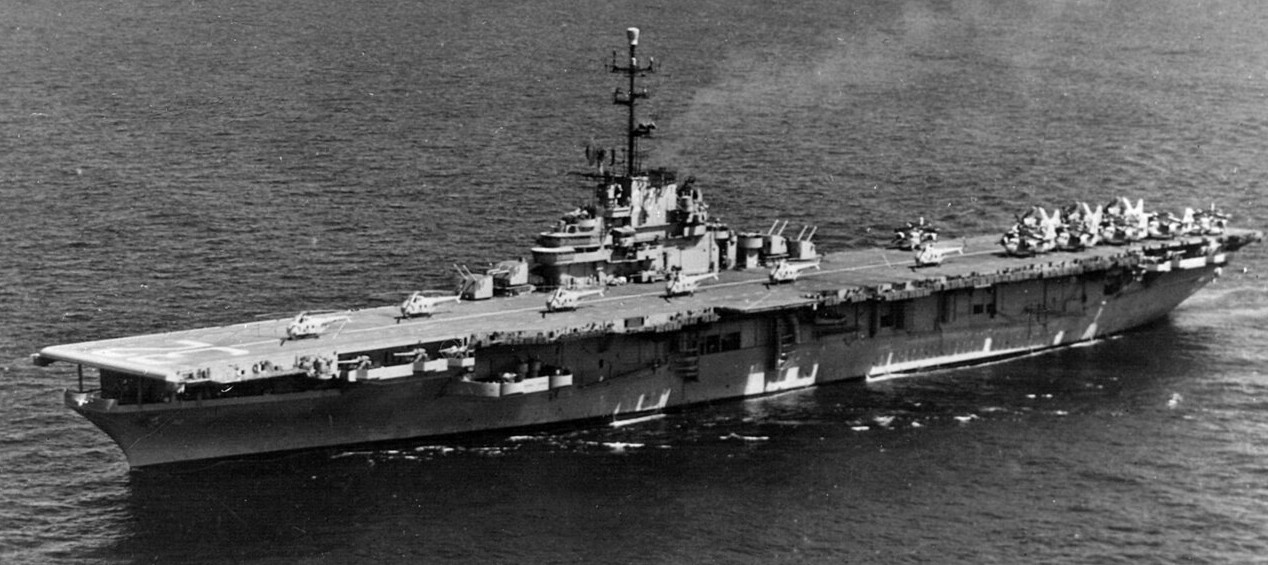

(USN Photo)
USS Leyte (CVS-32) underway, circa 1957. On deck are six Sikorsky HO4S helicopters, six Grumman S2F Tracker and three Douglas AD Skyraider aircraft.
USS Leyte (CV/CVA/CVS-32, AVT-10) was one of 24 Essex-class aircraft carriers built during and shortly after World War II for the United States Navy. The ship was the third US Navy ship to bear the name. Leyte was commissioned in April 1946, too late to serve in World War II. She spent most of her career in the Atlantic, Caribbean, and Mediterranean, but also saw service in the Korean War, in which she earned two battle stars. She was reclassified in the early 1950s as an attack carrier (CVA), then as an Antisubmarine Aircraft Carrier (CVS), and finally (after inactivation) as an aircraft transport (AVT). Unlike most of her sister ships, Leyte received no major modernizations, and thus throughout her career retained the classic appearance of a Second World War Essex-class ship. She was decommissioned in 1959 and sold for scrap in 1970. (Wikipedia)

(USN Photo)
USS Leyte (CV-32) on 10 May 1946, four weeks after her commissioning. Note that she is still painted in wartime Measure 21 camouflage.
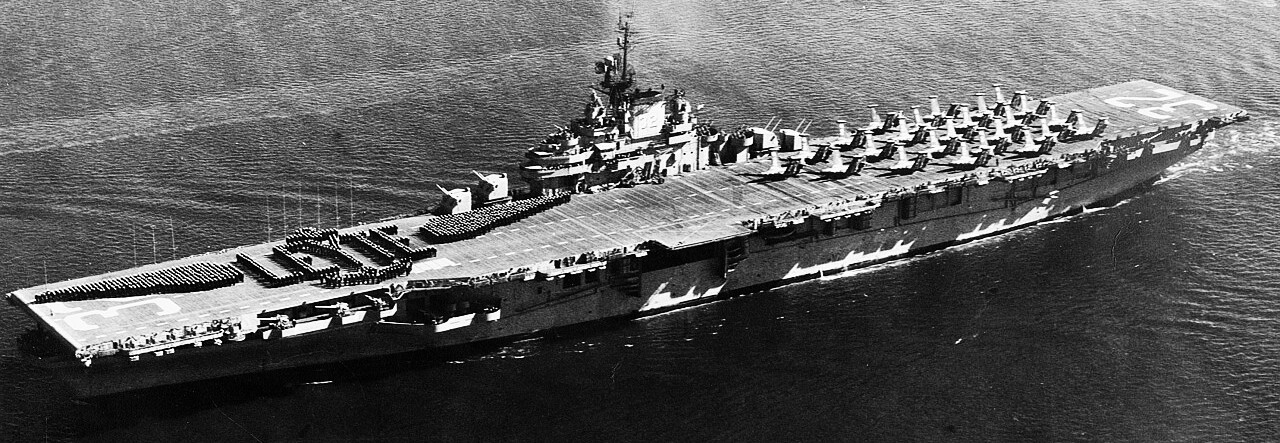

(USN Photo)
USS Leyte (CV-32) crew spelling out the name of the ship c1950. Note the Grumman F9F-2 Panthers of fighter squadron VF-31 Tomcatters positioned on the after end of the flight deck.
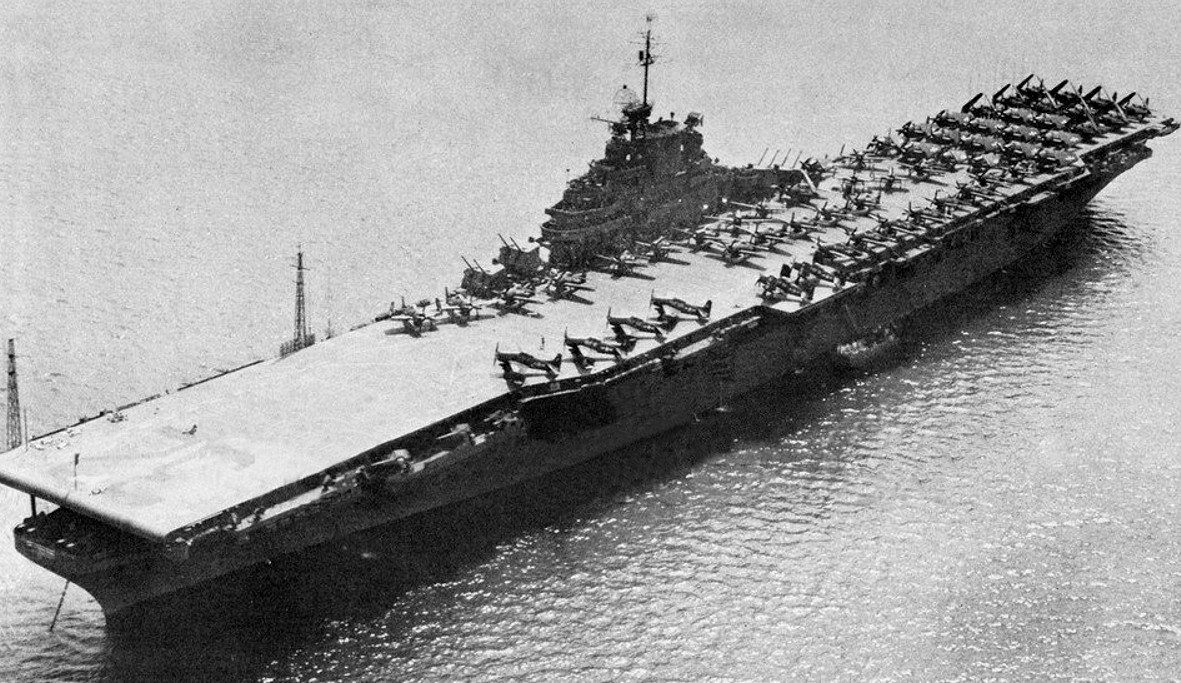

(USN Photo)
USS Leyte (CV-32) at anchor at Guantanmo Bay, Cuba. Leyte, with assigned Carrier Air Group 18 (CVG-18), was on her shakedown cruise to the Caribbean from 16 September to 12 December 1946.

(USN Photo)
USS Leyte (CV-32) underway with other elements of the 2nd Fleet during “Operation Frigid” in 1948.

(USN Photo)
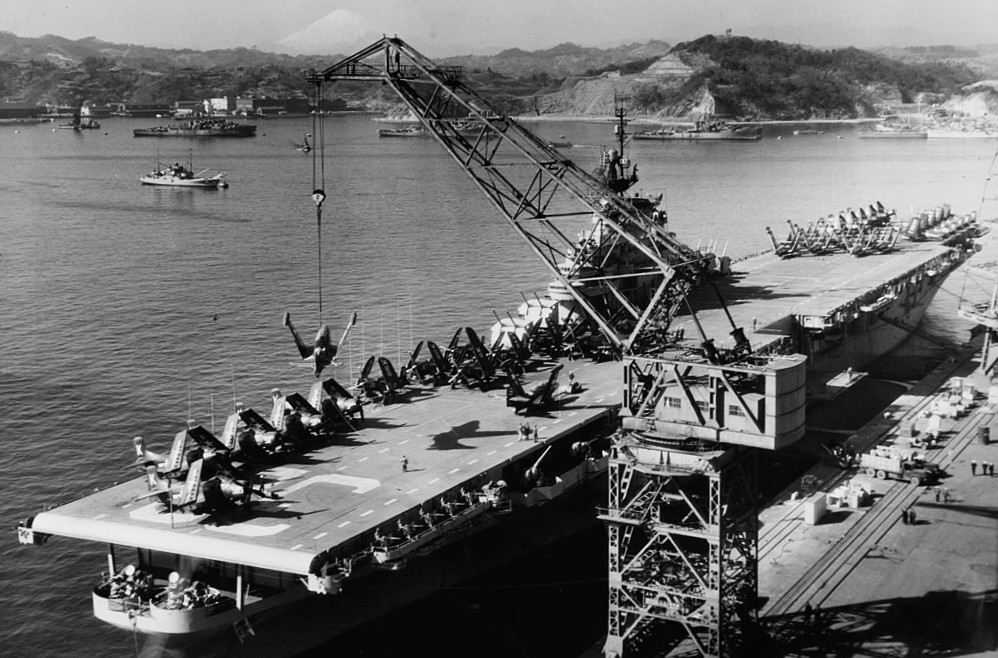
USS Leyte (CV-32) loading aircraft at Yokosuka, Japan, for transportation to the United States, at the end of her Korean War combat tour on 24 January 1951. Several decommissioned frigates (PF) are moored in groups across the harbour background and snow-capped Mount Fuji is visible in the left distance.

(USN Photo)
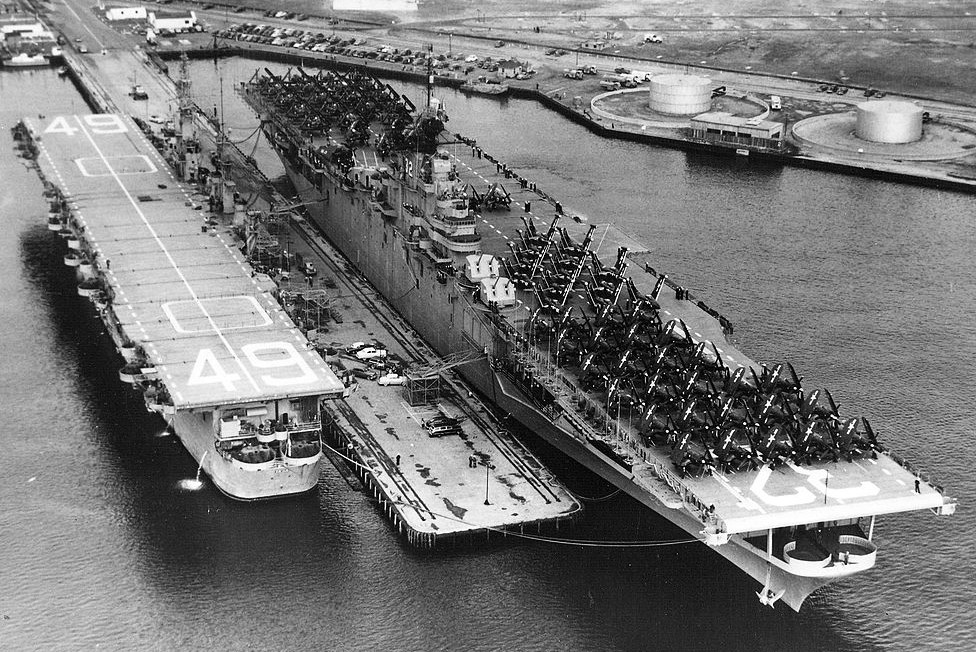
USS Leyte (CV-32) and USS Wright (CVL-49) moored at Naval Air Station Quonset Point, Rhode Island, c1950.

(USN Photo)
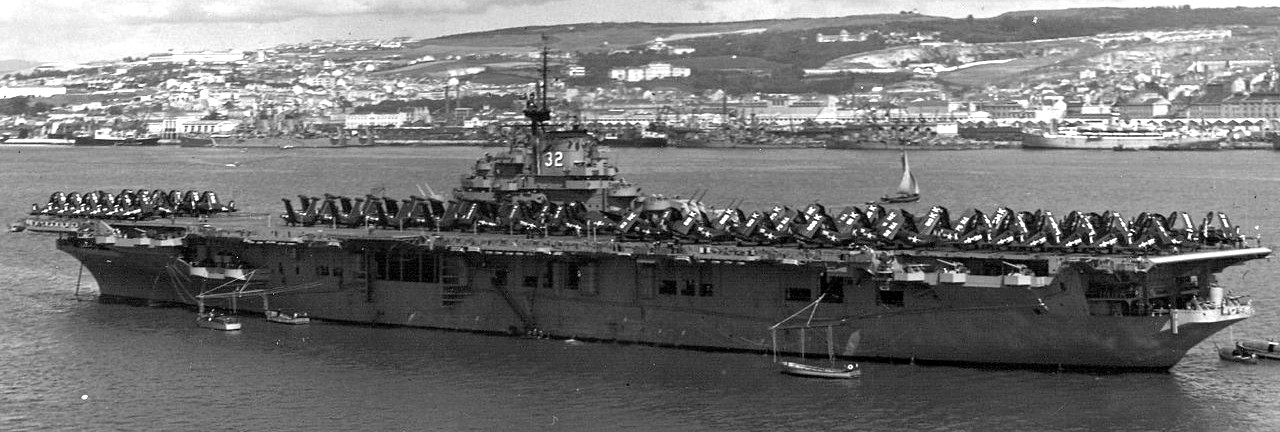
USS Leyte (CV-32) at anchor c1950..

(USN Photo)
U.S. Navy fleet oiler USS Canisteo (AO-99) refuels the aircraft carrier USS Leyte (CV-32) and the destroyer USS Purdy (DD-734) during U.S. Atlantic Fleet Operations on 4 March 1949. USS Caloosahatchee (AO-98) refuels USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVB-42) in the distance. Aircraft of Carier Air Group 9 (CVAG-9) are parked on Leyte‘s deck.
USS Kearsarge (CV-33)

(USN Photo)
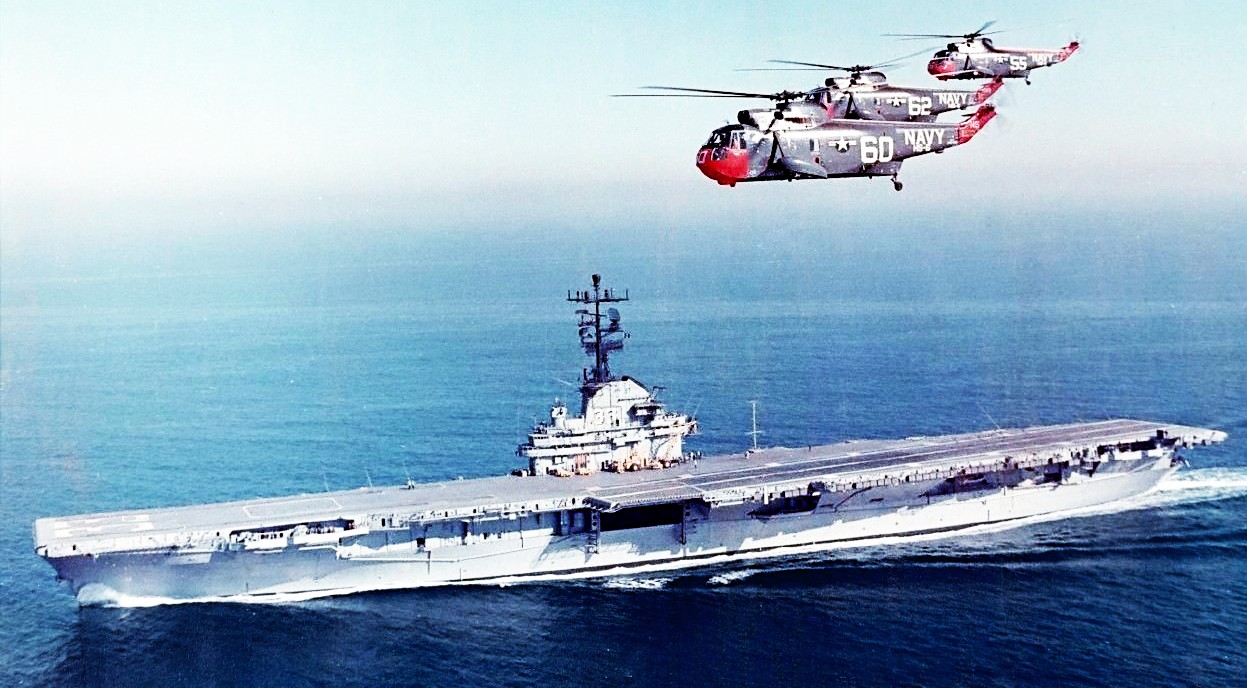
Three Sikorsky SH-3A Sea King from Helicopter Anti-Submarine Squadron 6 (HS-6) “Indians”, flying over the aircraft carrier USS Kearsarge (CVS-33). HS-6 was assigned to Carrier Anti-submarine Air Group 53 (CVSG-53) aboard Kearsarge. The picture was taken after the 1962 FRAM-modernisation, but the carrier still carries the SPS-8A radar. Also, the Sea Kings are not yet painted in the grey/white scheme, therefore the date is therefore probably 1962–1964.
USS Kearsarge (CV/CVA/CVS-33) was one of 24 Essex-class aircraft carriers completed during or shortly after the Second World War for the United States Navy. The ship was the third US Navy ship to bear the name, and was named for a Civil War-era steam sloop. Kearsarge was commissioned in March 1946. Modernized in the early 1950s as an attack carrier (CVA), she served in the Korean War, for which she earned two battle stars. In the late 1950s she was further modified to become an anti-submarine carrier (CVS). Kearsarge was the recovery ship for the last two crewed Project Mercury space missions in 1962–1963. She completed her career serving in the Vietnam War, earning five battle stars. She was decommissioned in 1970, and sold for scrap in 1974. (Wikipedia)

(USN Photo)
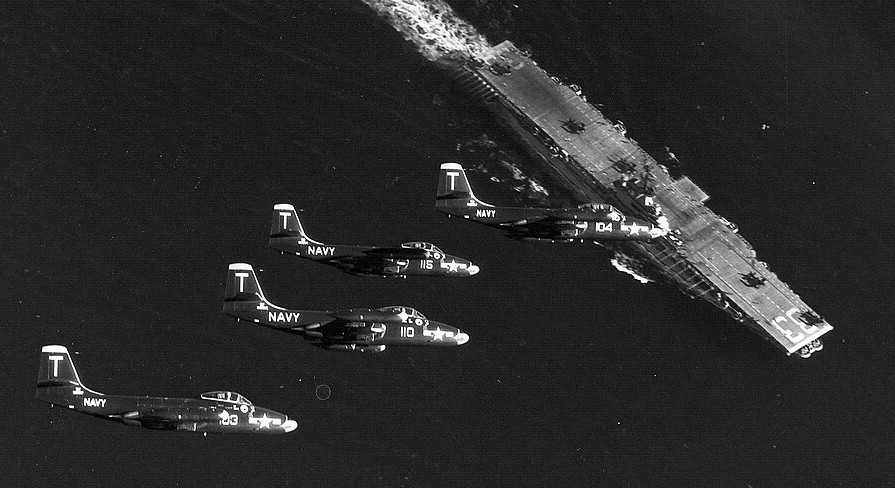
Four U.S. Navy McDonnell F2H-2 Banshee from fighter Squadron VF-11 Red Rippers fly over the aircraft carrier USS Kearsarge (CV-33) following a combat mission. Kearsarge was deployed to Korea with Carrier Air Group 101 (CVG-101) from 11 August 1952 to 17 March 1953.

(USN Photo)
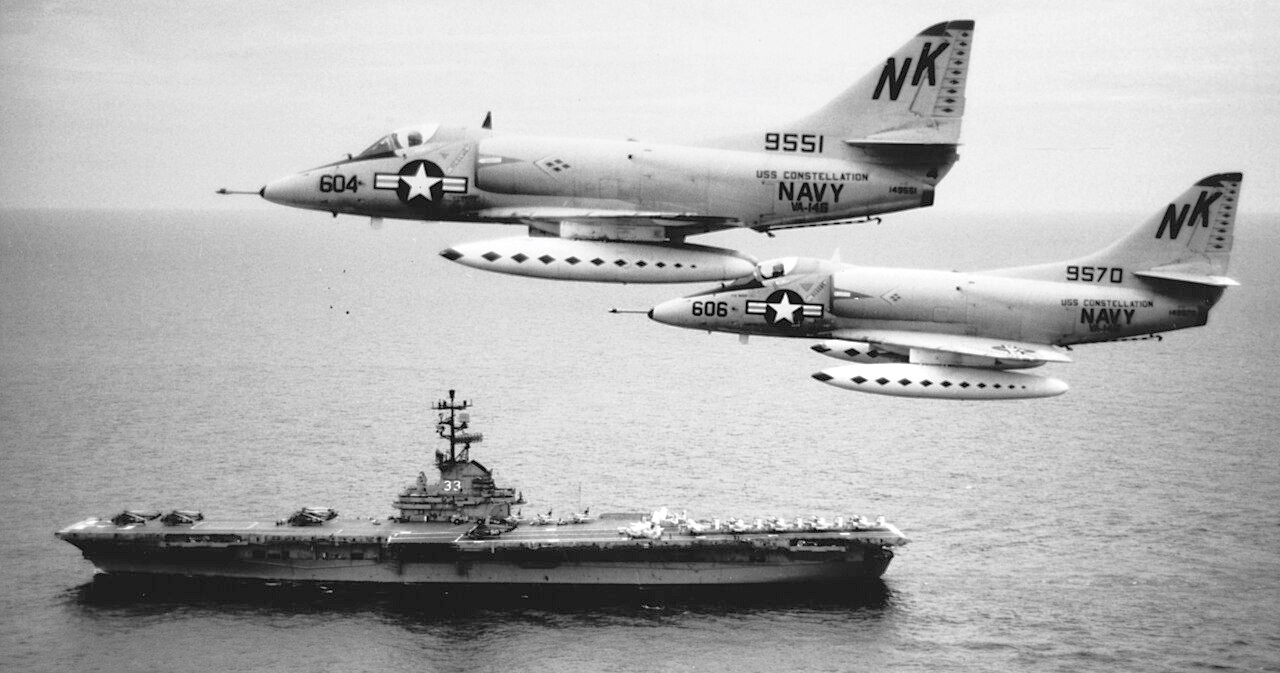
Two Douglas A-4C Skyhawk (BuNos. 149551 and 149570) of Attack Squadron 146 (VA-146) “Blue Diamonds” fly past the anti-submarine aircraft carrier USS Kearsarge (CVS-33). VA-146 was deployed as part of Carrier Air Wing 14 (CVW-14) on board the USS Constellation (CVA-64) to the Western Pacific and Vietnam from 5 May 1964 to 1 February 1965. Planes of CVW-14 took part in the August 1964 strikes against North Vietnamese PT-boat bases as a result of the Tonkin Gulf Incident. Aircraft BuNo. 149551 was later converted to the A-4L standard and in 1982 sold to Malaysia as a A-4PTM. USS Kearsarge, with assigned Carrier Anti-Submarine Air Group 53 (CVSG-53), was deployed to the Western Pacific an Vietnam from 19 June to 16 December 1964.

(USN Photo)
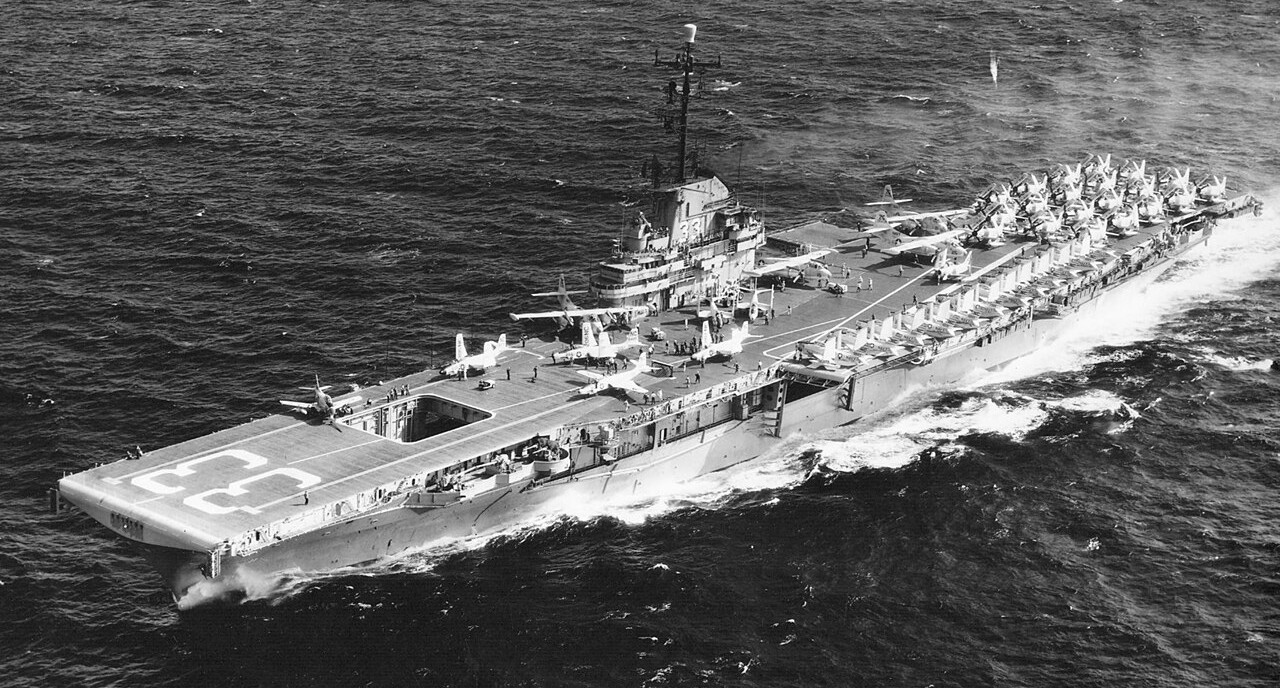
USS Kearsarge (CVA 33) arrived in Nagoya, Japan, on 30 September 1959, following a 400 mile high speed run. Helicopters were sent immediately to evacuate stranded Japanese and medical teams were dispatached to treat the sick and injured and inoculate against disease, 7 October 1959.

(USN Photo)
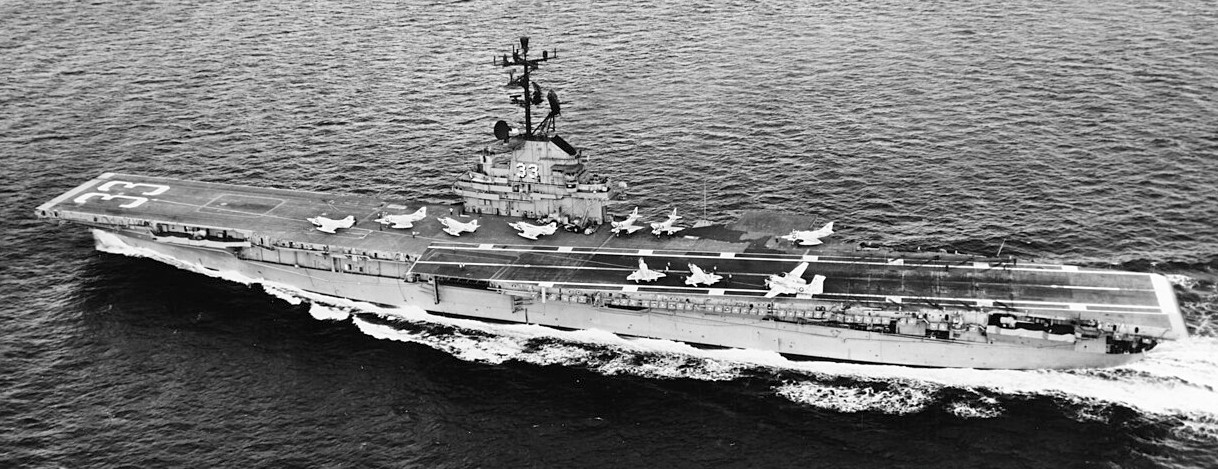
USS Kearsarge (CVS-33) at sea, 12 December 1965. Although being an anti-submarine carrier, she has nine Douglas A-4C Skyhawk attack jets on her flight deck, as well as one Grumman S-2 Tracker anti-submarine plane. Note: The Skyhawks wear the tail code “NG” of Attack Carrier Air Wing 9 (CVW-9). This wing, however, was assigned to USS Enterprise (CVAN-65) for a deployment from Norfolk, Virginia (USA) to Alameda, Califronia, and from there then to Vietnam from 26 October 1965 to 21 June 1966.

(USN Photo)
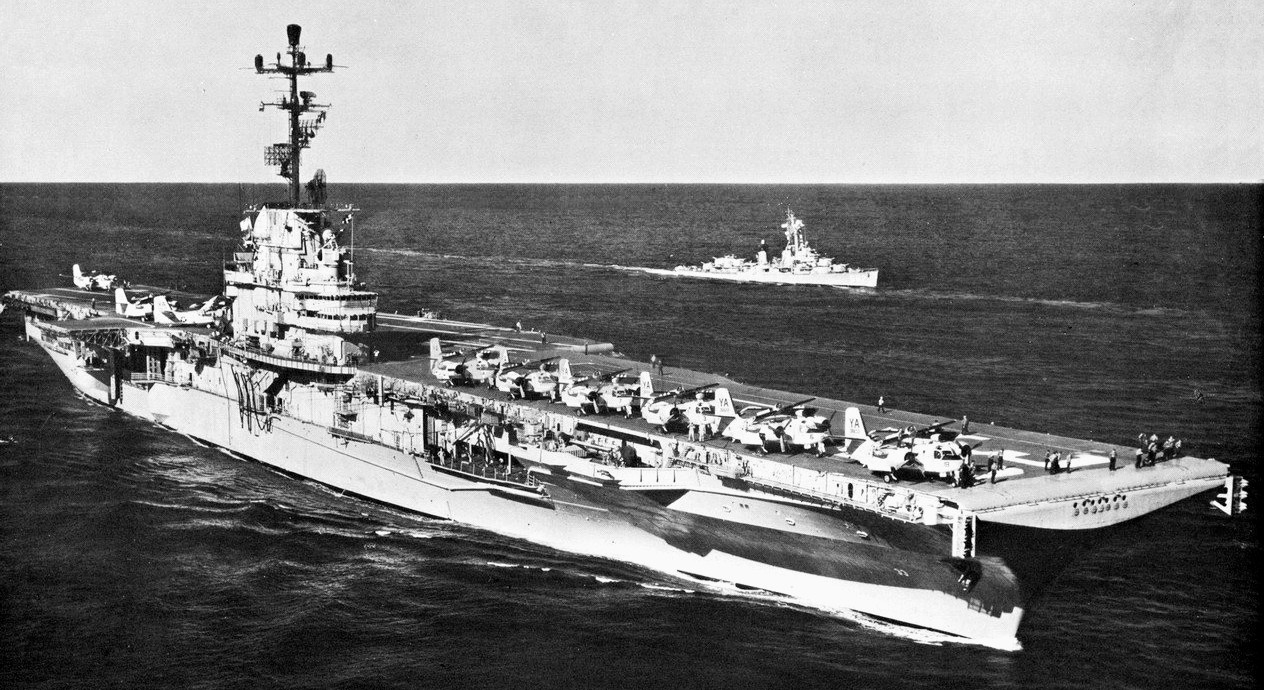
USS Kearsarge (CVS-33) underway during her first cruise as an anti-submarine carrier. Kearsarge was deployed to the Western Pacific from 5 September 1959 to 15 March 1960. The destroyer USS Porterfield (DD-682) is visible in the distance.

(USN Photo)
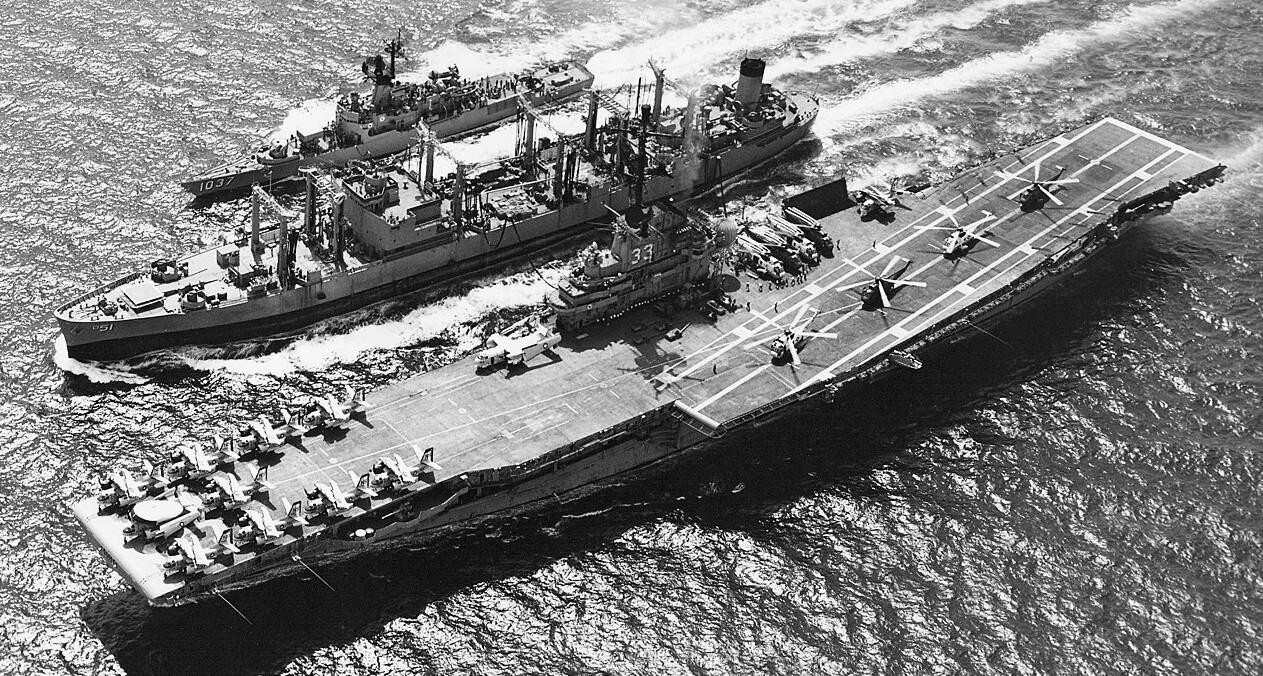
U.S. Navy oiler USS Ashtabula (AO-51) refuels the aircraft carrier USS Kearsarge (CVS-33) and destroyer escort USS Bronstein (DE-1037) in the Tonkin Gulf. Kearsarge was deployed to Vietnam with Carrier Anti-Submarine Air Group 53 (CVSG-53) from 29 March to 4 September 1969. This was her last deployment before her decommissioning on 15 January 1970. Note the fifferent colour schemes of the Sikorsky SH-3A Sea King helicopters of Helicopter Anti-Submarine Squadron HS-6 Indians. The dark-painted Sea Kings were often stripped of their ASW-gear, armed, and used to rescue downed aviators from Vietnam.

(USN Photo)
USS Kearsarge (CVS-33) underway off Guadalupe on 12 March 1968. Kearsarge, with assigned Carrier Anti-Submarine Air Group 53 (CVSG-53), was deployed to the Western Pacific and Vietnam from 18 August 1967 to 6 April 1968.
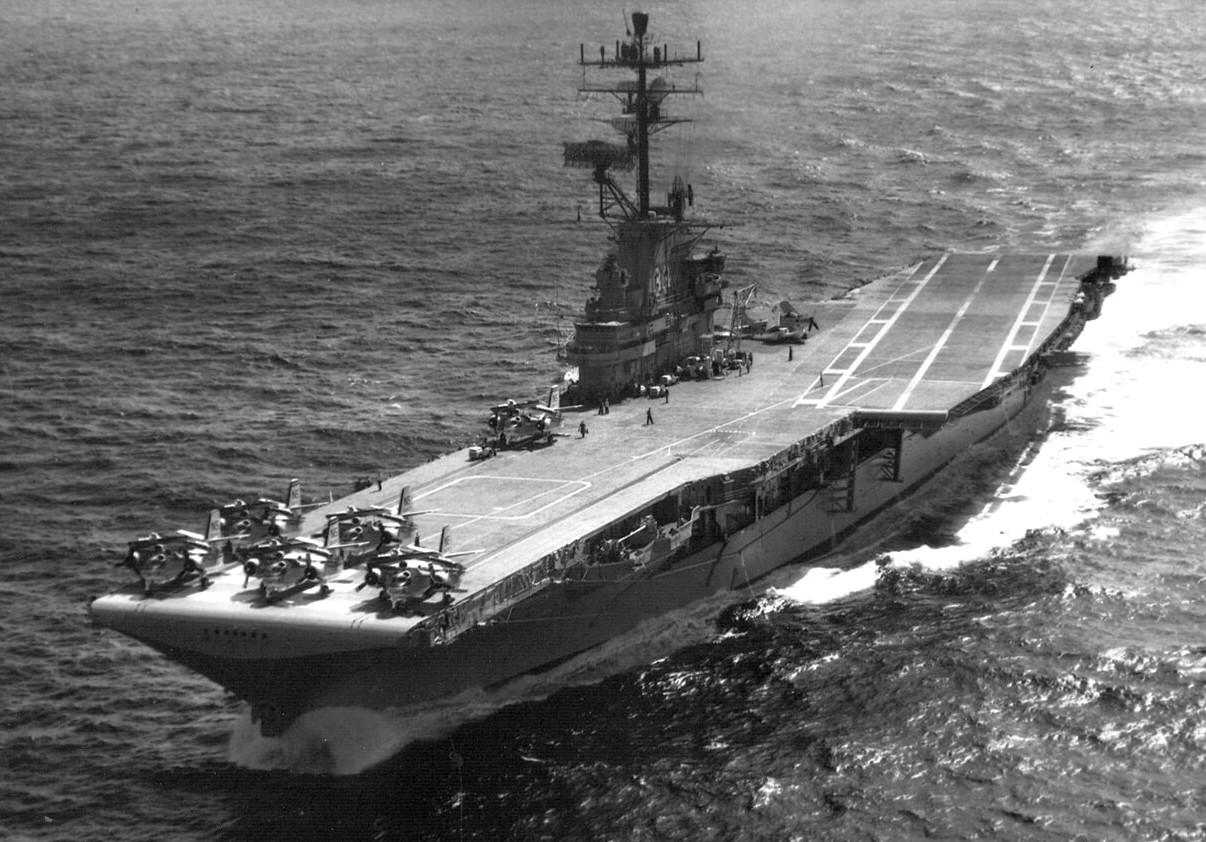

(USN Photo)
USS Kearsarge (CVS-33) underway. On deck are aircraft of Carrier Anti-Submarine Air Group 53 (CVSG-53). from august to October 1962, Kearsarge supported the recovery of the NASA Mercury-Atlas 8 mission, finally recovering the “Sigma 7” capsule in the Pacific missile range on 3 October 1962.

(USN Photo)
The crew of the USS Kearsarge (CVS-33) spells out the words “Mercury 9” on the ship’s flight deck while on the way to the recovery area where astronaut Gordon Cooper was expected to splash down in his “Faith 7” Mercury space capsule. The destroyers USS Fletcher (DD-445) and USS John A. Bole (DD-755) are steaming with Kearsarge.
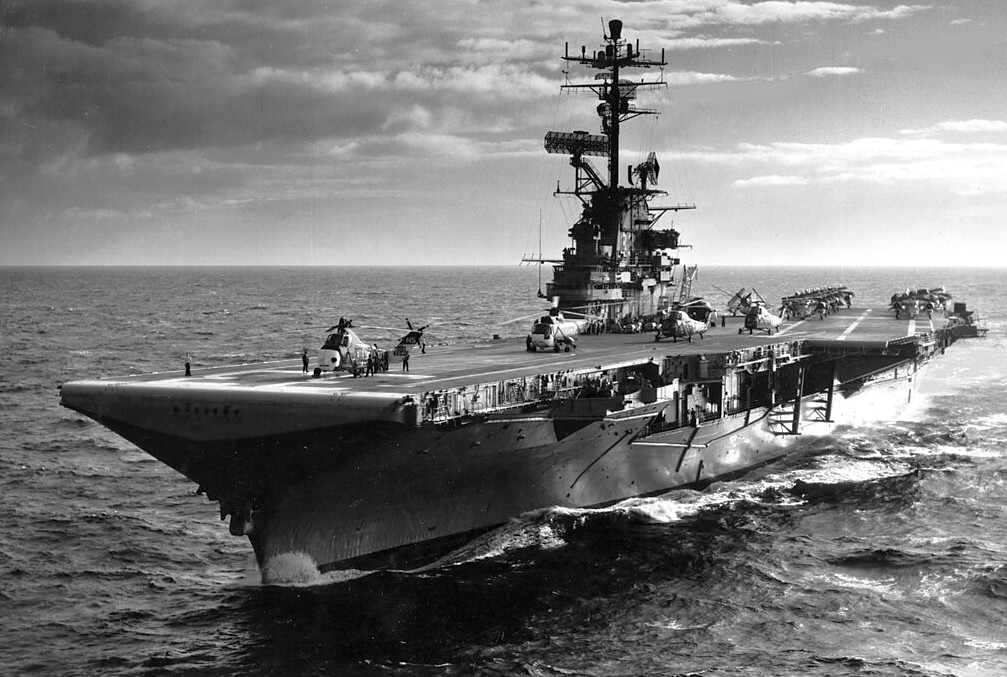

(USN Photo)
USS Kearsage (CVS-33) underway at sea off Oahu, Hawaii (USA), on 5 September 1962. Kearsarge, with assigned Carrier Anti-Submarine Air Group 53 (CVCG-53), was deployed off Oahu for the recovery of the Mercury-Atlas 8 (“Sigma 7”) space mission from 1 August to 3 October 1962.
