Aircraft Carriers of the USN:
USS Forrestal (CV-59), USS Saratoga (CV-60), USS Ranger (CV-61), USS Independence (CV-62), USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63), USS Constellation (CV-64), USS Enterprise (CVN-65), USS America (CV-66), USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67)
USS Forrestal (CV-59)
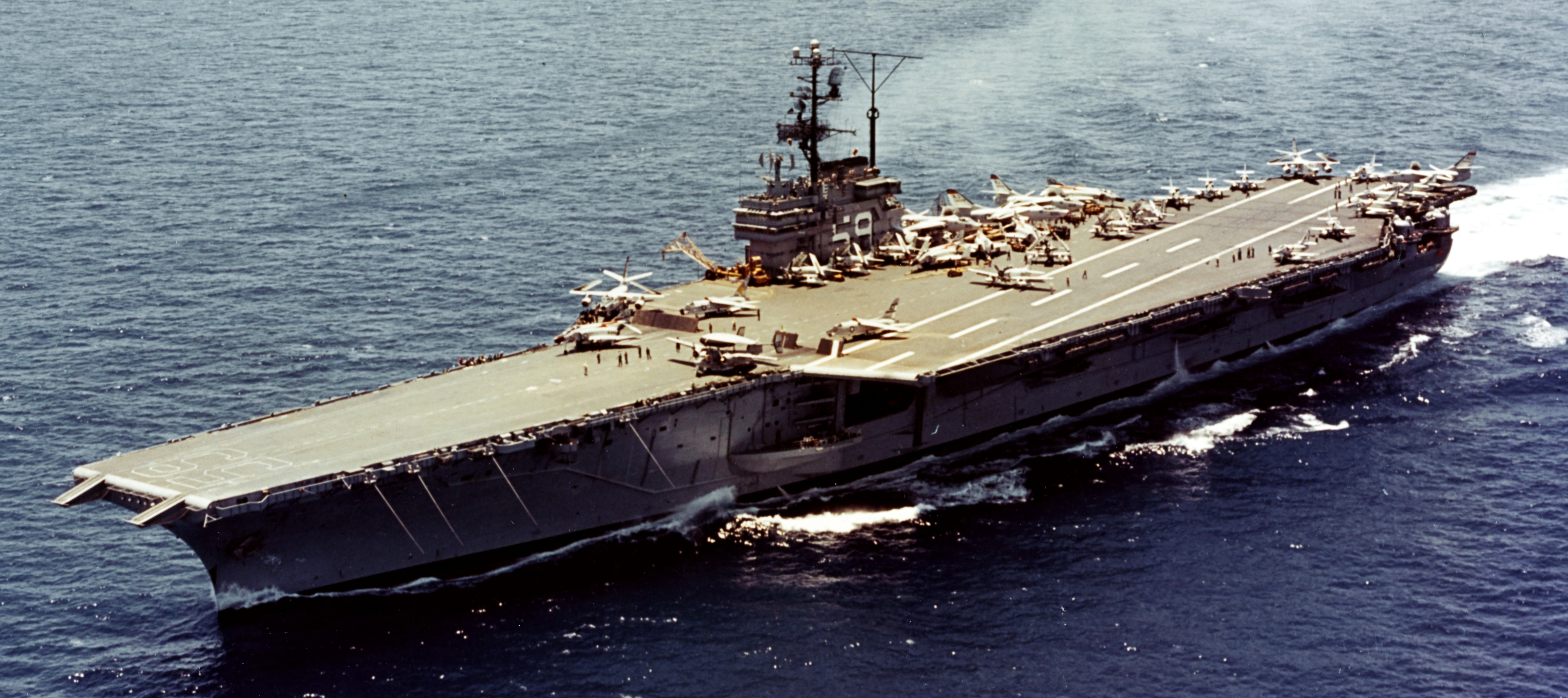

(USN Photo)
USS Forrestal (CVA-59) underway at sea while preparing for her fifth deployment. Forrestal, with assigned Carrier Air Group 8 (CVG-8) was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea from 3 August 1962 to 2 March 1963. Note that the carrier has McDonnell F4H-1 Phantom II jet fighters of Fighter Squadron 74 (VF-74) “Be-Devilers” in her air group. This was the first operational deployment of the Phantom II.
USS Forrestal (CVA-59) (later CV-59, then AVT-59), was a supercarrier named after the first United States Secretary of Defense James Forrestal. Commissioned in 1955, she was the United States’ first completed supercarrier, and was the lead ship of her class. The other carriers of her class were USS Saratoga, USS Ranger and USS Independence. She surpassed the Second World War Imperial Japanese Navy carrier Shinano as the largest carrier yet built, and was the first designed to support jet aircraft. The ship was affectionately called “The FID”, because her namesake was the first Secretary of Defense, FID standing for “First In Defense”. This is also the slogan on the ship’s insignia and patch. She suffered a number of highly publicized fires on board, most notably a 1967 fire in which 134 sailors died and 161 more were injured. Forrestal served for nearly four decades in the Atlantic, Mediterranean, and Pacific. She was decommissioned in 1993, and made available as a museum. Attempts to save her were unsuccessful, and in February 2014 she was towed to Brownsville, Texas, to be scrapped. Scrapping was completed in December 2015. (Wikipedia)
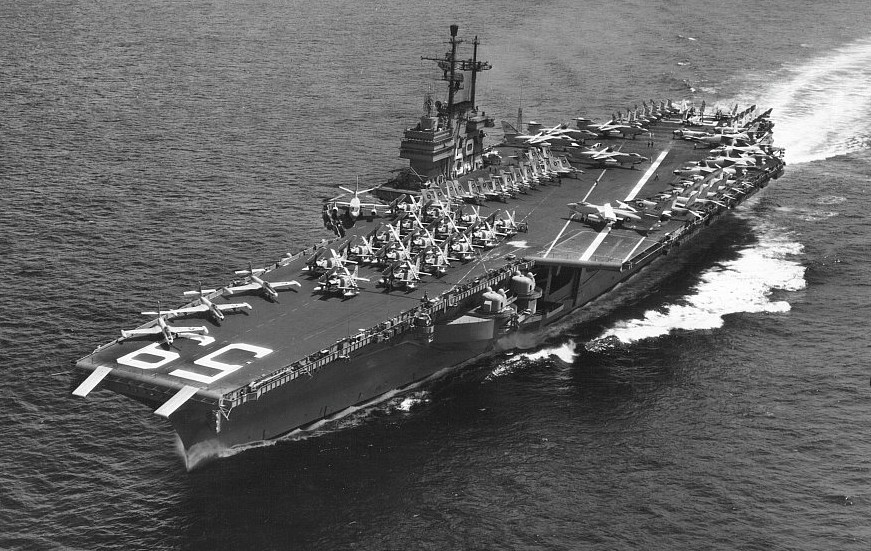

(USN Photo)
USS Forrestal (CVA-59) underway at sea in 1957. Forrestal, with assigned Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1), was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea from 15 January to 22 July 1957. From 16 August to 22 October, she took part in the NATO exercise “Strikeback” in the North Atlantic.

(USN Photo)
USS Forrestal (CVA-59) in 1955.

(USN Photo)
U.S. Navy Vought RF-8A Crusader (BuNo 146895) of Photographic Reconnaissance Squadron 62 (VFP-62) Det.59 “Fighting Photos” and two F-8C (BuNo 146932 and 145592) of Fighter Squadron 103 (VF-103) “Sluggers” fly over the aircraft carrier USS Forrestal (CVA-59), circa in August 1962. Both squadrons were assigned to Carrier Air Group Eight (CVG-8) aboard the Forrestal for a deployment to the Mediterranean Sea from 3 August 1962 to 2 March 1962. The F-8Cs are armed with AIM-9B Sidewinder missiles.
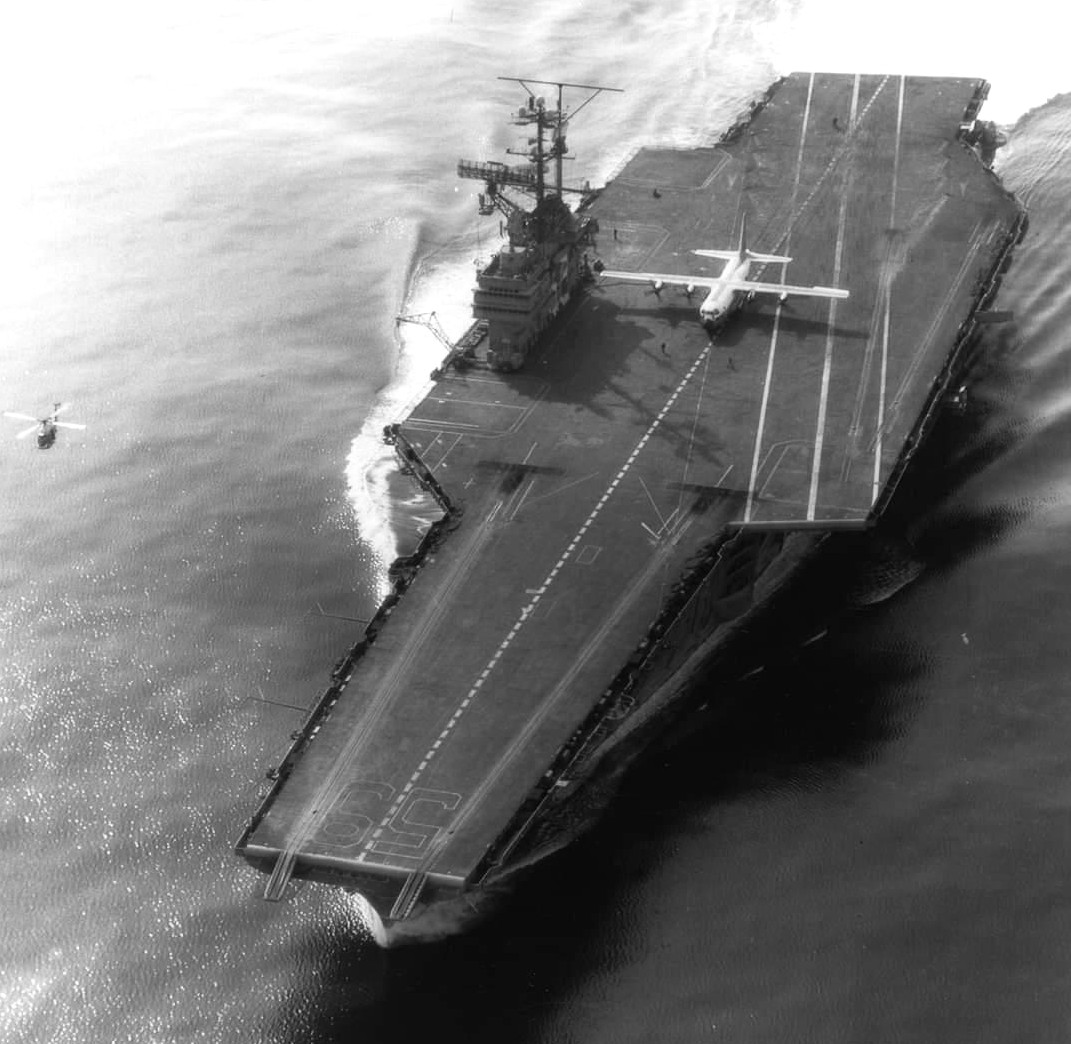

(USN Photo)
U.S. Navy Lockheed KC-130F Hercules (BuNo 149798) from Transport Squadron 1 (VR-1), loaned to the U.S. Naval Air Test Center aboard the aircraft carrier USS Forrestal (CVA-59) on 10 October 1963. Official description: “Forrestal made history in November 1963 when on the 8th, 21st and 22nd, LT James H. Flatley III and his crew members, LCDR [W. W.] ‘Smokey’ Stovall and Aviation Machinist’s Mate (Jets) 1st Class Ed Brennan, made [29 touch-and-go landings and] 21 full-stop landings and takeoffs in a Lockheed C-130F Hercules aboard the ship. The tests were conducted 500 miles [800 km] out in the North Atlantic off the coast of Massachusetts. In so doing, Forrestal and the C-130 set a record for the largest and heaviest airplane landing on a Navy aircraft carrier. The Navy was trying to determine if the big Hercules could serve as a ‘Super-COD’ — a ‘Carrier On-board Delivery’ aircraft. The problem was there were no aircraft which could provide resupply to a carrier in mid ocean. The Hercules was stable, reliable, and had a long cruising range and high payload.” “The tests were more than successful. At 85,000 pounds [39,000 kg], the C-130F came to a complete stop within 267 feet [81.4 meters], and at the maximum load [121,000 pounds, 55,000 kg], the plane used only 745 feet [227.1 meters] for take-off [and 460 feet, 140.2 meters, for landing]. The Navy concluded that with the C-130 Hercules, it would be possible to lift 25,000 pounds [11,000 kg] of cargo 2,500 miles [4,000 km] and land it on a carrier. However, the idea was considered a bit too risky for routine COD operations. The C-2A Greyhound program was developed and the first of these planes became operational in 1965. For his effort, the Navy awarded LT Flatley the Distinguished Flying Cross.”
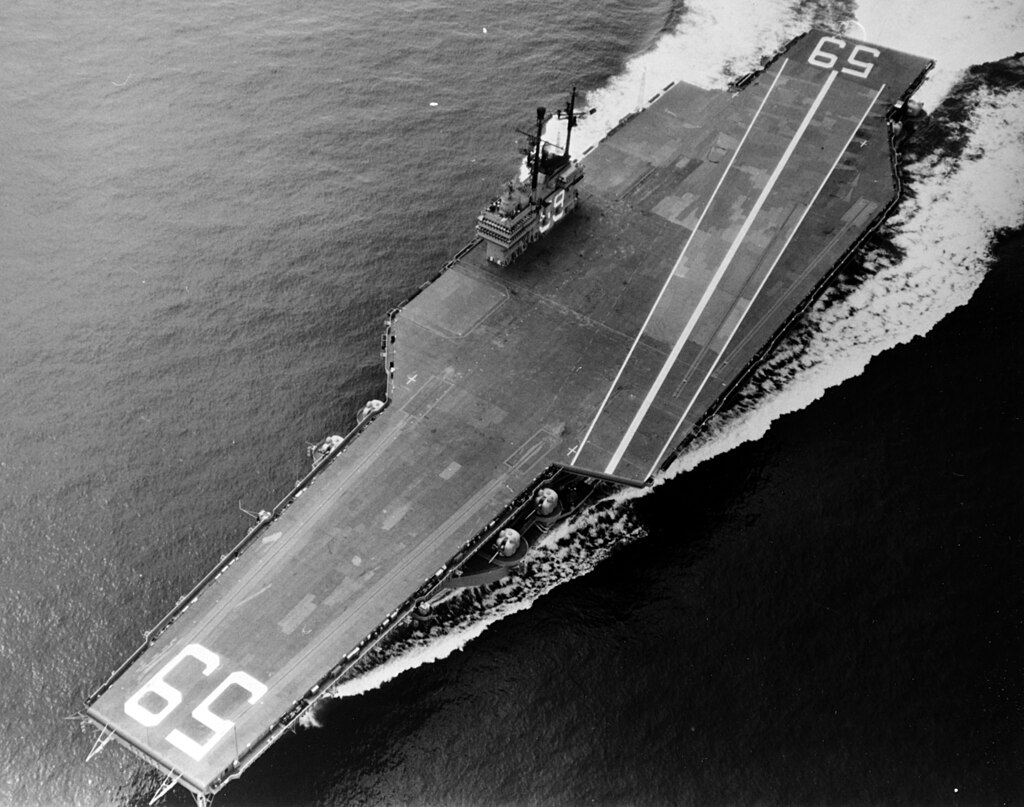

(USN Photo)
USS Forrestal (CVA-59): Underway on trials, 29 September 1955, just prior to commissioning.

(USN Photo)
USS Forrestal (CV-59) aerial starboard quarter, June 1982.
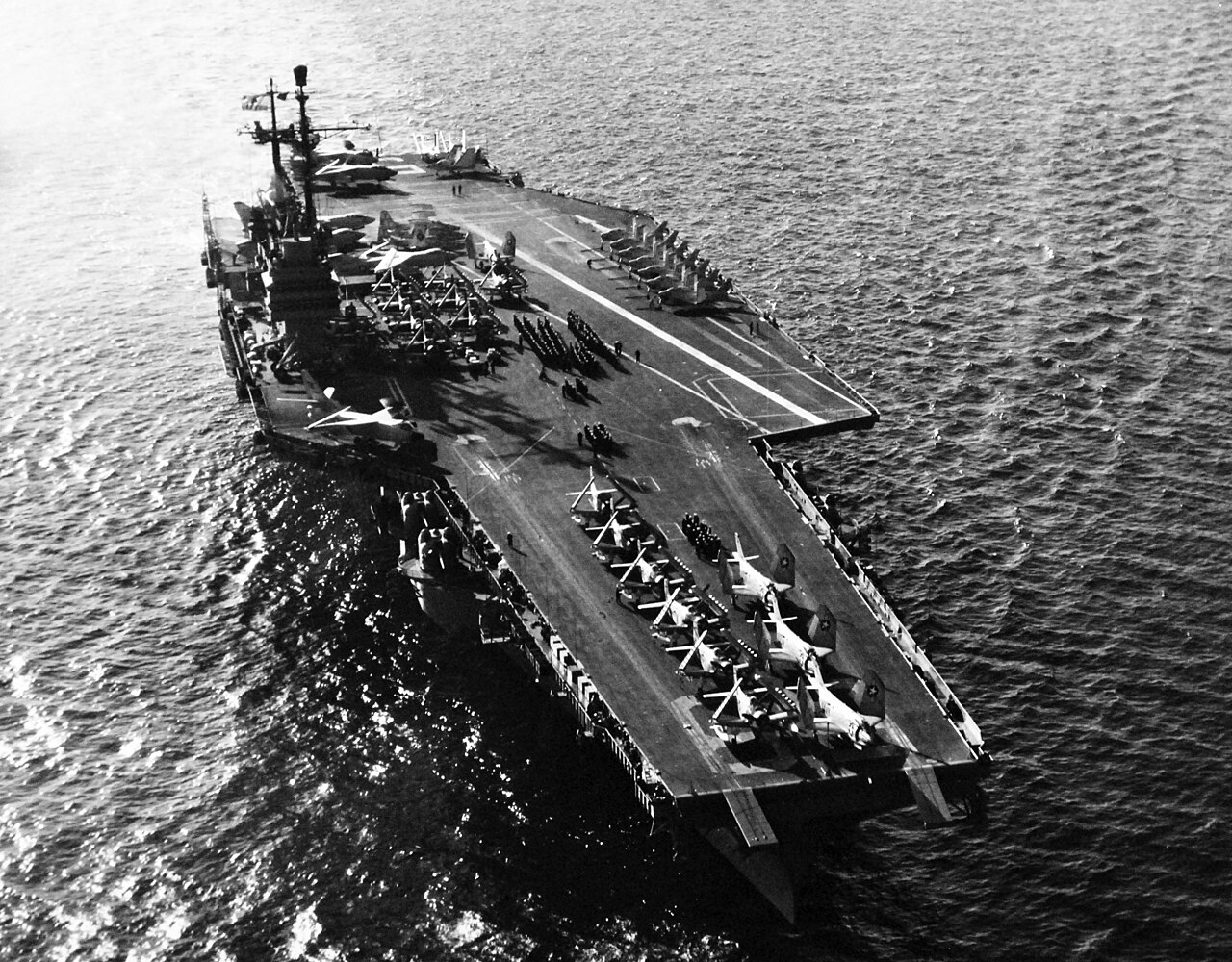

(USN Photo)
USS Forrestal (CV-59) with its air group embarked while on maneuvers with the Sixth Fleet. The wide white line running diagonally across the flight deck is used by landing aircraft to aid lining up for landing. Landing and launching may be accomplished simultaneously on the Navy’s latest “flat tops,” greatly increasing the ships operating efficiency. The propeller driven AD Skyraiders on the forward flight deck, famous for low support work during the Korean War, are used for anti-submarine warfare and low altitude by the fleet. 21 October 1957.
USS Saratoga (CV-60)
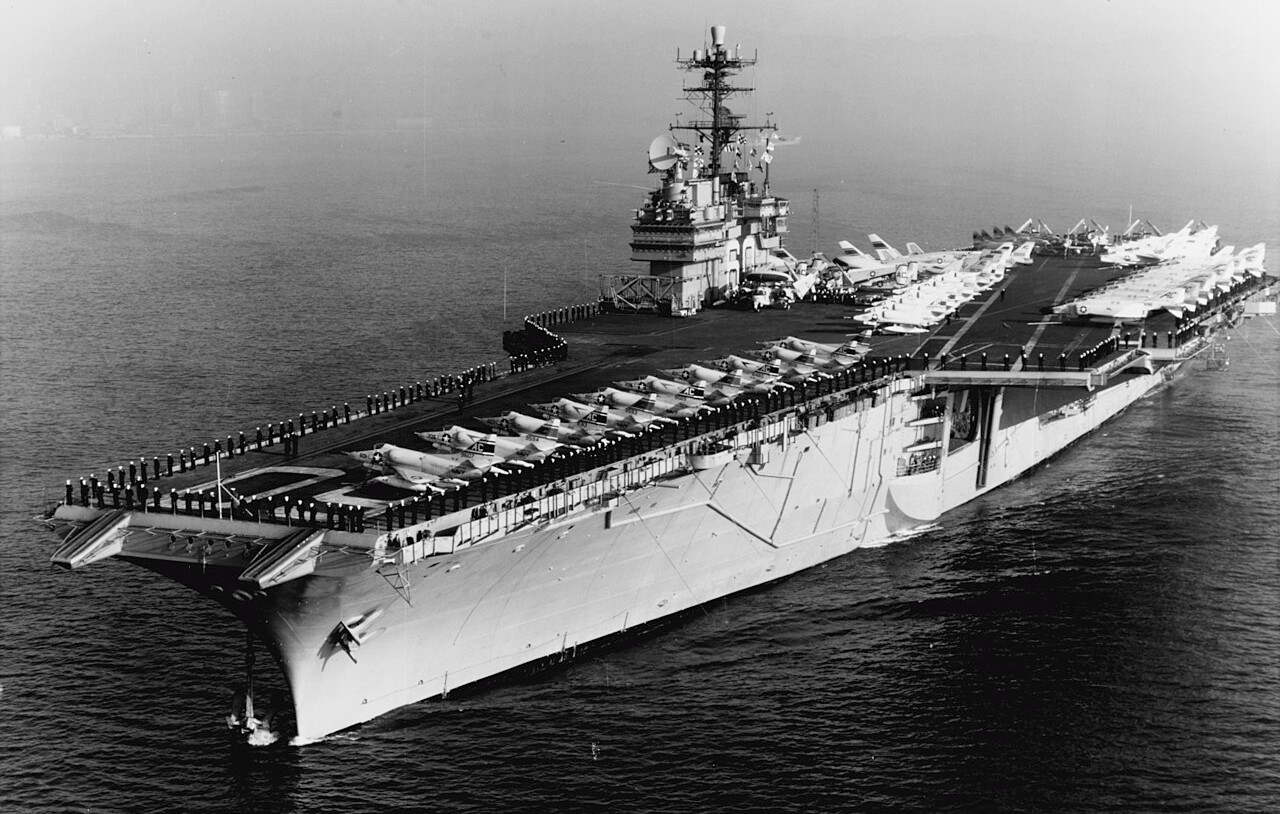

(USN Photo)
USS Saratoga (CVA-60) with her crew manning the rail on the flight deck, as she arrives in Barcelona, Spain, 12 February 1965. Saratoga, with assigned Attack Carrier Air Wing 3 (CVW-3), was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea from 28 November 1964 to 12 July 1965.
USS Saratoga (CV/CVA/CVB-60) was the second of four Forrestal-class supercarriers built for the United States Navy in the 1950s. Saratoga was the sixth U.S. Navy ship, and the second aircraft carrier, to be named for the Battles of Saratoga in the American Revolutionary War. Commissioned in 1956, she spent most of her career in the Mediterranean, but also participated during the Vietnam War, receiving one battle star for her service. One of her last operational duties was to participate in Operation Desert Storm. Saratoga was decommissioned in 1994, and was stored at Naval Station Newport in Newport, Rhode Island. Multiple unsuccessful attempts were made to preserve her as a museum ship. The Navy paid ESCO Marine of Brownsville, Texas, one cent to take the ship for dismantling and recycling. On 15 September 2014, ex-Saratoga arrived in Brownsville, Texas, to be scrapped. Scrapping was completed by early 2019. (Wikipedia)
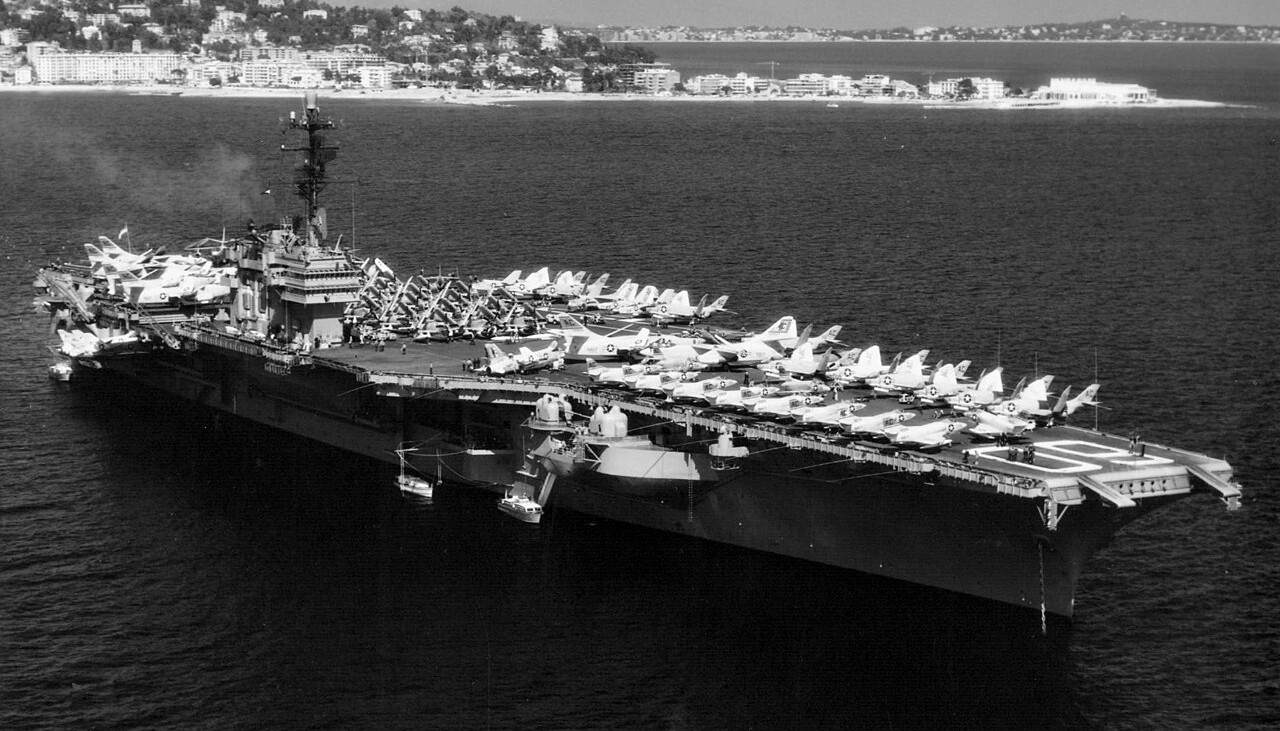

(USN Photo)
USS Saratoga (CVA-60) at anchor off Cannes, France. Saratoga, with Carrier Air Group 3 (CVG-3) embarked, was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea from 1 February to 1 October 1958.
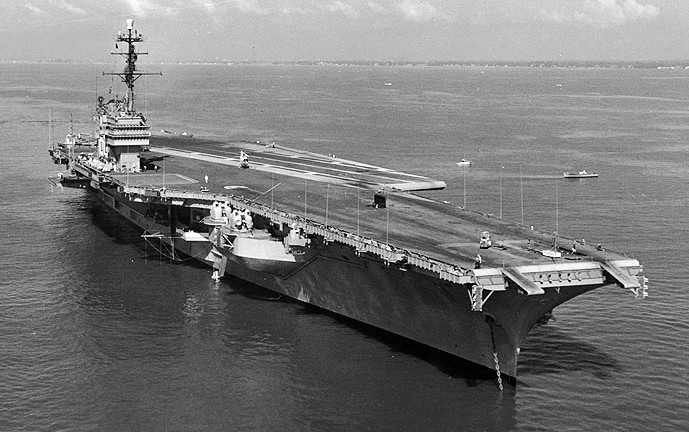

(USN Photo)
USS Saratoga (CVA-60) at her anchorage in Hampton Roads, Virginia (USA), during the International Naval Review, 12 June 1957.
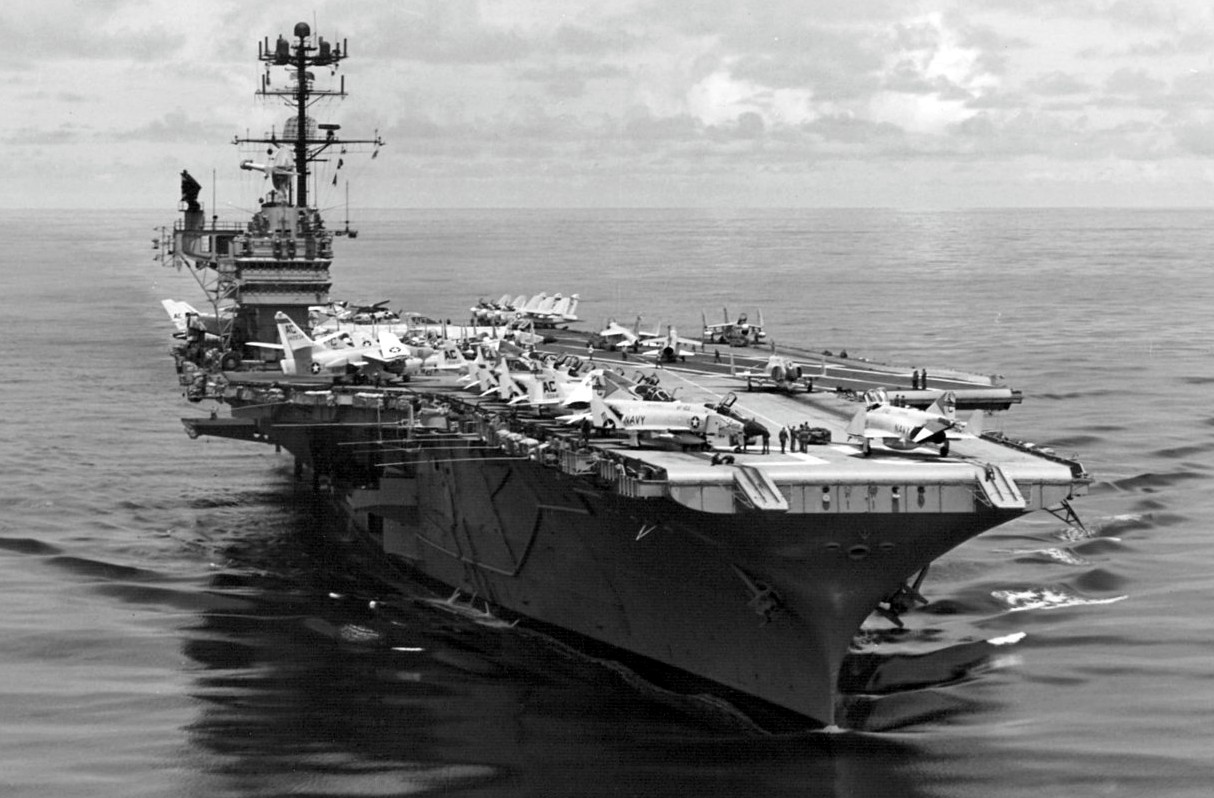

(USN Photo)
USS Saratoga (CVA-60) underway in the Mediterranean Sea in November 1969. Saratoga, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 3 (CVW-3), was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea from 9 July 1969 to 22 January 1970.
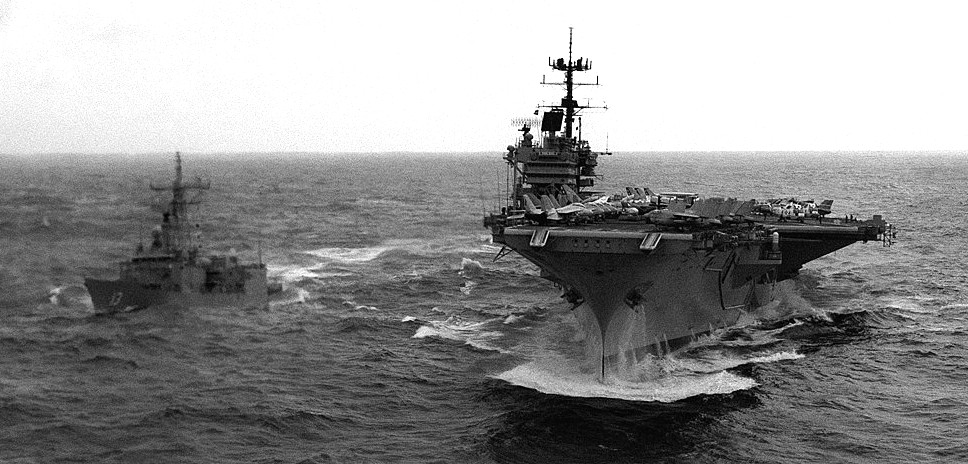

(USN Photo)
USS Saratoga (CVA-60) underway in heavy seas while en route to the Mediterranean Sea. The guided missile frigate USS Samuel Eliot Morison (FFG 13), 7 April 1984.
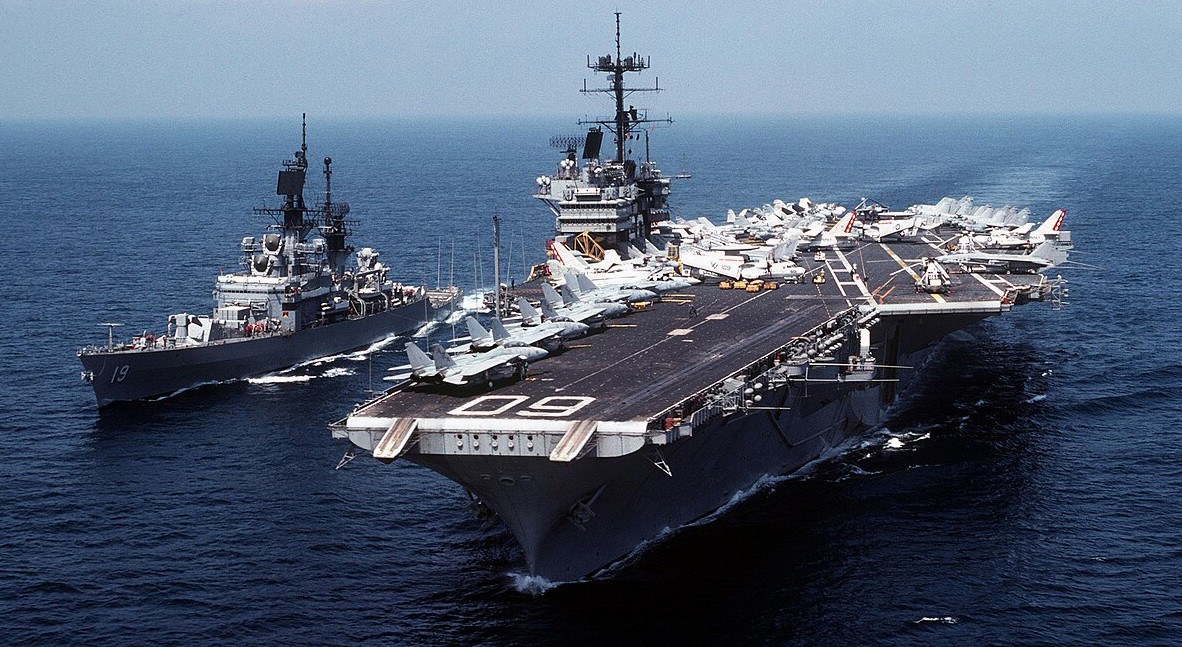

(USN Photo)
USS Saratoga (CV-60) and the guided missile cruiser USS Dale (CG-19) underway in the Mediteranean Sea on 15 April 1984. Saratoga, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 17 (CVW-17) was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea from 2 April to 20 October 1984.
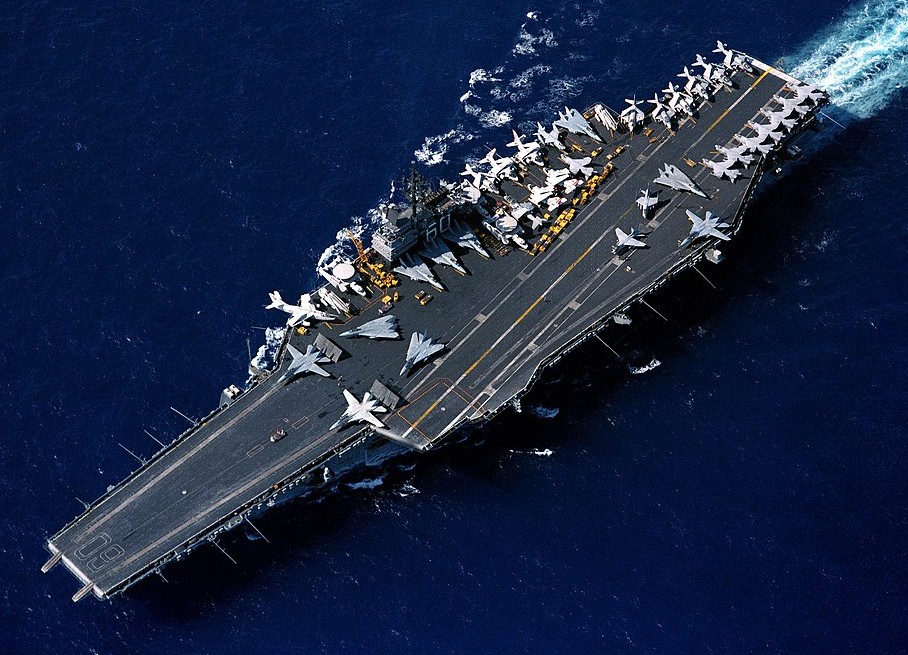

(USN Photo)
USS Saratoga (CV 60) underway, 15 November 1985.

(USN Photo)
USS Saratoga (CV 60), the fast combat support ship USS Seattle (AOE 3) and the frigate USS Garcia (FF 1040) participating in an underway replenishment in the Mediterranean Sea, 10/21/1985
USS Ranger (CV-61)
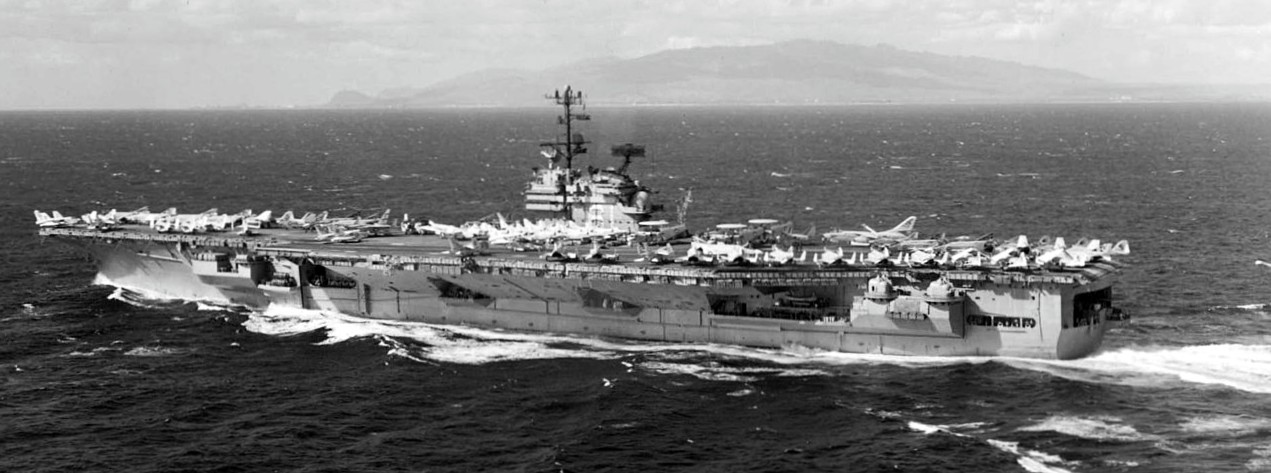

(USN Photo)
USS Ranger (CVA-61) underway off Hawaii (USA), in November 1967. Ranger, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 2 (CVW-2), was deployed to Vietnam from 4 November 1967 to 25 May 1968.
The seventh USS Ranger (CV/CVA-61) was the third of four Forrestal-class supercarriers built for the United States Navy in the 1950s. Although all four ships of the class were completed with angled decks, Ranger had the distinction of being the first U.S. carrier built from the beginning as an angled-deck ship. Commissioned in 1957, she served extensively in the Pacific, especially the Vietnam War, for which she earned 13 battle stars. Near the end of her career, she also served in the Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf. Ranger was decommissioned in 1993, and was stored at Bremerton, Washington, until March 2015. She was then moved to Brownsville for scrapping, which was completed in November 2017. (Wikipedia)

(USN Photo)
USS Ranger (CVA-61) at sea during her third deployment on 26 August 1961. Among the planes parked on her flight deck are eight Douglas A3D-2 Skywarrior twin-engine jet bombers of Heavy Attack Squadron 6 (VAH-6) “Fleurs”. VAH-6 was assigned to Carrier Air Group 9 (CVG-9) aboard the Ranger for a deployment to the Western Pacific from 11 August 1961 to 8 March 1962.
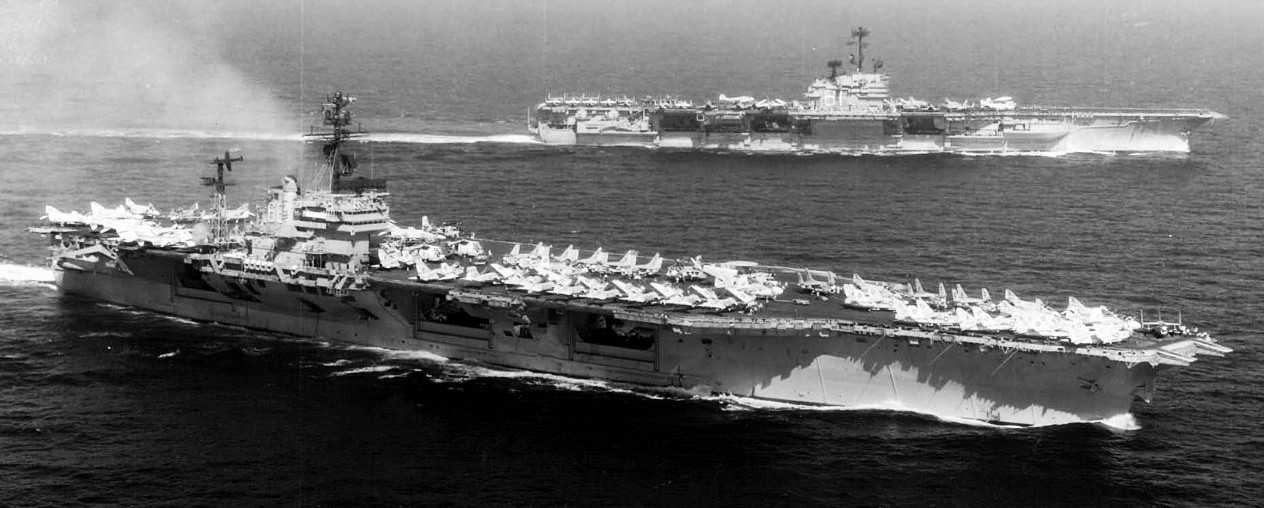

(USN Photo)
USS America (CVA-66), foreground, and USS Ranger (CVA-61) underway in the Gulf of Tonkin in January 1973. Ranger, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 2 (CVW-2), was deployed to Vietnam from 16 November 1972 to 22 June 1973. America, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 8 (CVW-8), was deployed to Vietnam from 5 June 1972 to 24 March 1973.
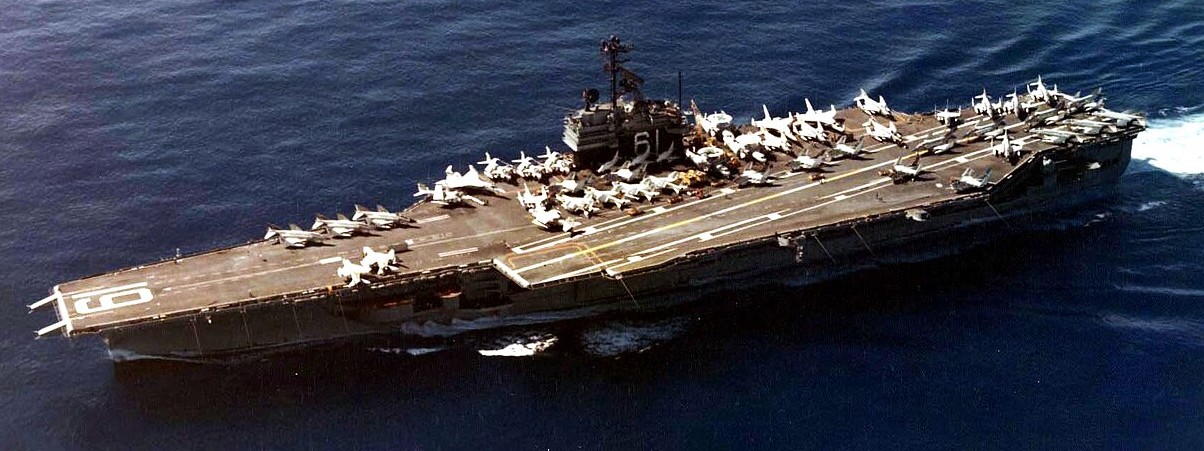

(USN Photo)
USS Ranger (CVA-61) underway in the Pacific Ocean in 1974. Ranger, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 2 (CVW-2), was deployed to the Western Pacific from 7 May to 18 October 1974.
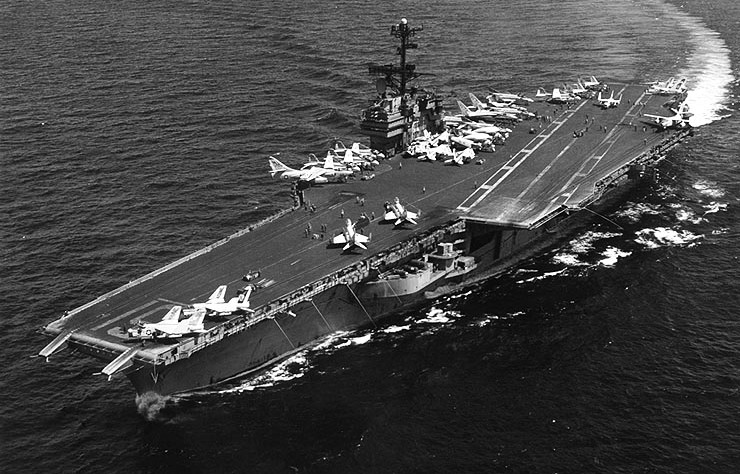

(USN Photo)
USS Ranger (CV-61) underway at sea, c1978.
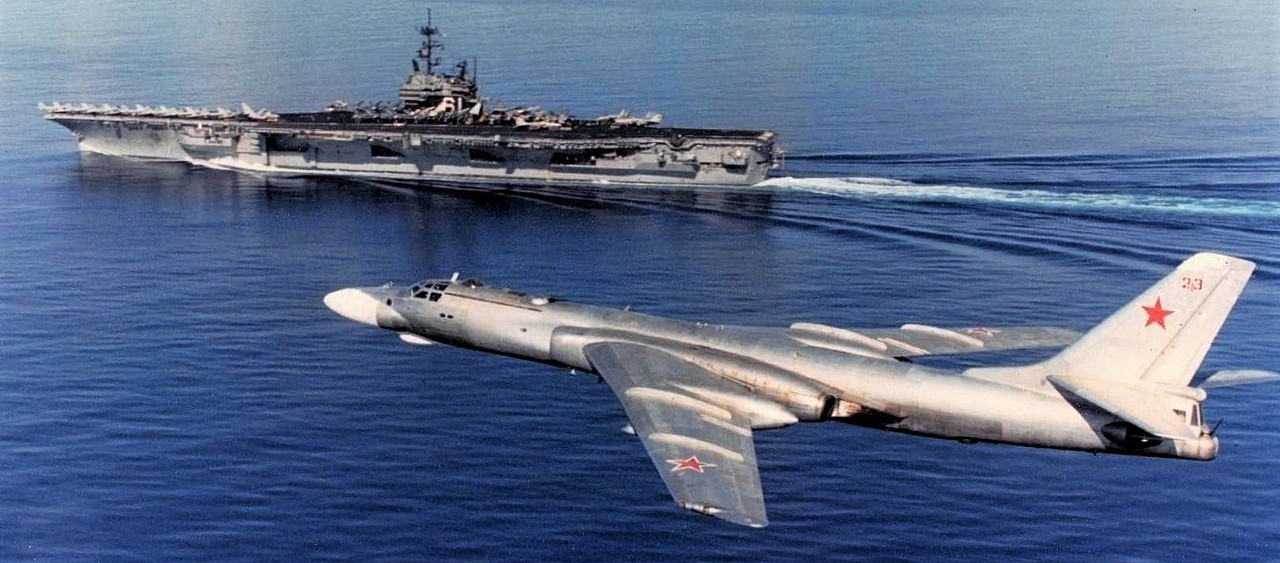

(USN Photo)
A Soviet Tupolev Tu-16K-10 Badger C flying past USS Ranger (CV-61) in 1989.
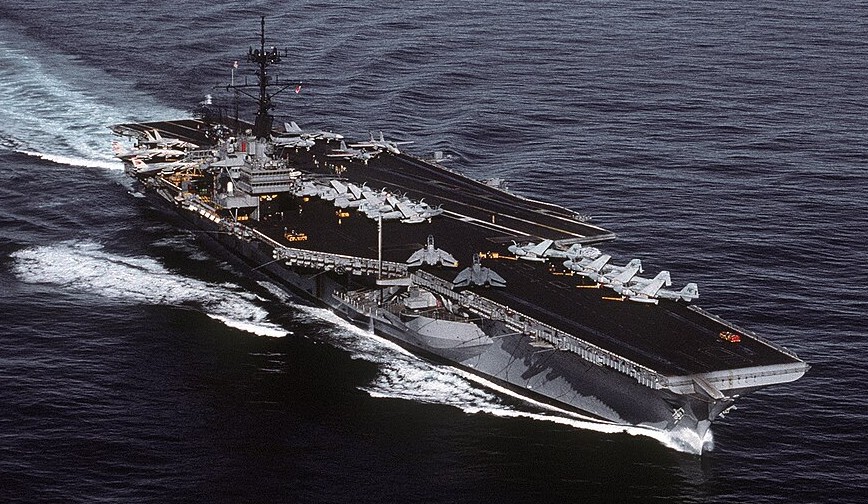

(USN Photo)
USS Ranger (CV 61) underway off the coast of Southern California, 1 December 1988.
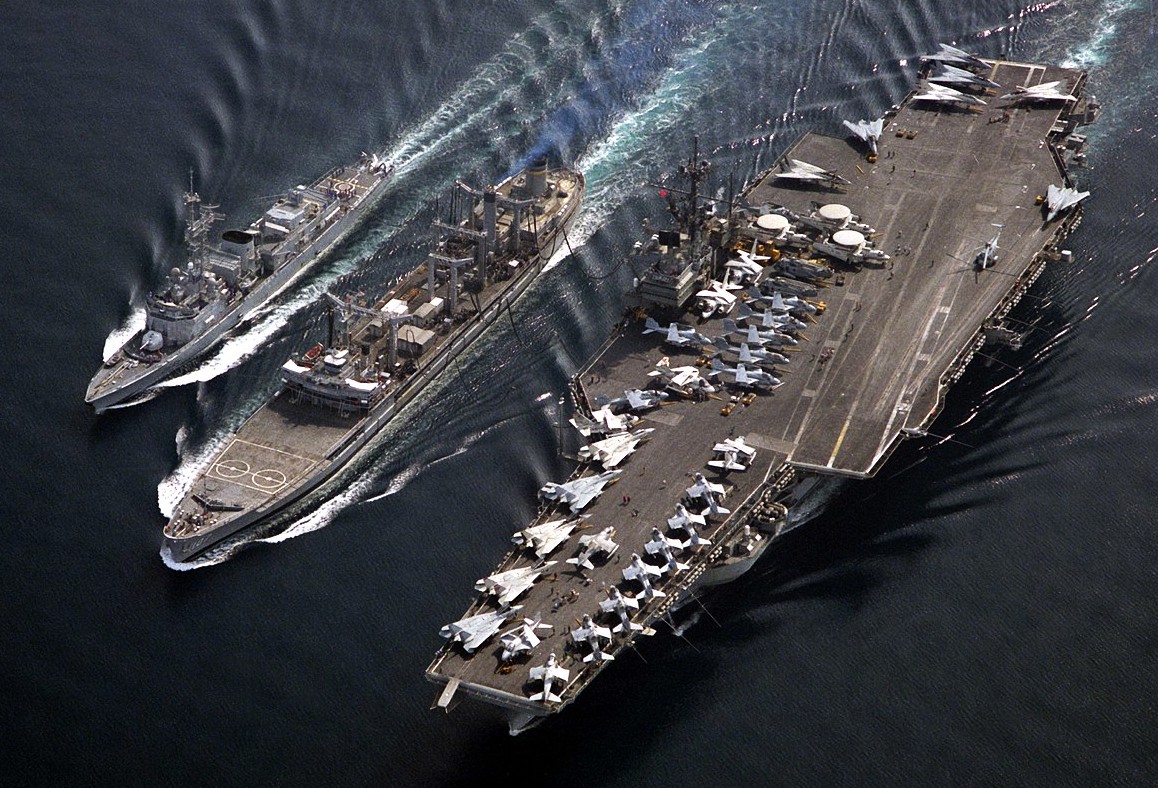

(USN Photo)
U.S. Military Sealift Command fleet oiler USNS Passumpsic (T-AO-107) conducting an underway replenishment of the U.S. Navy aircraft carrier USS Ranger (CV-61) and the French frigate Latouche-Tréville (D646) during the 1991 Gulf War.

(USN Photo)
USS Ranger (CV-61) and USS Independence (CV-62) during southern watch, 16 September 1992.
USS Independence (CV-62)
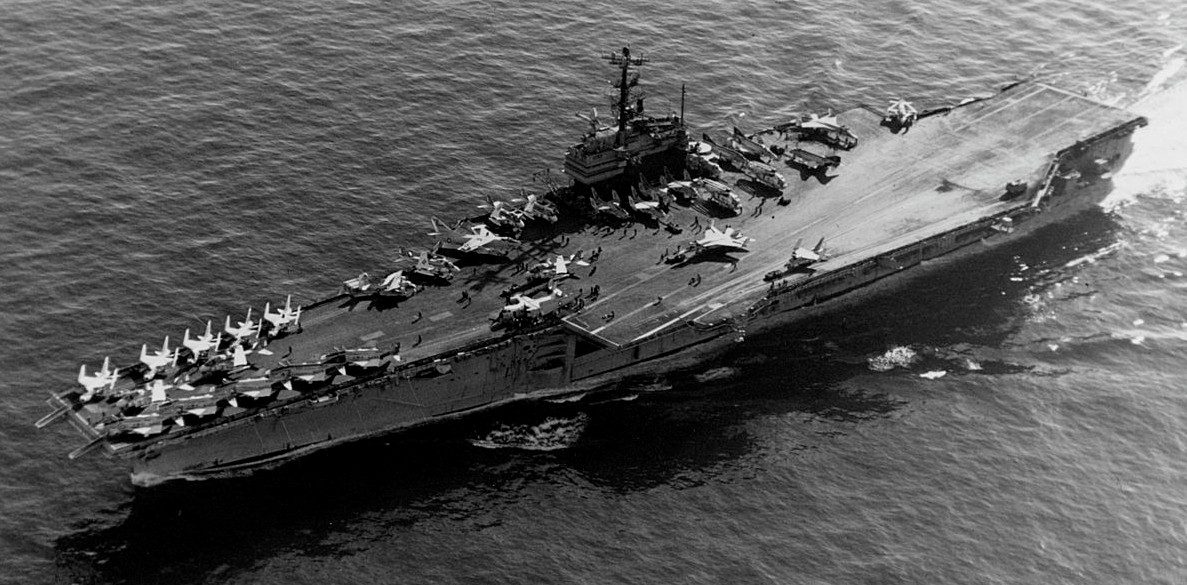

(USN Photo)
USS Independence (CV-62) underway in the eastern Mediterranean, 20 December 1973. Independence, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 7 (CVW-7), was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea from 21 June 1973 to 19 January 1974. During that cruise, she served as the test ship for the “CV-concept”, which integrated the anti-submarine squadrons (HS/VS) of the anti-submarine carriers (CVS) into the carrier air wing of the former attack carriers (CVA). Therefore, Independence was the first attack carrier to be redesignated “CV” from “CVA” on 28 February 1973.
The fifth USS Independence (CV/CVA-62) was an aircraft carrier of the United States Navy. She was the fourth and final member of the Forrestal class of conventionally powered supercarriers. She entered service in 1959, with much of her early years spent in the Mediterranean Fleet. Independence was decommissioned in 1998 after 39 years of active service. After 19 years stored at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Bremerton, Washington, it was towed to Brownsville, Texas in 2017 with scrapping completed by early 2019. (Wikipedia)

(USN Photo)
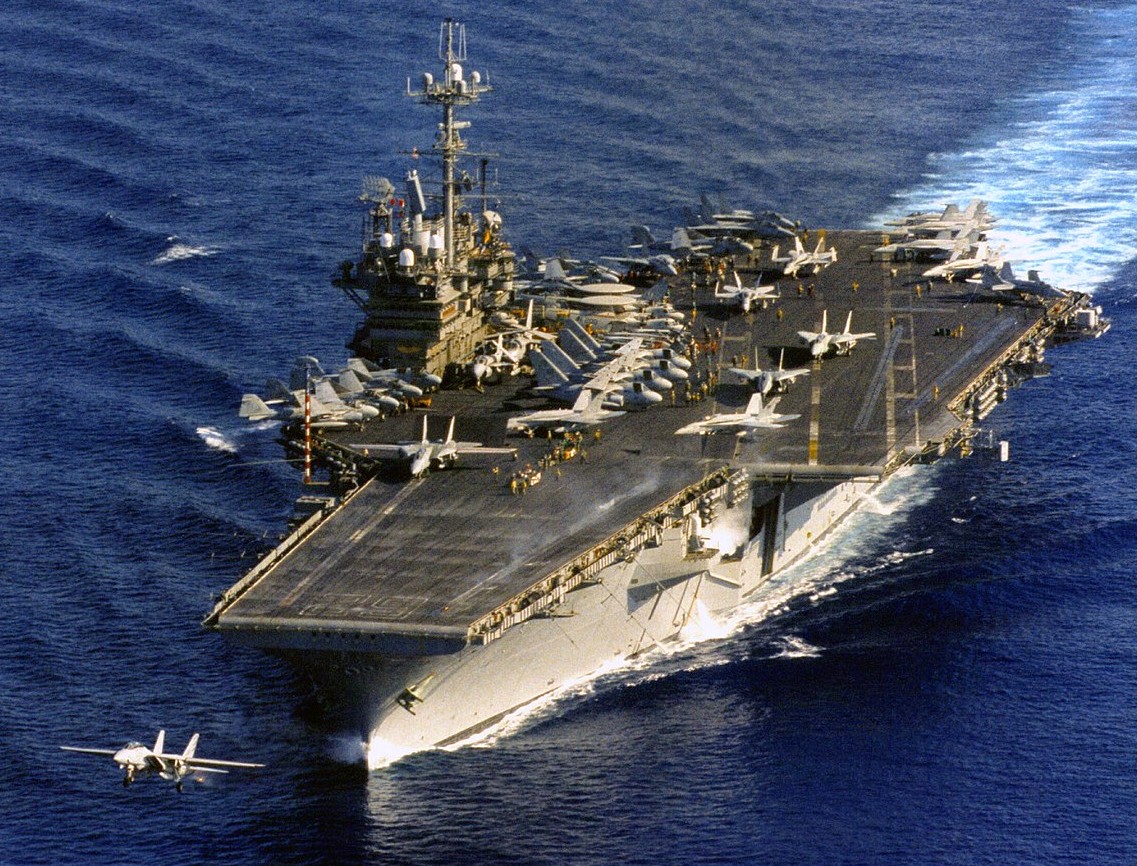
USS Independence (CV-62) underway as a Grumman F-14A Tomcat of Fighter Squadron 154 (VF-154) “Black Knights” is launched during flight operations, 10 March 1996. Independence, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 5 (CVW-5), was deployed to the Western Pacific from 9 February to 27 March 1996.

(USN Photo)
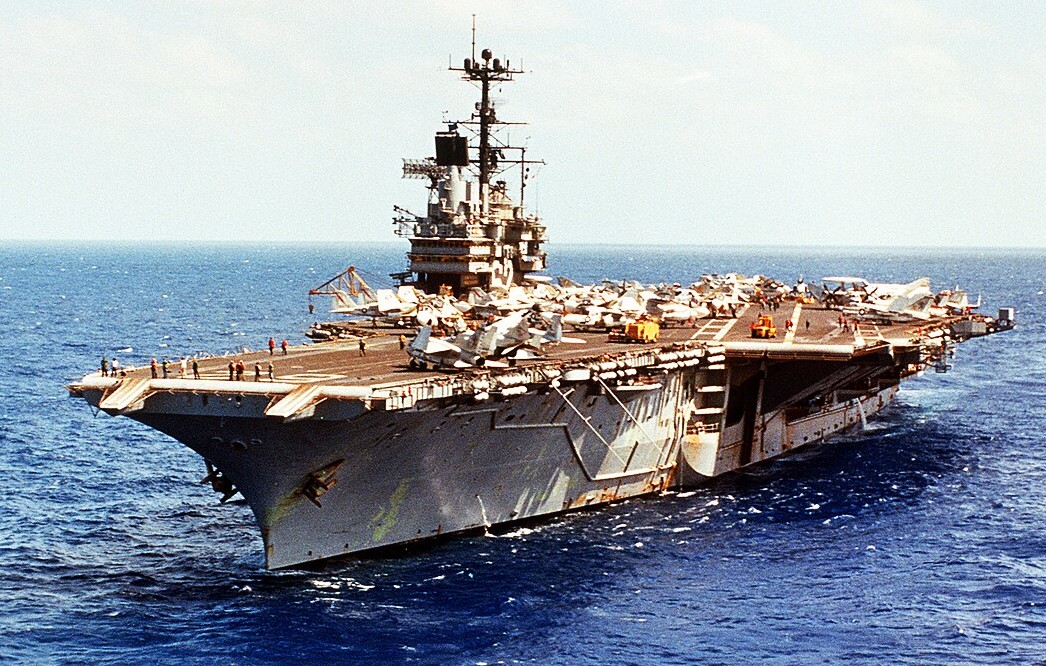
USS Independence (CV-62) underway in the Atlantic Ocean while headed from Saint Thomas, Virgin Islands, to Norfolk, Virginia, on 4 May 1979.

(USN Photo)
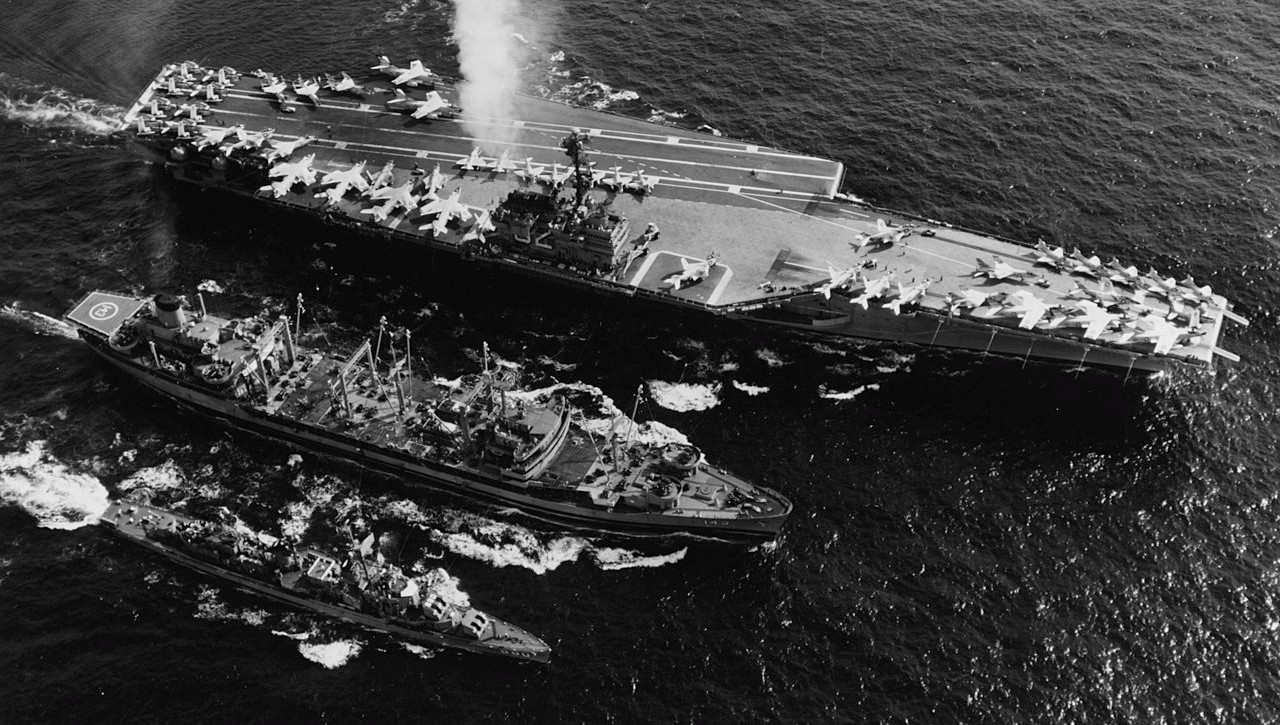
U.S. Navy fleet oiler USS Neosho (AO-143) refuels the aircraft carrier USS Independence (CVA-62) and the radar picket destroyer USS Dyess (DDR-880), during Atlantic fleet operations, 9 July 1961.

(USN Photo)
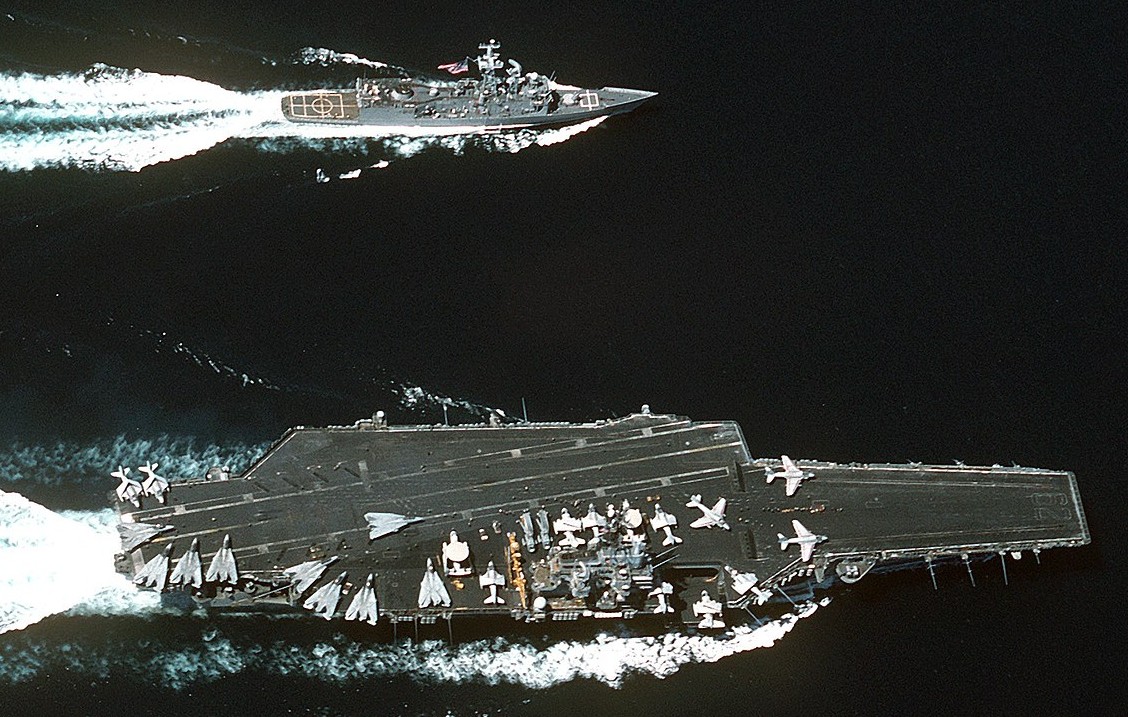
USS Independence (CV-62) and the guided missile frigate USS Curts (FFG-38) underway on 27 August 1994. Independence, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 5 (CVW-5), was deployed to the Western Pacific from 19 July to 29 August 1994.
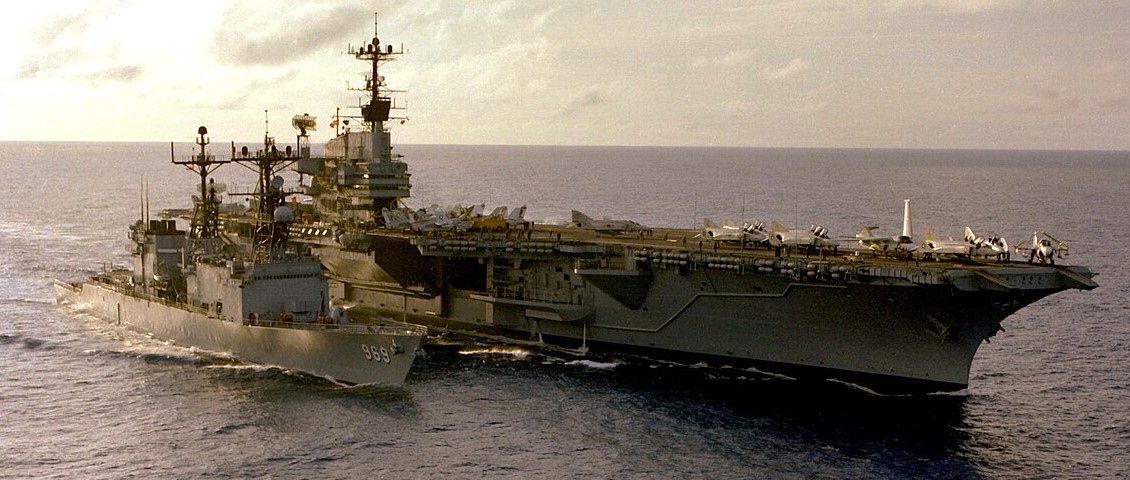

(USN Photo)
USS Independence (CV-62) underway with the destroyer USS Peterson (DD-969) alongside, 27 May 1979.
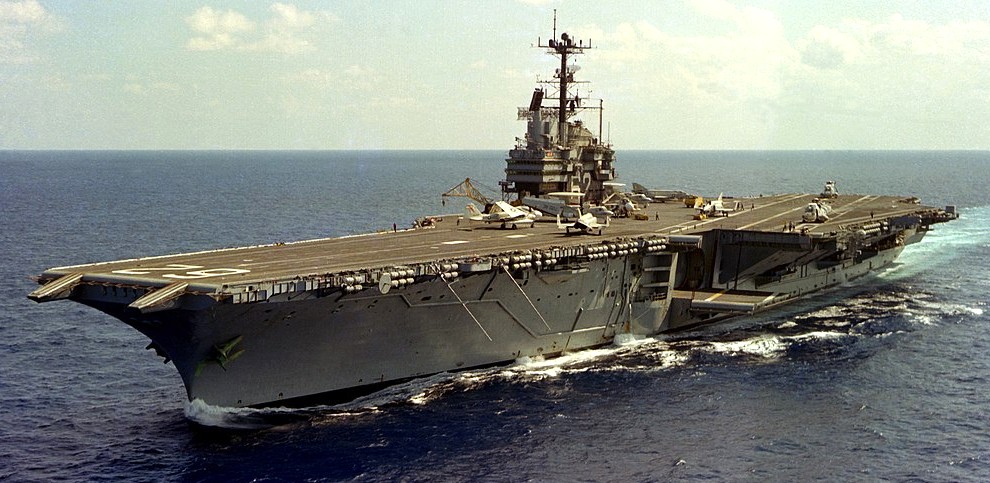

(USN Photo)
USS Independence (CV-62) underway, 19 January 1979.
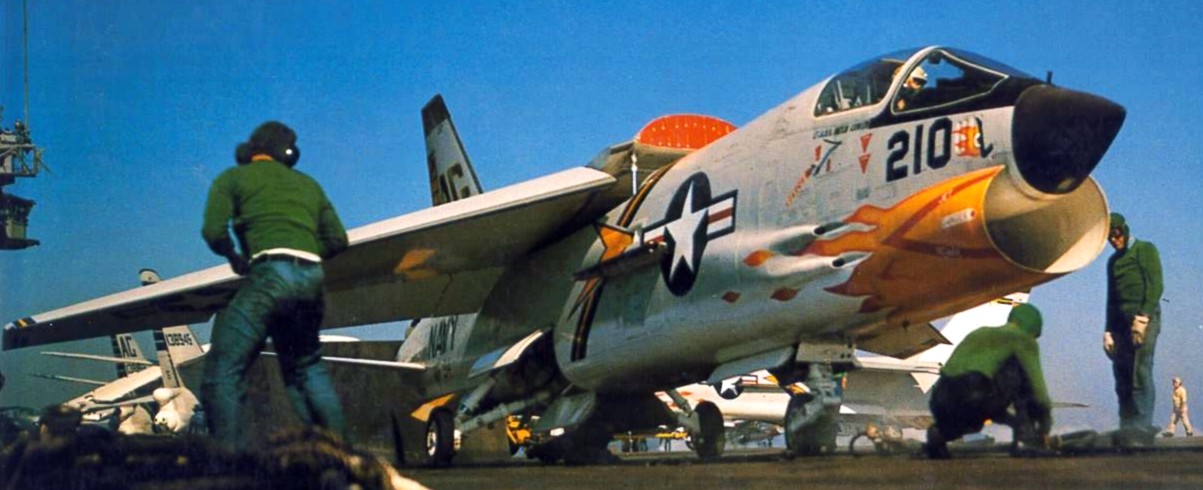

(USN Photo)
Vought F-8C Crusader from Fighter Squadron VF-84 Jolly Rogers on the catapult of the aircraft carrier USS Independence (CVA-62). VF-84 was assigned to Carrier Air Wing 7 (CVW-7) aboard the Independence for a deployment to the Mediterranean Sea from 6 August 1963 to 4 March 1964.
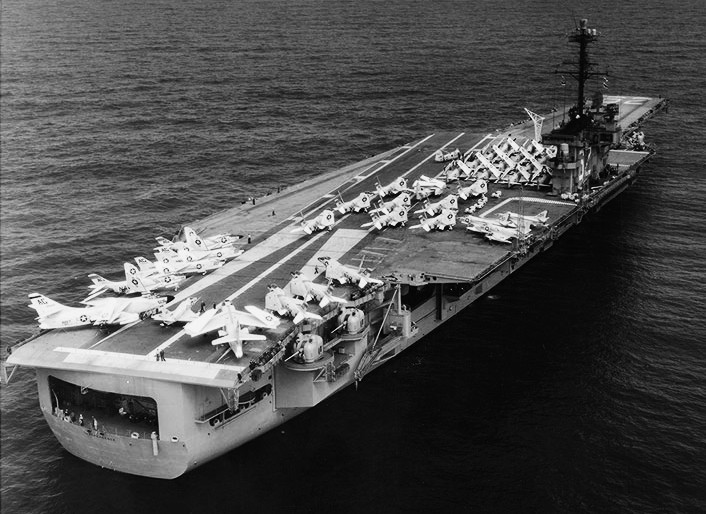

(USN Photo)
USS Independence (CVA-62) photographed in April 1959, during her shakedown cruise. Planes on deck include the following types from Carrier Air Group 7 (CVG-7): Douglas A3D “Skywarrior” (including BuNo 135420, an A3D-1), Heavy Attack Squadron VAH-1 Smokin’ Tigers; Douglas A4D-2 “Skyhawk” (including BuNos 142708 and 142712), Attack Squadron VA-86 Sidewiders; McDonnell F3H-2 “Demon” (including BuNos 143434, 143447, 143448 and 143474), Fighter Squadron VF-41 Black Aces; Vought F8U-1 “Crusader” (including BuNos 145386 and 145429), VF-11 Red Rippers. Note paint pattern on the carrier’s landing path.

(USN Photo)
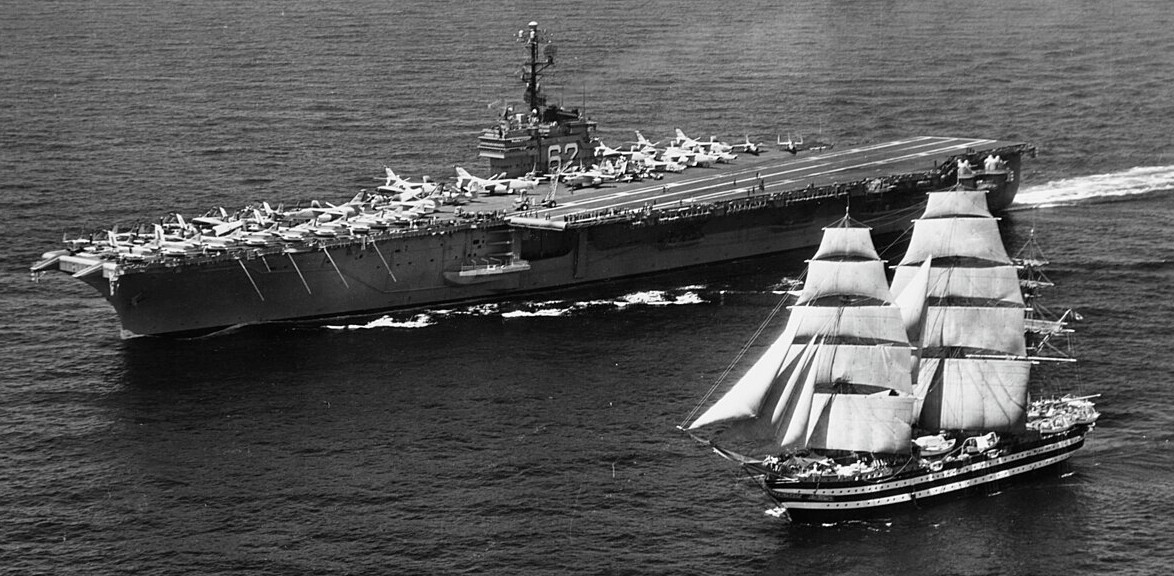
USS Independence (CVA-62) underway with the Italian Marina Militare training ship Amerigo Vespucci on 12 July 1962. Independence, with assigned Carrier Air Group 7 (CVG-7), was deployed to the Mediterreanean Sea from 19 April to 27 August 1962.

(USN Photo)
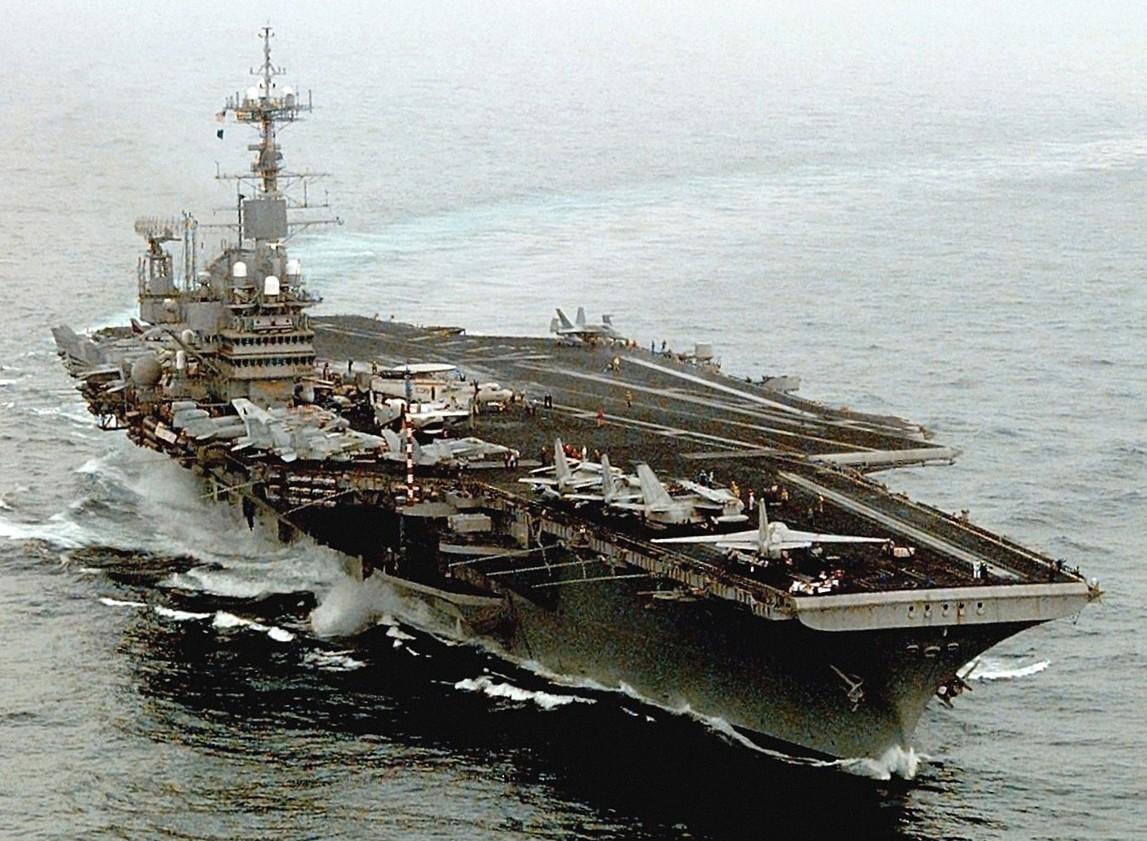
USS Independence (CV-62) operates in the Persian Gulf on 11 February 1998 in support of Operation “Southern Watch”. Independence and its embarked Carrier Air Wing 5 (CVW-5) were deeployed to the Western Pacific and the Indian Ocean from 23 January to 5 June 1998. This was the last deployment before Independence was decommissioned on 30 September 1998.

(USN Photo)
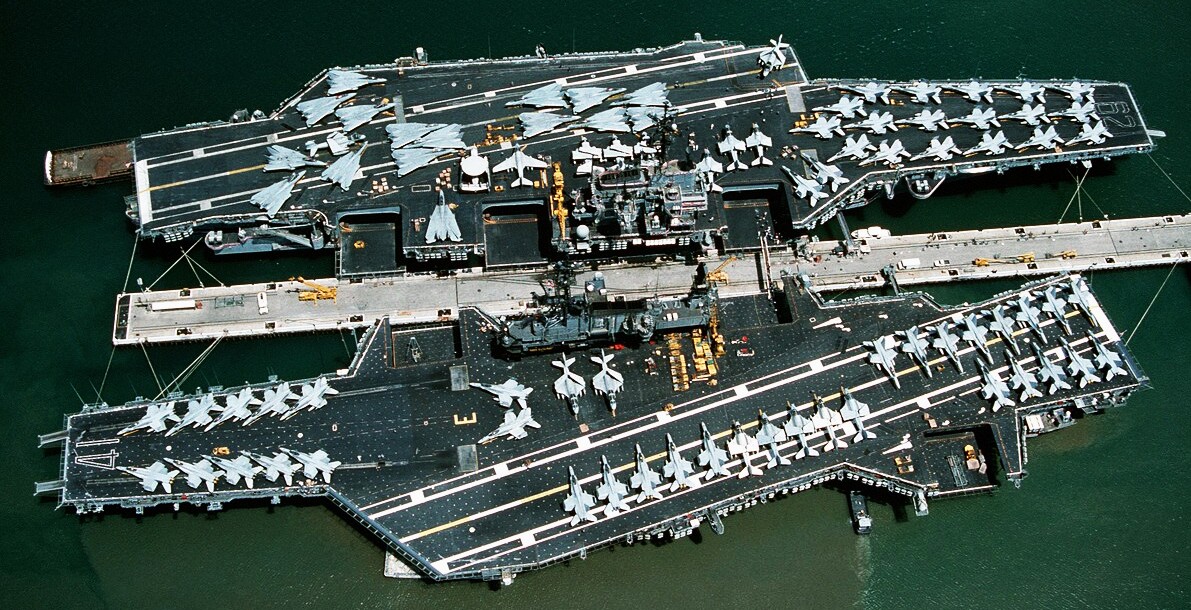
An aerial view of various aircraft lining the flight decks of the U.S. Navy aircraft carrier USS USS Independence (CV-62), top, and USS Midway (CV-41) moored beside each other at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, Hawaii (USA), on 23 August 1991. Midway was en route from Naval Station, Yokosuka, Japan, to Naval Air Station North Island, California (USA), where it was decommissioned on 11 April 1992. Independence travelled to Yokosuka to take over as the U.S. Navy’s forward-based aircraft carrier.
USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63)

(USN Photo)
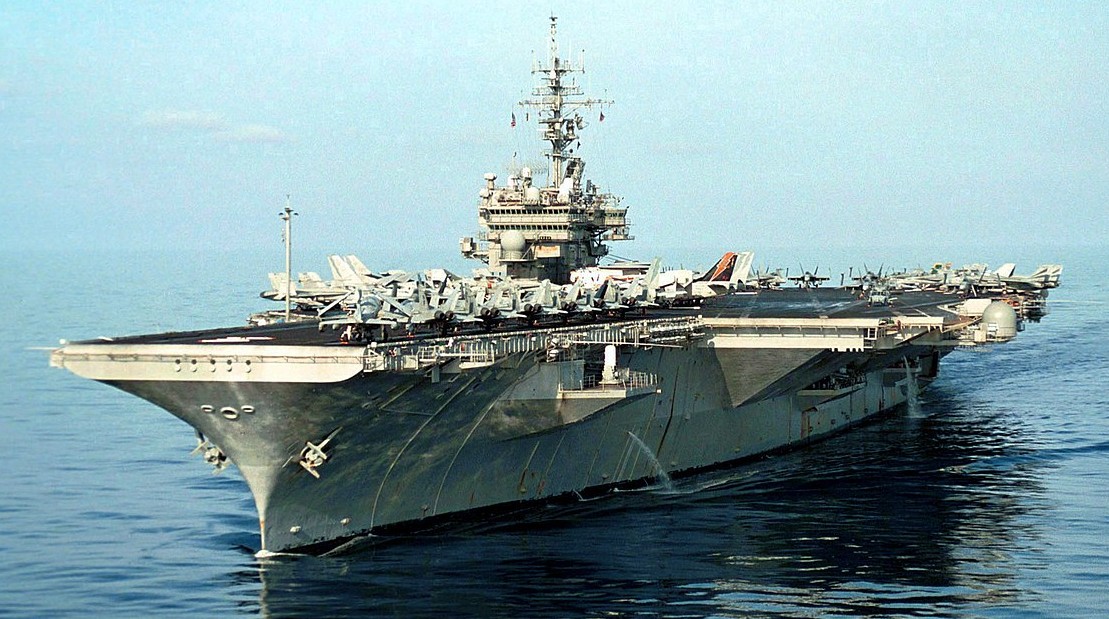
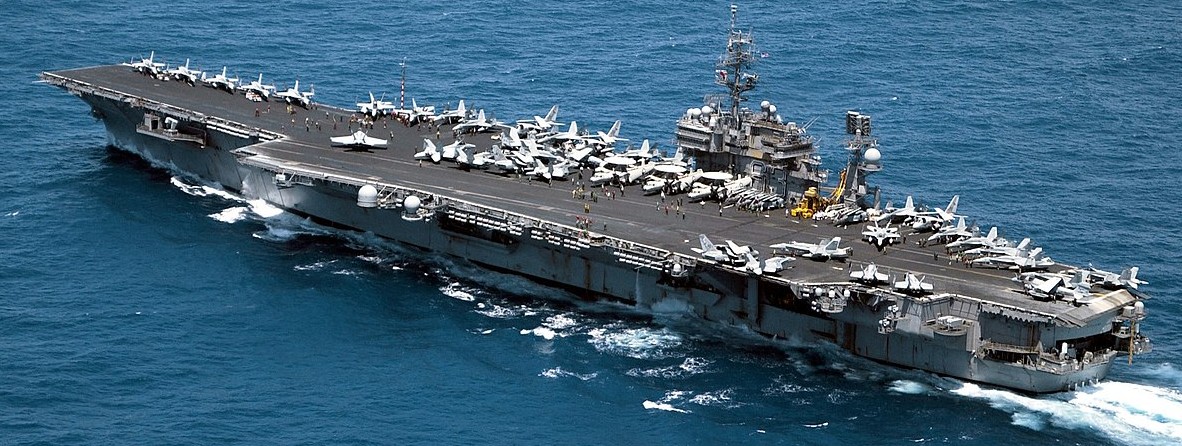
USS Kitty Hawk (CV 63) operating in the calm South China Seas, 3 April 2001.
USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63), formerly CVA-63, was a United States Navy supercarrier. She was the second naval ship named after Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, the site of the Wright brothers’ first powered airplane flight. Kitty Hawk was the first of the three Kitty Hawk-class aircraft carriers to be commissioned and the last to be decommissioned. Kitty Hawk was laid down by the New York Shipbuilding Corporation, Camden, New Jersey, on 27 December 1956. The ship was launched on 21 May 1960, sponsored by Mrs. Camilla F. McElroy, wife of Defense Secretary Neil H. McElroy. Kitty Hawk was launched by flooding her drydock; the conventional slide-down method was ruled out because of her mass and the risk that she might hit the Philadelphia shore on the far side of the Delaware River. The ship was commissioned 29 April 1961, at Philadelphia Naval Shipyard, Captain William F. Bringle in command. With the decommissioning of Independence on 30 September 1998, Kitty Hawk became the United States warship with the second-longest active status, after the sailing ship USS Constitution (Enterprise passed her in 2012; these two aircraft carriers were two of the three carriers to fly the First Navy Jack). For ten years, Kitty Hawk was the forward-deployed carrier at Yokosuka Naval Base in Yokosuka, Japan. In October 2008, she was replaced in this role by George Washington. Kitty Hawk returned to the United States and had her decommissioning ceremony on 31 January 2009. She was officially decommissioned on 12 May 2009 after 48 years of service.[6] Kitty Hawk was replaced by George H. W. Bush. She was stricken from the Naval Vessel Register on 20 October 2017, and was designated for disposal by dismantling a few days later. On 15 January 2022 Kitty Hawk left Puget Sound Naval Shipyard under tow en route to Brownsville, Texas, for scrapping, arriving there on 31 May 2022. (Wikipedia)

(USN Photo)
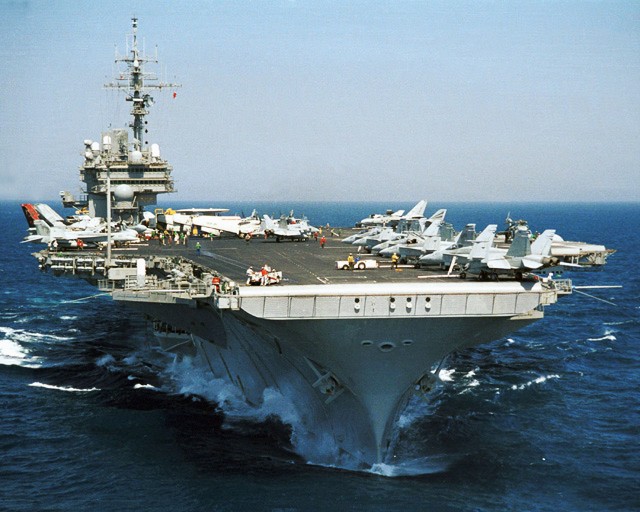
USS Kitty Hawk (CV 63) underway while conducting flight operations in the Philippine Sea, 7 May 2004.

(USN Photo)
USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63) underway, circa 1999-2001, with Carrier Air Wing 5 (CVW-5) aboard.

(USN Photo)
USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63) prepares to anchor in Hong Kong’s Victoria Harbor. 28 April 2008.

(Andreyevich Photo)
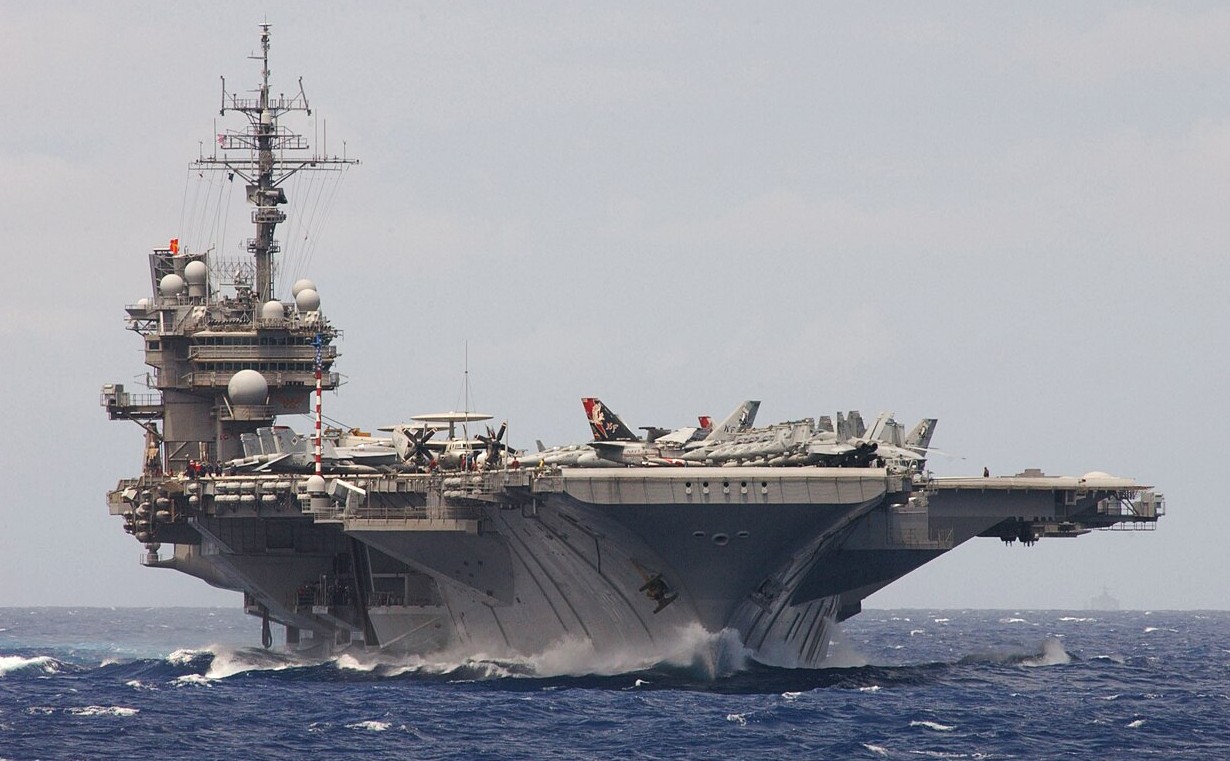
USS Kitty Hawk in Sydney, Australia, 2007.

(USN Photo)
USS Kitty Hawk (CV 63) plows through the waters of the Pacific Ocean as it makes its approach to the oiler USNS Yukon (T-AO 202) during a replenishment-at-sea evolution on 9 August 2004.

(USN Photo)
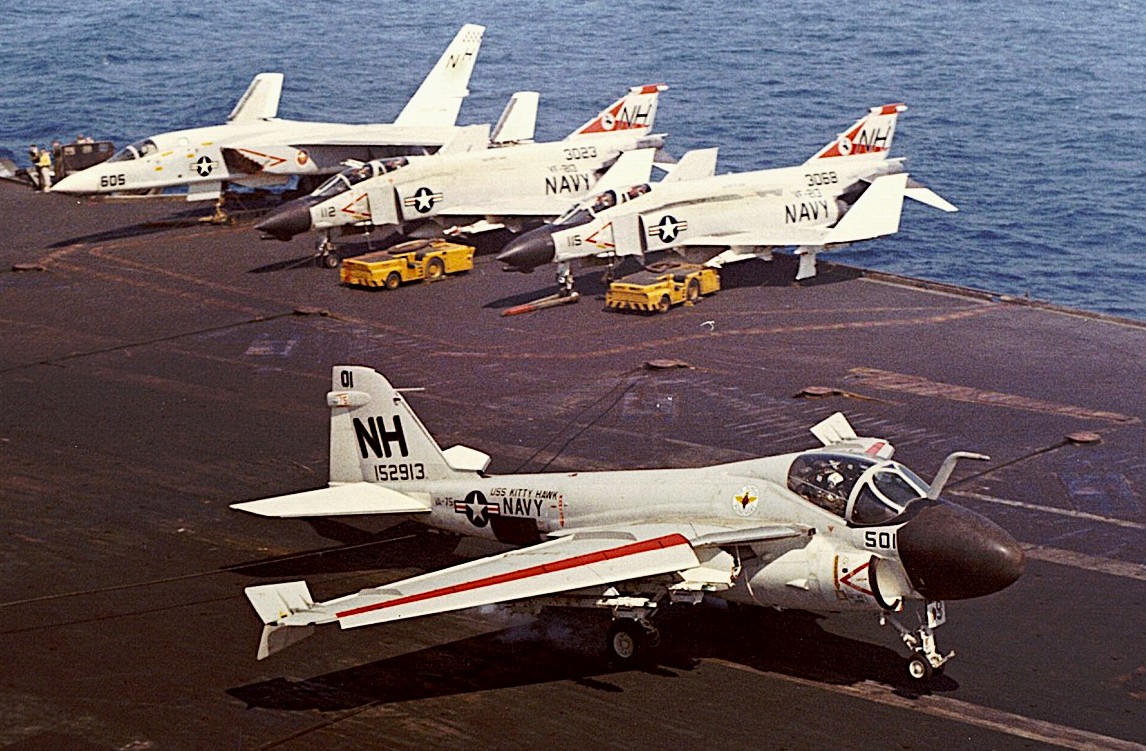
U.S. Navy Grumman A-6A Intruder (BuNo 152913) from Attack Squadron VA-75 Sunday Punchers lands on the aircraft carrier USS Kitty Hawk (CVA-63) off Vietnam on 2 March 1968. In the background are two McDonnell F-4B Phantom II (BuNo 153023, 153068) from fighter squadron VF-213 Black Lions and a North American RA-5C Vigilante (BuNo 150831) from Heavy Reconnaissance Squadron RVAH-11 Checkertails. All aircraft were assigned to Attack Carrier Air Wing 11 (CVW-11) aboard the Kitty Hawk for a deployment to Vietnam from 18 November 1967 to 28 June 1968.

(USN Photo)
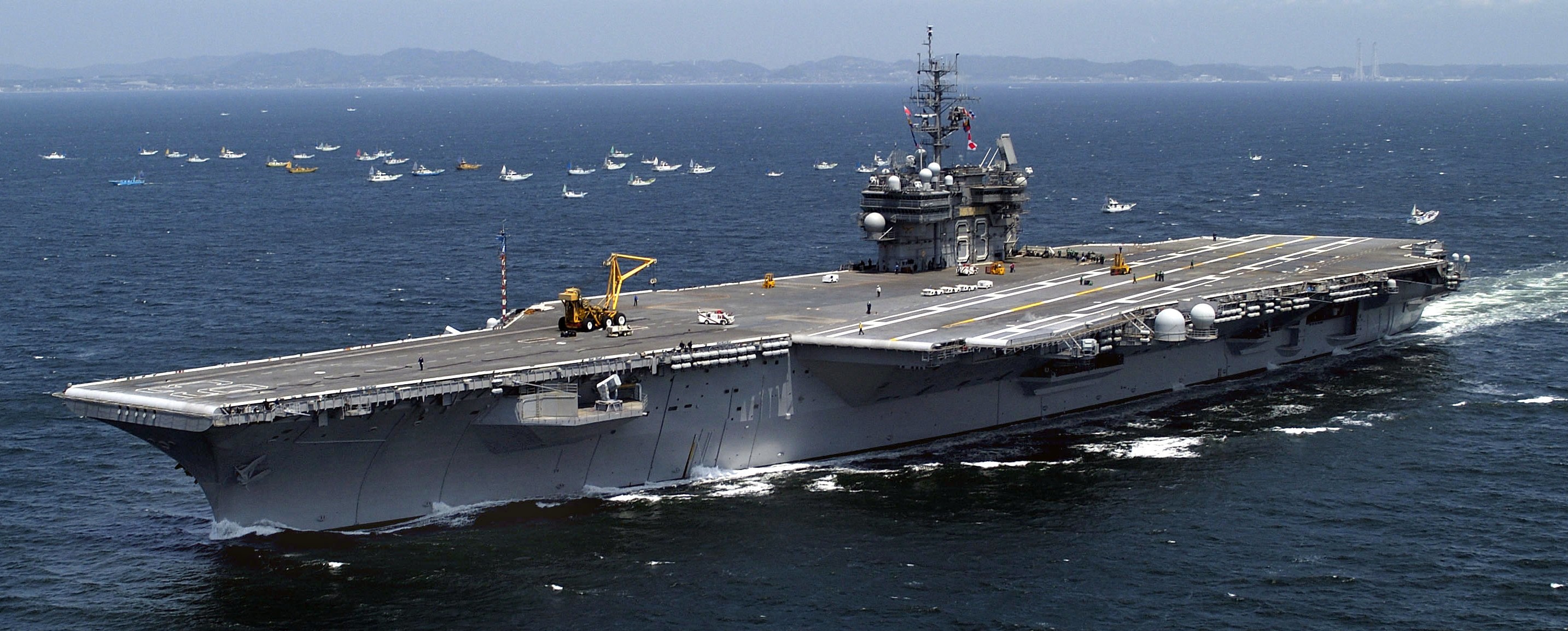
USS Kitty Hawk (CV 63) sails past a small group of Japanese fishing vessels and heads toward Sagami Bay to conduct precision anchor checks during her post upkeep underway period in the western Pacific Ocean. Kitty Hawk demonstrated power projection and sea control as a forward-deployed aircraft carrier, operating from Yokosuka, Japan. 17 May 2005.

(USN Photo)
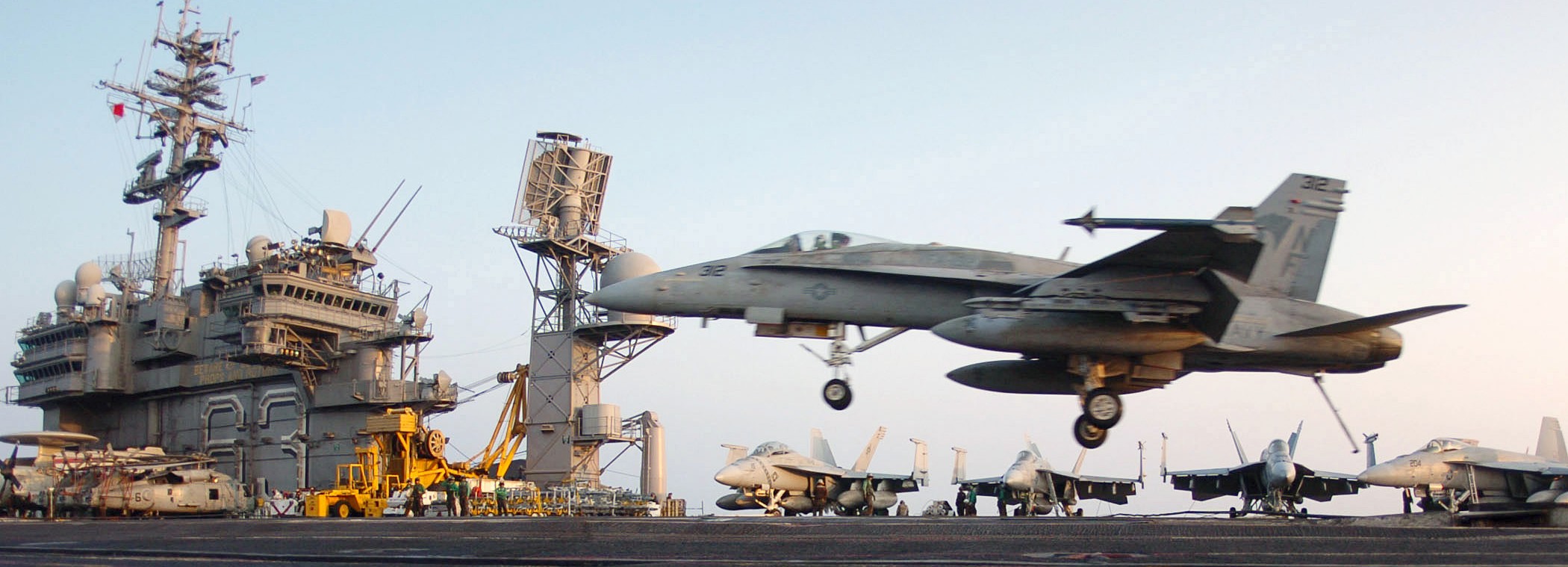
US Navy (USN) F/A-18C Hornet, Strike Fighter Squadron One Nine Two (VFA-192), Golden Dragons, Naval Air Facility (NAF) Atsugi, Japan, prepares for an arrested landing aboard the USN Aircraft Carrier USS Kittyhawk (CV 63). 10 August 2005.

(USN Photo)
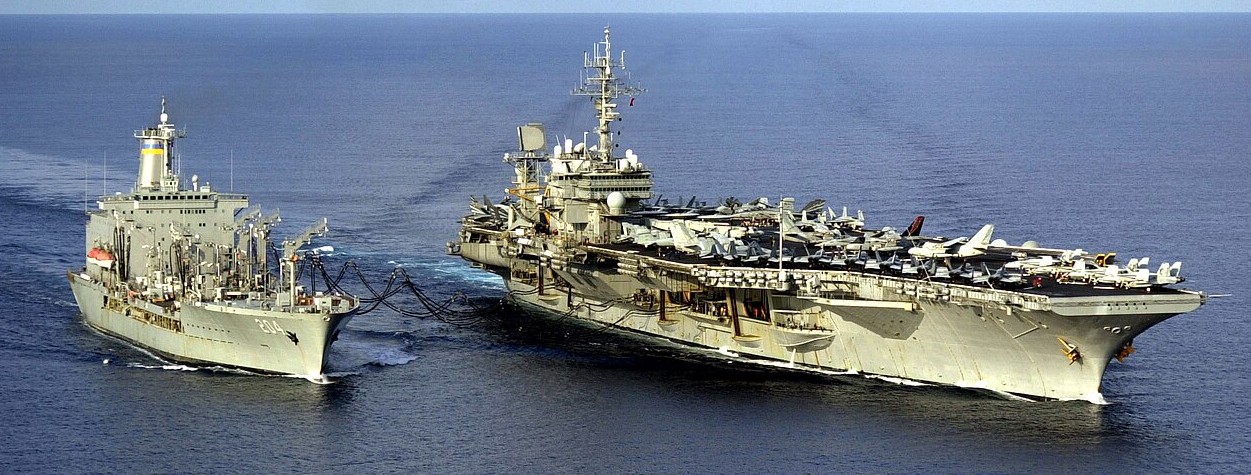
USS Kitty Hawk and USNS Rappahannock (T-AO 204) steam along side each other during a replenishment at sea (RAS). A RAS allows ships to continue conducting their missions without having to return to port for food, fuel, or other needed supplies. Kitty Hawk is conducting work-ups in preparation for an upcoming regularly scheduled deployment. Kitty Hawk was the Navy’s only permanently forward deployed aircraft carrier and ws homeported in Yokosuka, Japan.

(USN Photo)
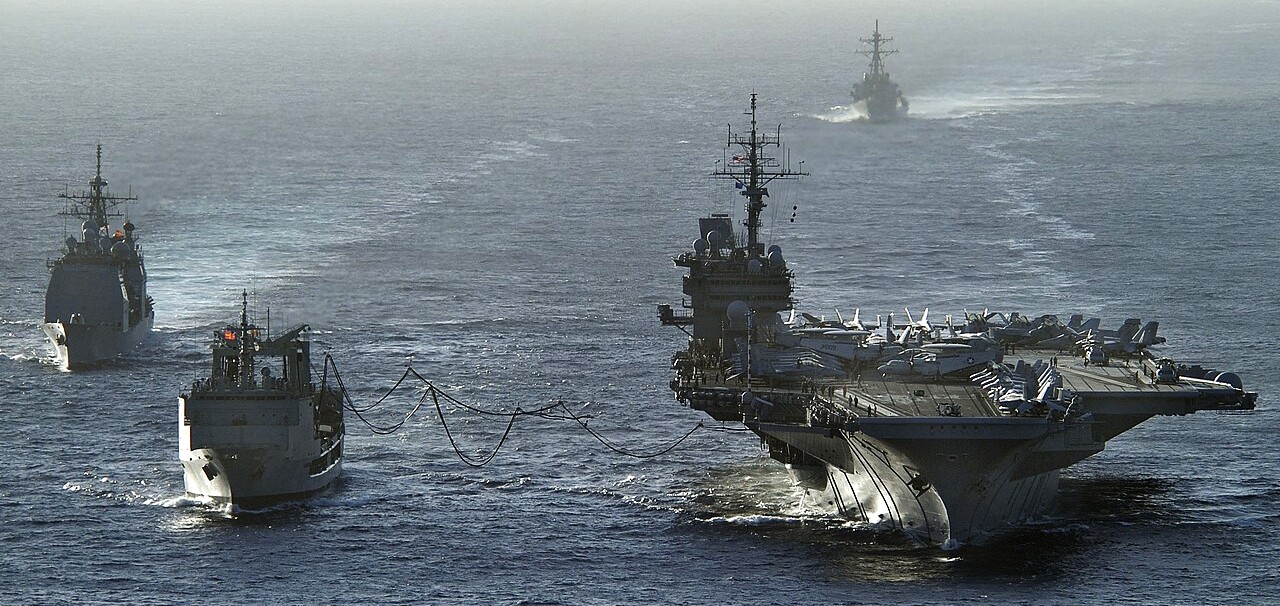
USS Kittyhawk (CV 63) receives fuel during a replenishment at sea from the Royal Australian Navy auxiliary oiler replenishment vessel HMAS Success (AOR 304) as U.S. Navy guided missile cruiser USS Cowpens (CG 63) steams alongside and guided missile destroyer USS John Paul Jones (DDG 53) trails behind, on 14 June 2005.
USS Constellation (CV-64)
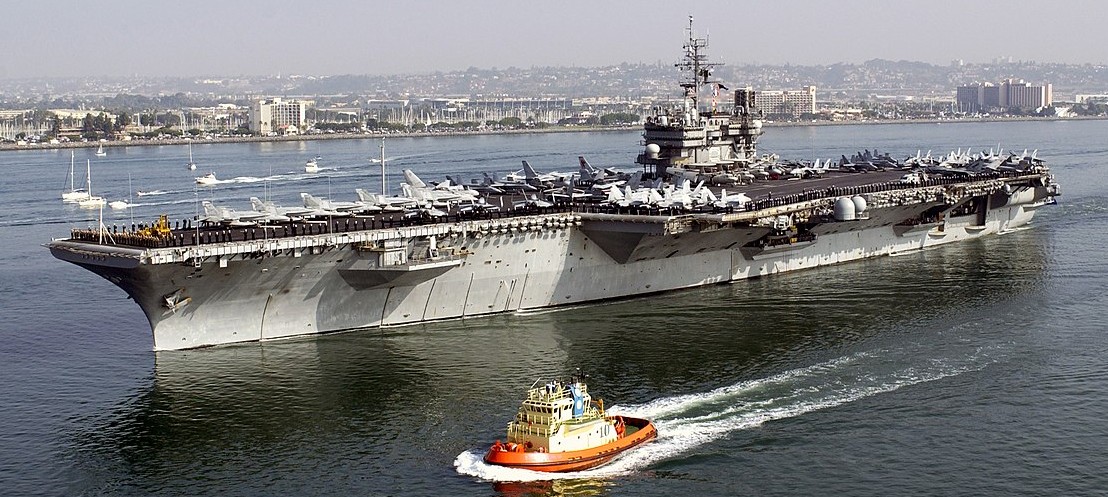

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CV 64) departs Naval Air Station North Island at the start of a regularly scheduled six-month deployment in support of Operation Enduring Freedom. Constellation carries aircraft assigned to Carrier Air Wing Two (CVW-2).
USS Constellation (CVA-64/CV-64) was a Kitty Hawk-class supercarrier and the third ship of the United States Navy to be named in honour of the “new constellation of stars” on the flag of the United States. One of the fastest ships in the Navy, as proven by her victory during a battlegroup race held in 1985, she was nicknamed “Connie” by her crew and officially as “America’s Flagship”. The contract to build Constellation was awarded to the New York Naval Shipyard on 1 July 1956, and her keel was laid down 14 September 1957 at the New York Navy Yard. She was christened and launched 8 October 1960, sponsored by Mary Herter (wife of Secretary of State Christian Herter). Constellation was delivered to the Navy 1 October 1961, and commissioned on 27 October 1961, with Captain T. J. Walker in command.[2] At that time, she had cost about US$264.5 million.[3] Constellation was the last conventional U.S. aircraft carrier (as of January 2021) to be built at a yard other than Newport News Shipbuilding & Drydock Company. Constellation was scrapped at Brownsville, Texas, in 2015–2017. (Wikipedia)
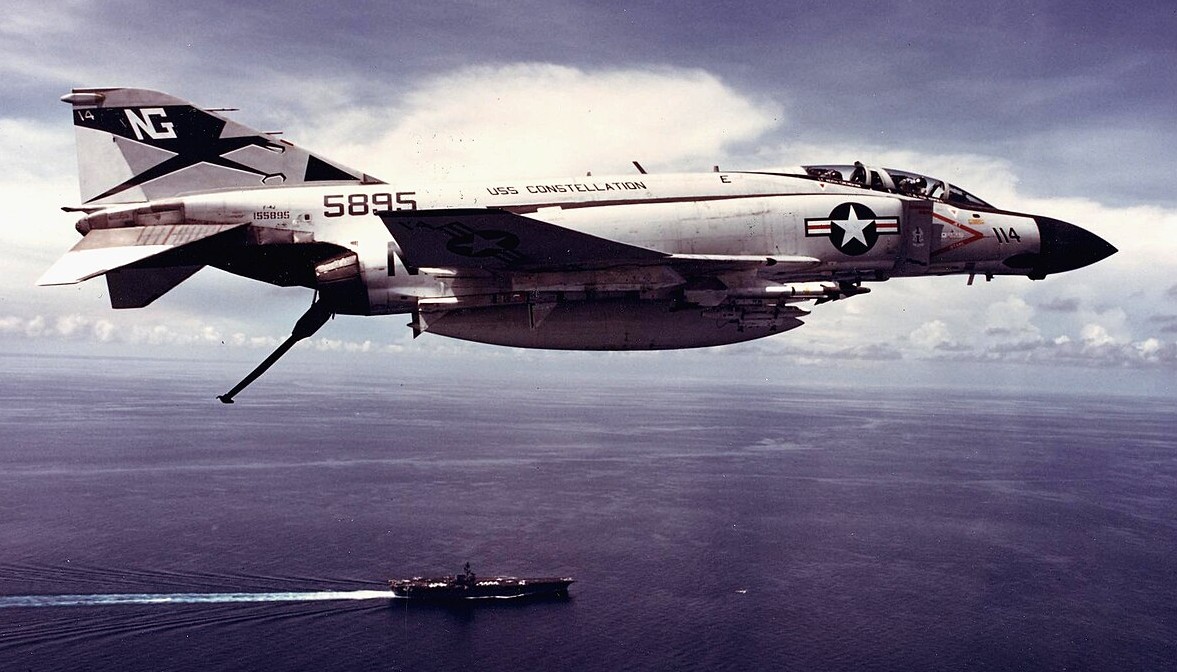

(USN Photo)
U.S. Navy McDonnell Douglas F-4J Phantom II (BuNo 155895) of Fighter Squadron 96 (VF-96) “Fighting Falcons” in flight over the aircraft carrier USS Constellation (CVA-64). VF-96 was assigned to Attack Carrier Air Wing 9 (CVW-9) aboard the Constellation between 1971 and 1974. The aircraft is fully armed with AIM-7 Sparrow and AIM-9D Sidewinder missiles, indicating that this photo was probably taken during a deployment to Vietnam.
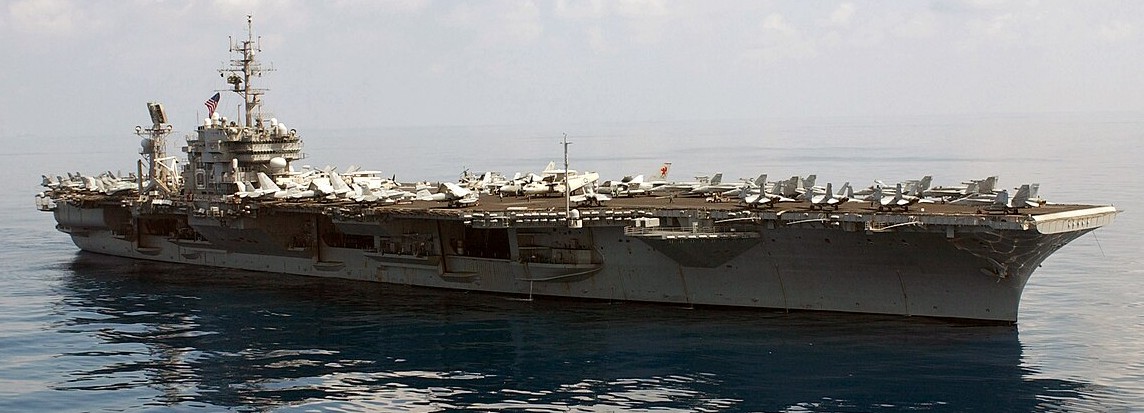

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CV-64) steams through the ocean en route to a liberty port call in Singapore, 30 November 2002.
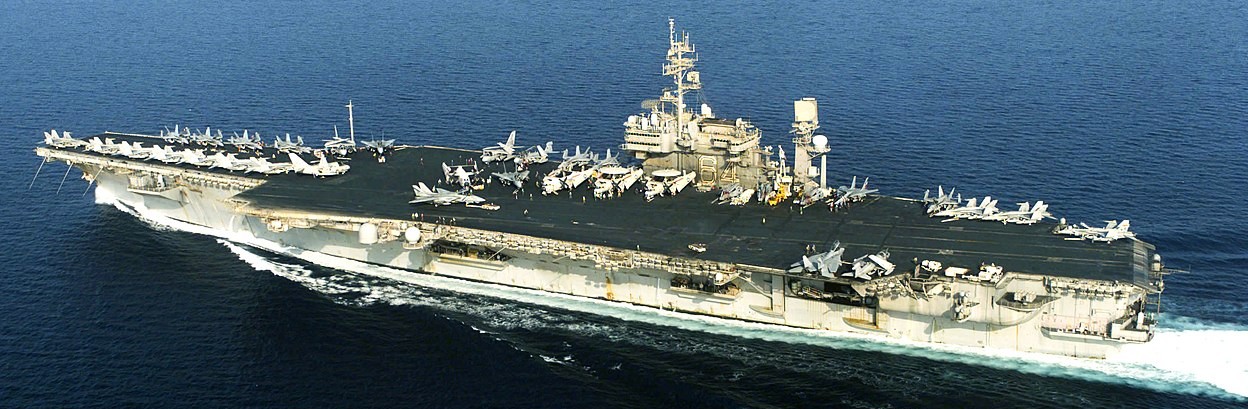

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CV 64) conducts flight operations in support of Operation Iraqi Freedom, the multi-national coalition effort to liberate the Iraqi people, eliminate Iraq’s weapons of mass destruction, and end the regime of Saddam Hussein. 10 April 2003.
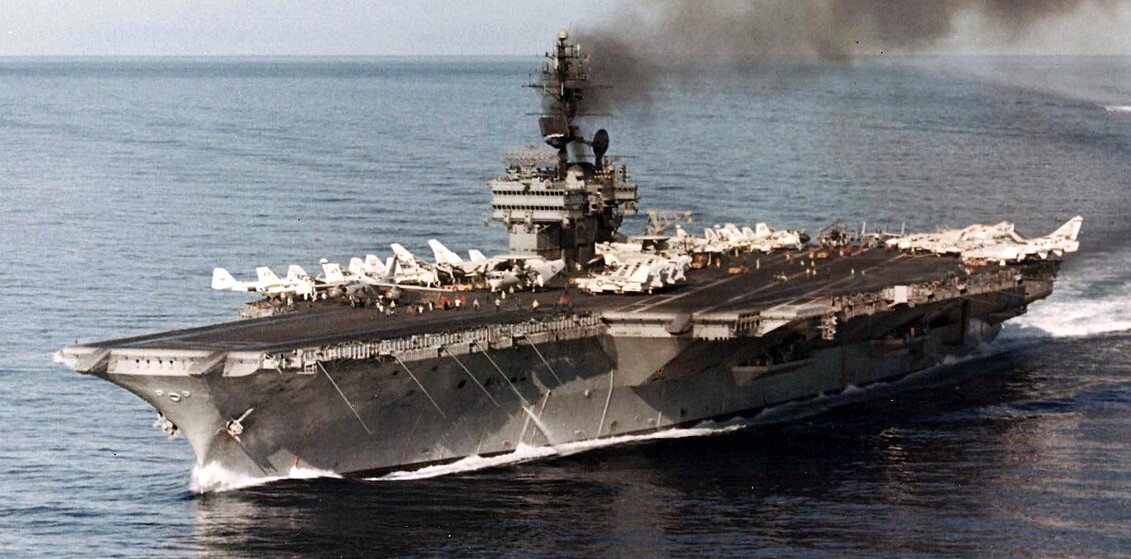

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CVA-64) underway. Constellation, with assigned Attack Carrier Air Wing 14 (CVW-14), was deployed to Vietnam from 29 May 1968 to 21 January 1969.
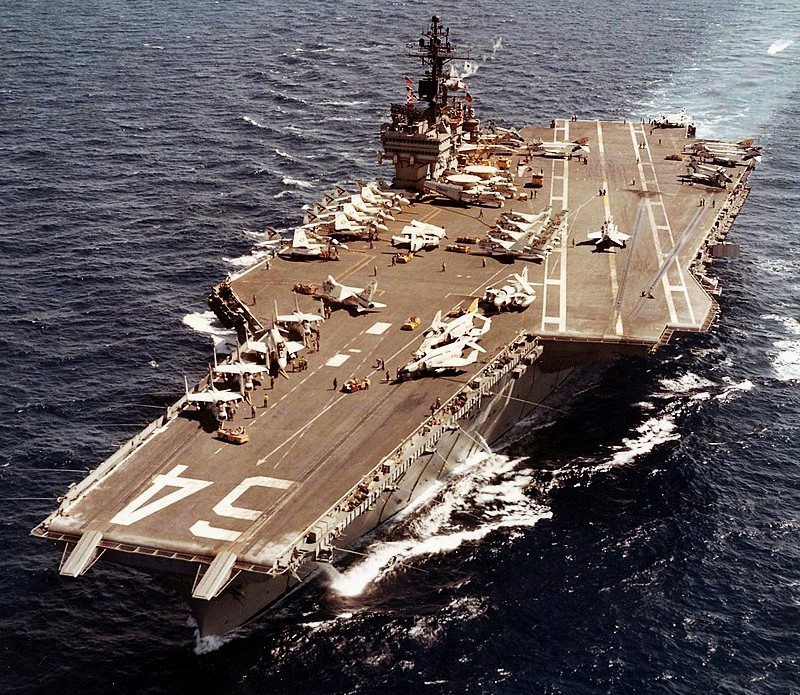

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CVA-64) underway at sea in April 1973. Constellation, with assigned Attack Carrier Air Wing 9 (CVW-9), was deployed to Vietnam from 5 January to 11 October 1973.
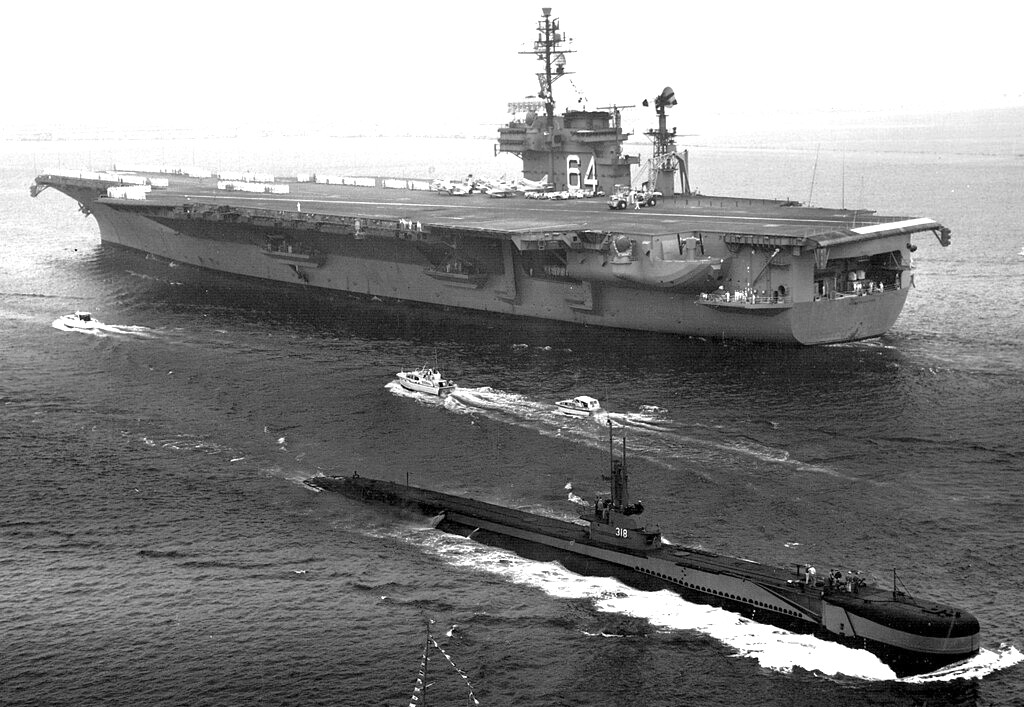

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CVA-64) steams past the submarine USS Baya (AGSS-318), in 1962. On deck of the Constellation are a few aircraft of Carrier Air Group 5 (CVG-5). Three squadrons and three detachments of CVG-5 accompanied the Constellation for her homeport change from the Atlantic to the Pacific from 25 July to 17 September 1962.
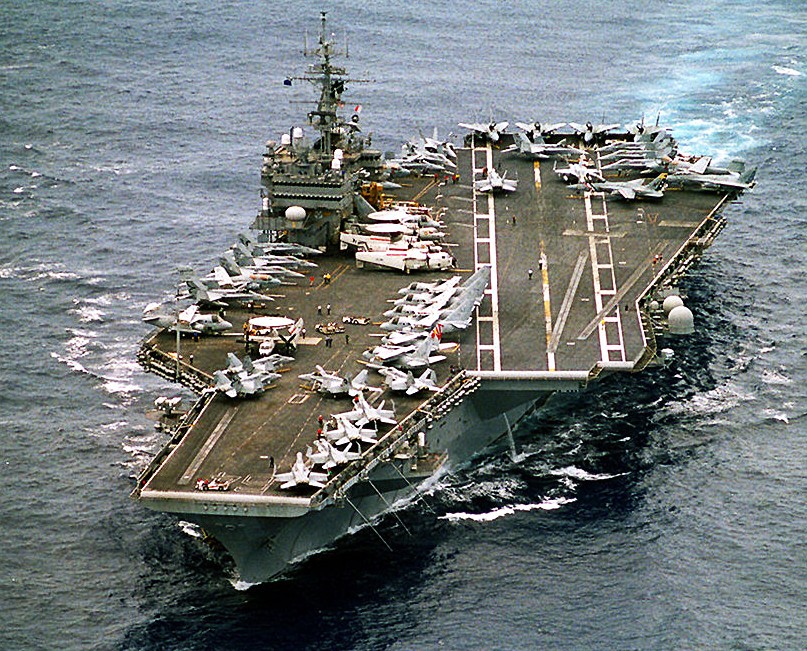

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CV 64) enroute to the Arabian Gulf to enforce no-fly zones and monitor shipping to and from Iraq. 14 April 1997.
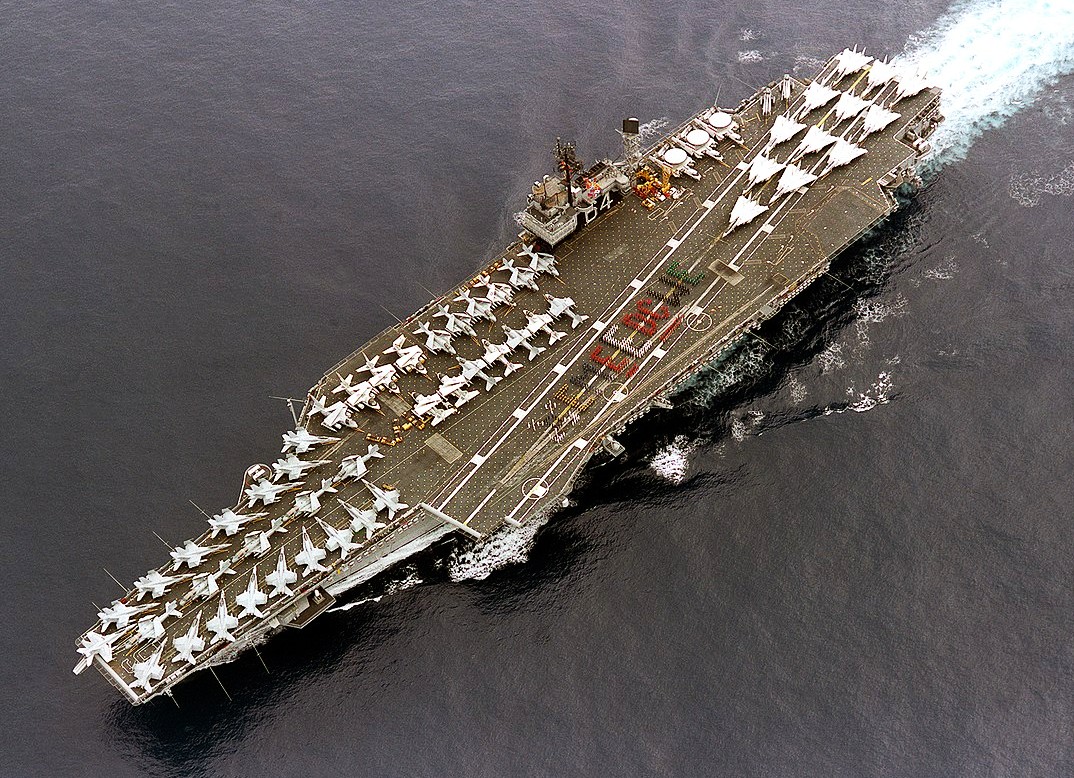

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CV-64) as crew members form the “Battle E” awards for excellence on the flight deck of the ship. 1 August 1986.

(USN Photo)
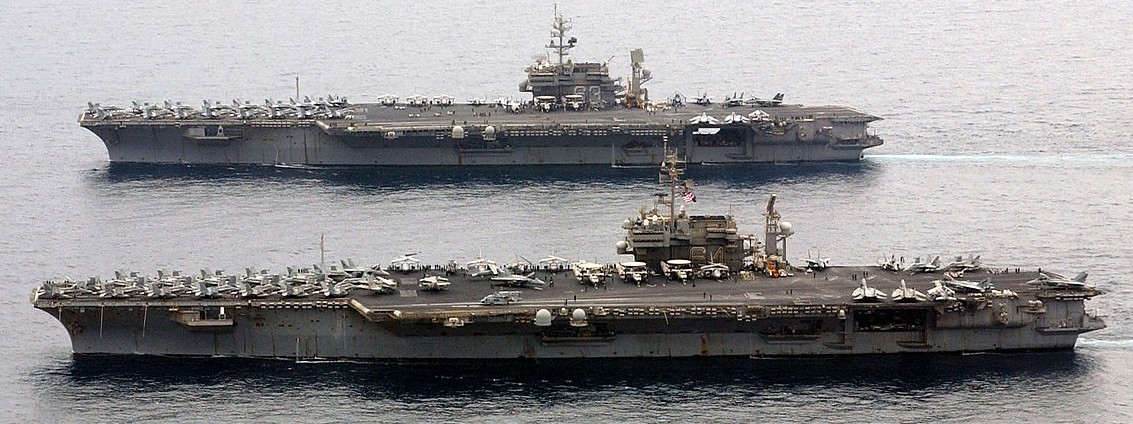
USS Constellation (CV 64) and USS Kitty Hawk (CV 63) steam alongside one another. 13 April 2003.

(USN Photo)
USS Constellation (CV-64) as it pulls into Perth, Australia, for a port call on her return transit to her homeport of San Diego, California. Constellation, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 2 (CVW-2), was deployed to the Western Pacific and the Indian Ocean from 2 November 2002 to 2 June 2003. This was her last deployment before her decommissioning on 7 August 2003.

(NASA ICE Photo)
Decommissioned aircraft carrier USS Constellation (CV-64) being towed through the Strait of Magellan. 24 Nov 2014.
USS Enterprise (CVN-65)

(USN Photo)
USS Enterprise (CVN-65) underway in the Atlantic Ocean on 14 June 2004.
USS Enterprise (CVN-65), formerly CVA(N)-65, is a decommissioned[3] United States Navy aircraft carrier. In 1958, she became the first nuclear-powered aircraft carrier in the United States Navy, and the world, as well as the eighth United States naval vessel to bear the name. Like her predecessor of the Second World War fame, she is nicknamed “Big E”. At 1,123 feet (342 m), she is the longest naval vessel ever built and the only ship of her class, which was originally planned to have five other ships. Her 93,284-long-ton (94,781 t) displacement ranks her class as the third-largest carrier class, after the Nimitz class and the Gerald R. Ford class. Enterprise had a crew of some 4,600 service members. Enterprise[12] was, at the time of inactivation, the third-oldest commissioned vessel in the United States Navy after the wooden-hulled USS Constitution and USS Pueblo (AGER-2). She was inactivated on 1 December 2012, and officially decommissioned on 3 February 2017, after over 55 years of service. She was stricken from the Naval Vessel Register the same day. The name has been adopted by the future Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carrier USS Enterprise (CVN-80). (Wikipedia)

(USN Photo)
U.S. Navy McDonnell Douglas F/A-18A Hornet from Strike Fighter Squadron VFA-161 Chargers approaching the the flight deck of the aircraft carrier USS Enterprise (CVN-65) on 1 July 1987. The carrier was en route to the Sea Fair Festival in Seattle, Washington (USA). VFA-161 was assigned to the short-lived Carrier Air Wing 10 (CVW-10, tail code “NM”). It was established in November 1986 and should have been assigned to the USS Independence (CV-62). However, it was only once deployed on the Enterprise for a short tour along the US Pacific coast and was disestablished again with all squadrons in November 1988.
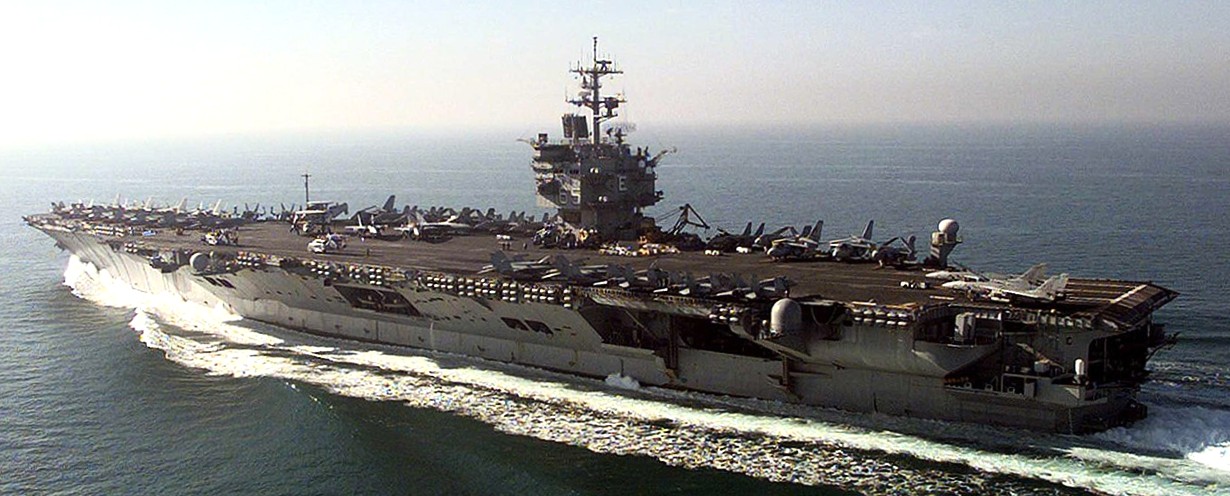

(USN Photo)
USS Enterprise (CVN 65) steams to the southern end of its operating area in the Persian Gulf the morning after the first wave of air strikes on Iraqi targets on 17 December 1998, in support of Operation Desert Fox. Note the large letter “E” on the back of the island.
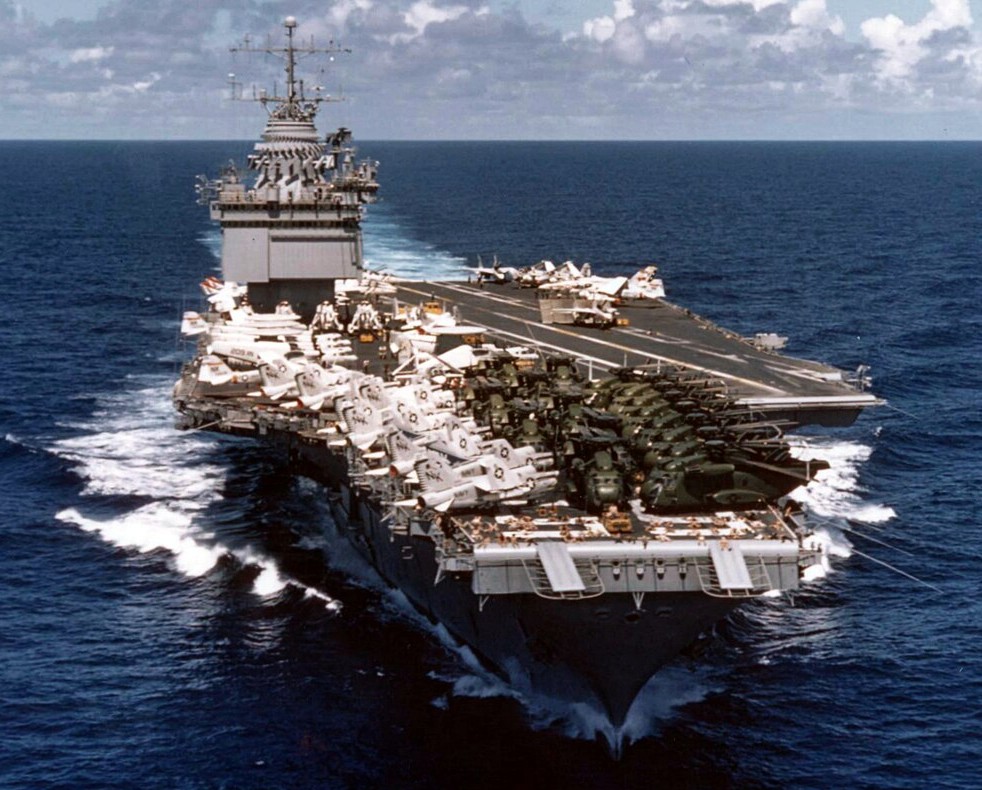

(USN Photo)
USS Enterprise (CVAN-65) underway returning to the United States from Western Pacific cruise that included the evacuation of Saigon. The aircraft on her deck include U.S. Marine Corps Sikorsky CH-53 Sea Stallion helicopters, which were hitching a ride home on board the ship. Note the men sunbathing on the forward part of the flight deck.
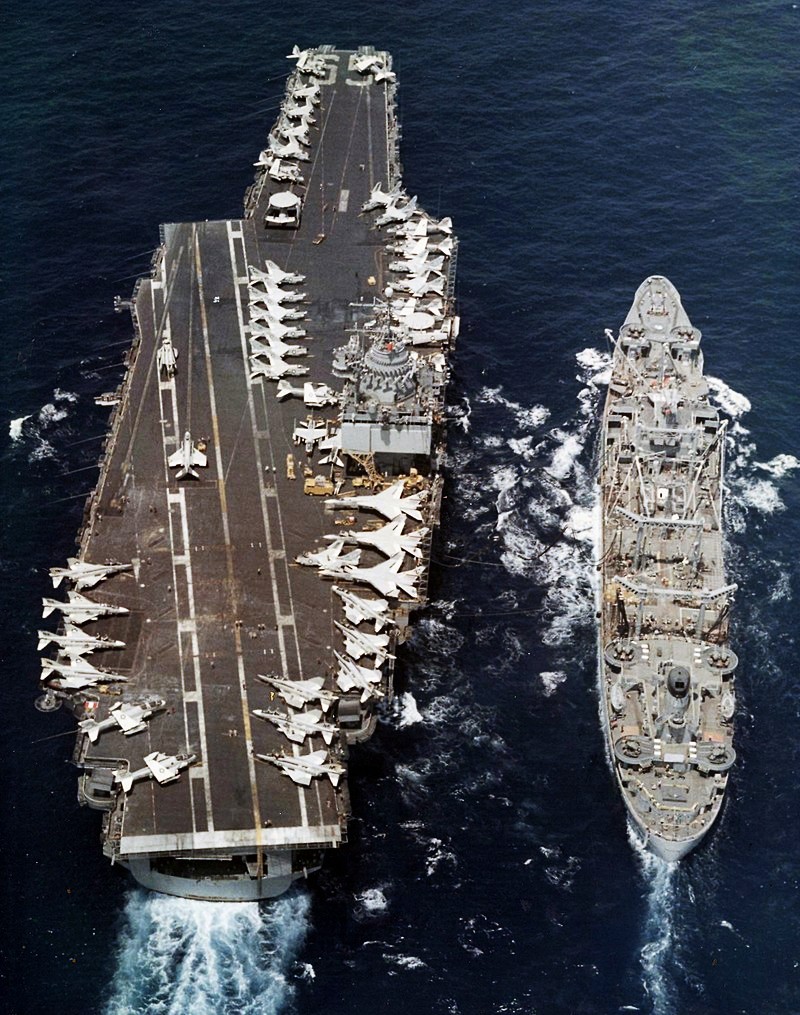

(USN Photo)
USS Enterprise (CVAN-65) being replenished by the fleet oiler USS Hassayampa (AO-145) in the South China Sea. The Big E was deployed with Attack Carrier Air Wing 14 (CVW-14) to Vietnam from 12 September 1972 to 12 June 1973.
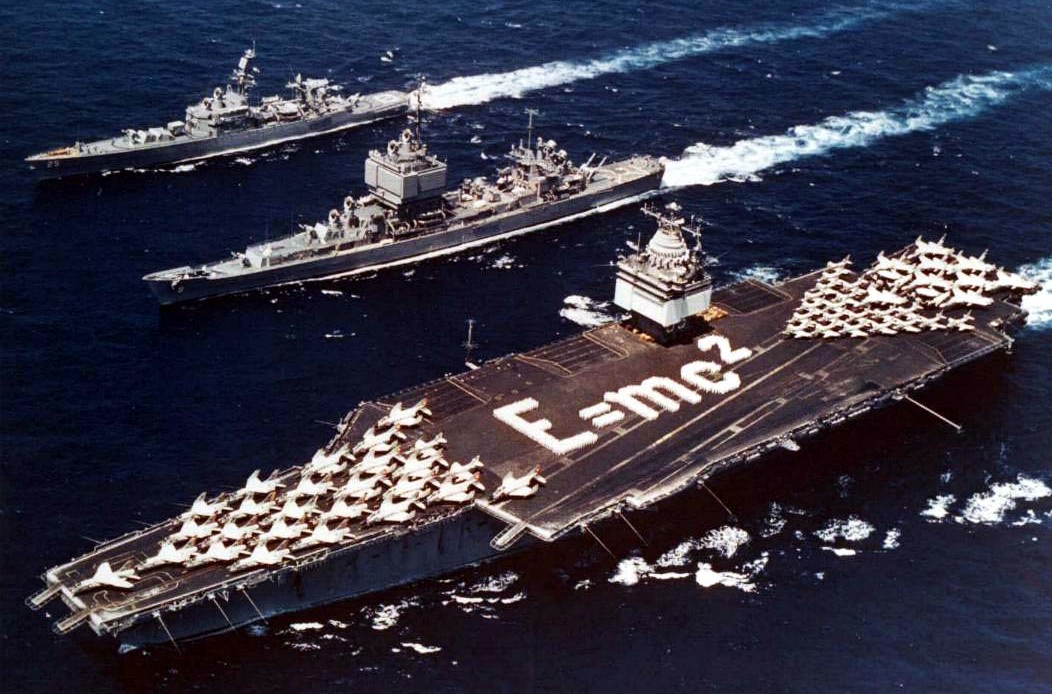

(USN Photo)
Operation Sea Orbit: on 31 July 1964, USS Enterprise (CVAN-65) (bottom), USS Long Beach (CGN-9) (center) and USS Bainbridge (DLGN-25) (top) formed “Task Force One,” the first nuclear-powered task force, and sailed 26,540 nmi (49,190 km) around the world in 65 days. Accomplished without a single refueling or replenishment, “Operation Sea Orbit” demonstrated the capability of nuclear-powered surface ships.
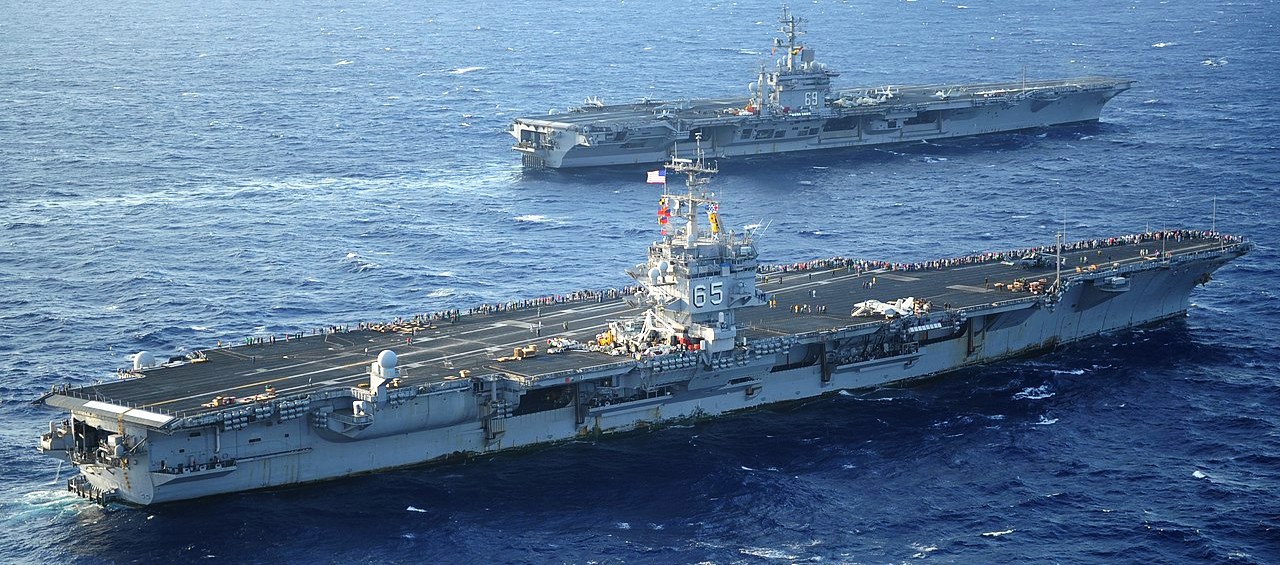

(USN Photo)
USS Enterprise (CVN 65) and USS Dwight D. Eisenhower (CVN 69) pass as Enterprise returns to homeport after completing a six-month deployment to the U.S. 5th and 6t Fleet areas of responsibility. Dwight D. Eisenhower is underway conducting carrier qualifications.
USS America (CV-66)
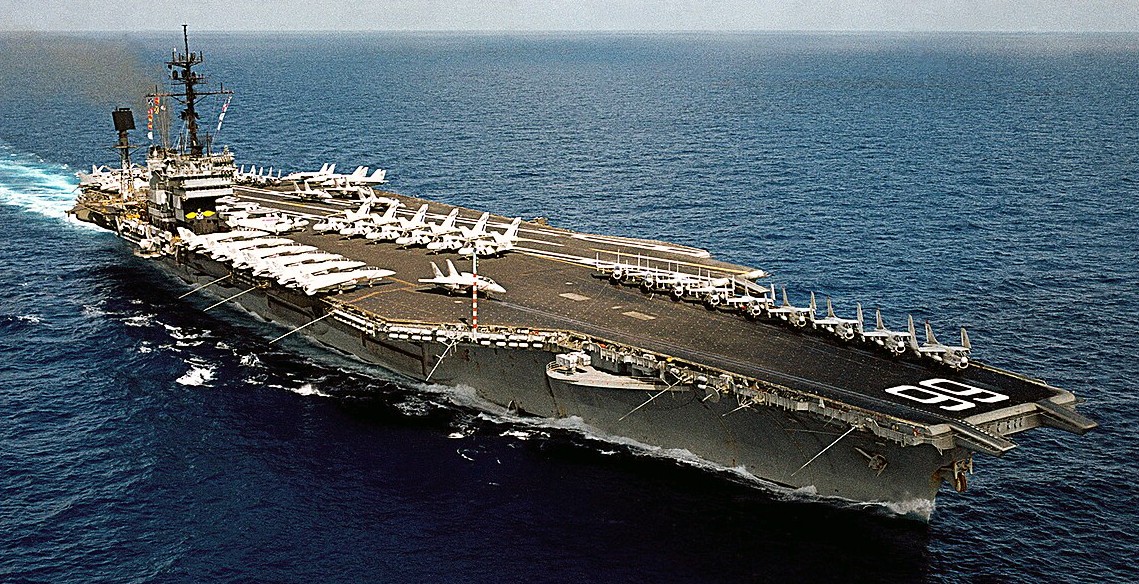

(USN Photo)
USS America (CV-66) underway in the Indian Ocean, 24 April 1983. America, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1), was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean from 8 December 1982 to 2 June 1983.
USS America (CVA/CV-66) was one of three Kitty Hawk-class supercarriers built for the United States Navy in the 1960s. Commissioned in 1965, she spent most of her career in the Atlantic and Mediterranean, but did make three Pacific deployments serving in the Vietnam War. She also served in the Persian Gulf War’s operations Desert Shield and Desert Storm. America was the first large aircraft carrier since Operation Crossroads in 1946 to be expended in weapons tests. In 2005, she was scuttled southeast of Cape Hatteras, after four weeks of tests, despite a large protest of former crew members who wanted to see her instituted as a memorial museum. She was the largest warship ever sunk. (Wikipedia)
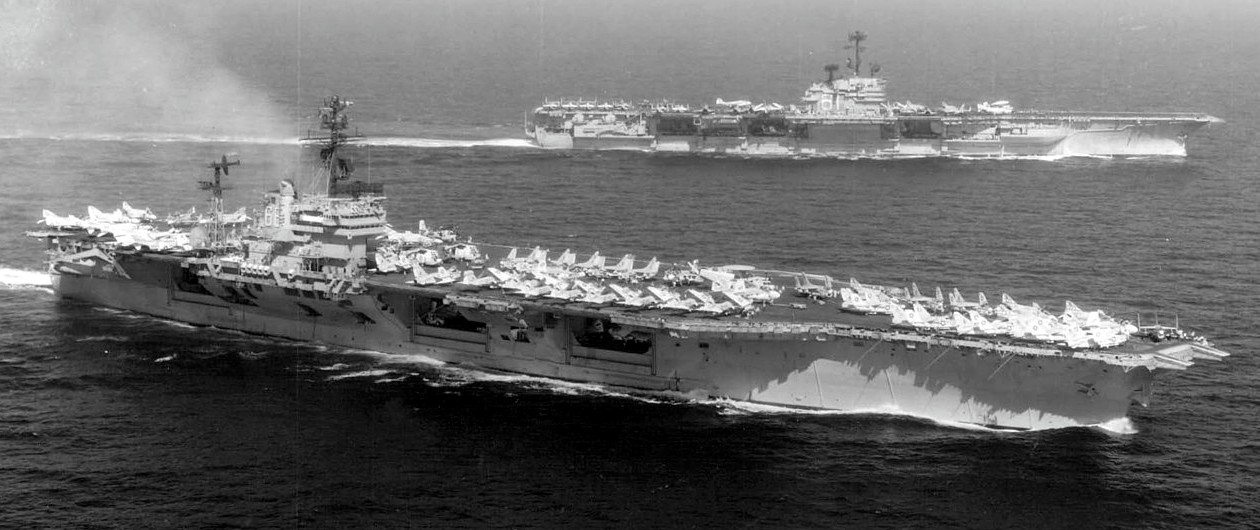

(USN Photo)
U.S. Navy aircraft carriers USS America (CVA-66), foreground, and USS Ranger (CVA-61) underway in the Gulf of Tonkin in January 1973. Ranger, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 2 (CVW-2), was deployed to Vietnam from 16 November 1972 to 22 June 1973. America, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 8 (CVW-8), was deployed to Vietnam from 5 June 1972 to 24 March 1973.
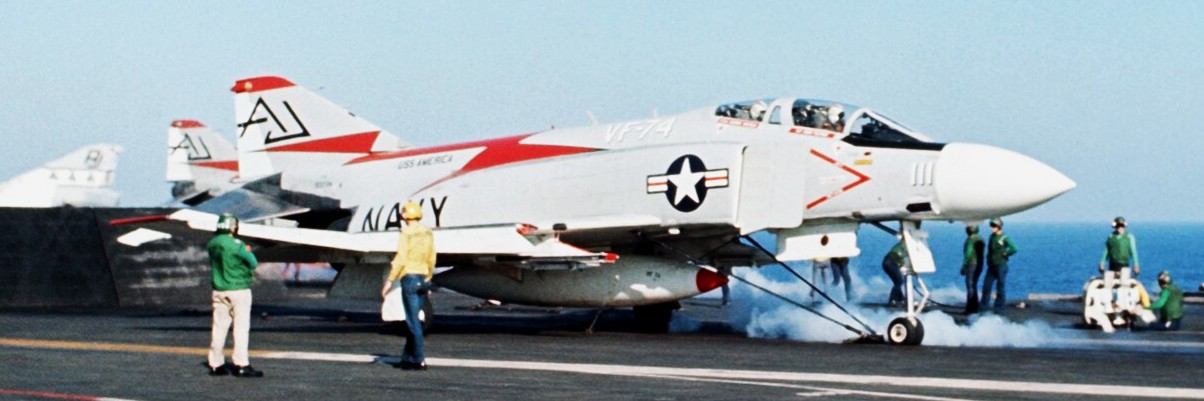

(USN Photo)
McDonnell Douglas F-4J Phantom II from fighter squadron VF-74 Be-Devilers is prepared for launch during flight operations aboard the attack aircraft carrier USS America (CVA-66). VF-74 was assigned to Attack Carrier Air Wing 8 (CVW-8) aboard the America for a deployment to Vietnam from 5 June 1972 to 24 March 1973.

(USN Photo)
Lockheed U-2 reconnaissance aircraft parked on the flight deck of the aircraft carrier USS America (CV 66). 18 October 1984.
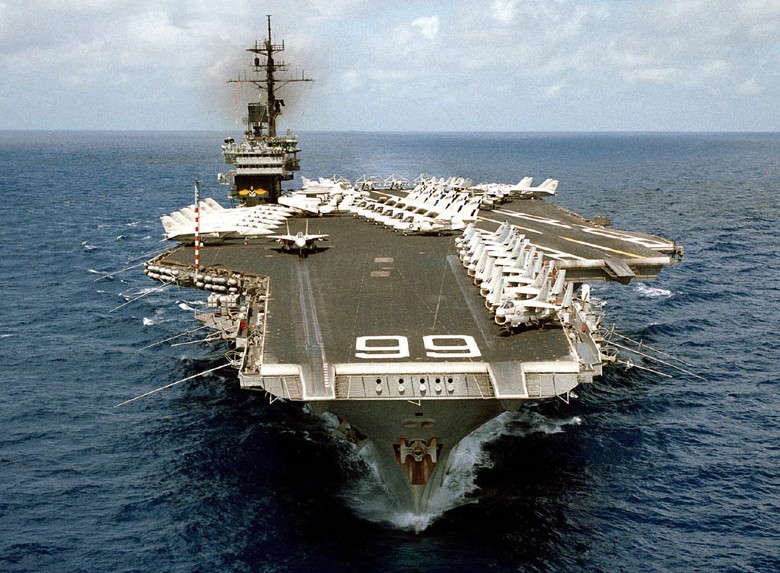

(USN Photo)
USS America (CV-66), underway in the Indian Ocean, 1983.

(USN Photo)
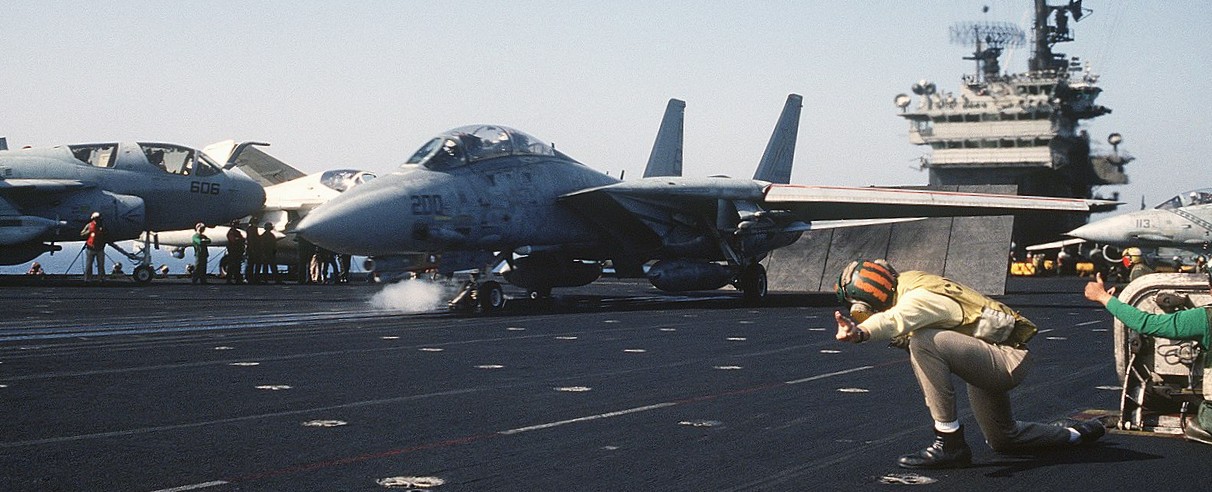
Grumman F-14A Tomcat aircraft from fighter squadron VF-33 Starfighters prepares to take off from the aircraft carrier USS America (CV-66) during flight operations off the coast of Libya. On 15 April 1986 America´s aircraft participated in “Operation El Dorado Canyon”, the bombing of Libya.

(USN Photo)
USS America (CV-66), underway in Norwegian waters during Exercise OCEAN SAFARI ’85.
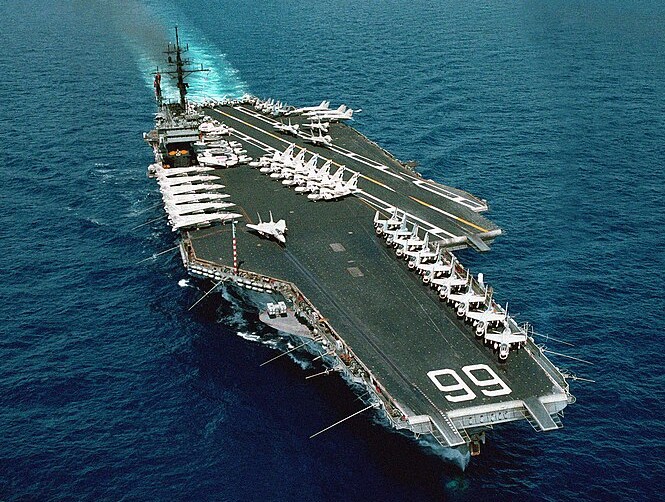

(USN Photo)
USS America (CV-66), underway, 24 April 1983.
USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67)
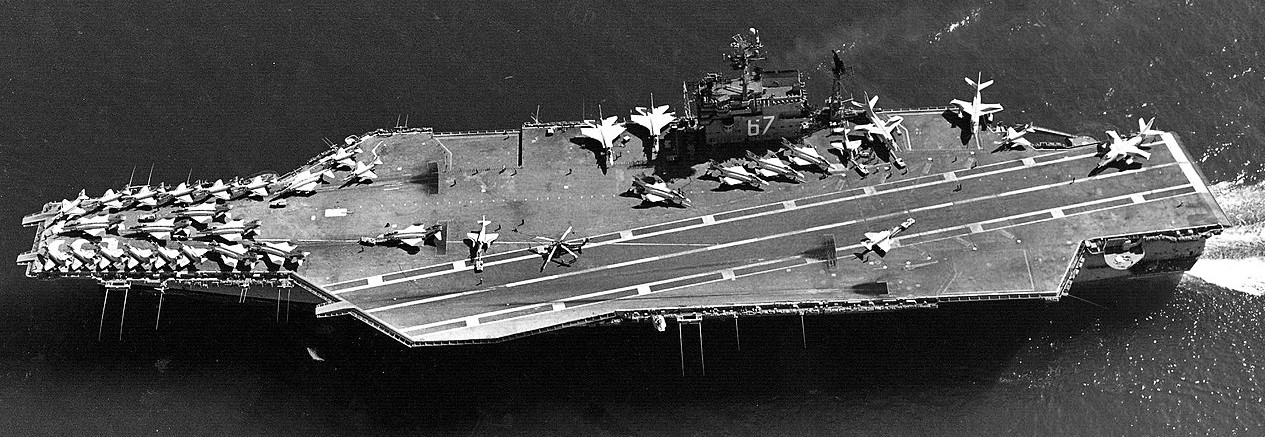

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CVA-67) underway in the Atlantic Ocean during her shakedown cruise between 2 November and 16 December 1968. On deck are aircraft of Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1). Note that the Mk 25 BPDMS Sea Sparrow-launchers have not yet been installed.
USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67) (formerly CVA-67), the only ship of her class, was an aircraft carrier, formerly of the United States Navy. Considered a supercarrier, she was a variant of the Kitty Hawk class, and the last conventionally-powered carrier built for the Navy, as all carriers since have had nuclear propulsion. Commissioned in 1968, the ship was named after John F. Kennedy, the 35th president of the United States. John F. Kennedy was originally designated a CVA, for fixed-wing attack carrier, however the designation was changed to CV, for fleet carrier. After nearly 40 years of service, John F. Kennedy was decommissioned on 1 August 2007. She was berthed at the NAVSEA Inactive Ships On-site Maintenance facility in Philadelphia, formerly the Philadelphia Naval Shipyard, and, until late 2017, was available for donation as a museum and memorial to a qualified organization. In late 2017, the Navy revoked her “donation hold” status and designated her for dismantling. On 16 January 2025, John F. Kennedy left the Philadelphia Naval Shipyard and started the voyage to Brownsville, Texas, where she will be scrapped. She arrived at Brownsville on 2 February 2025 for her final arrival. She has been succeeded by the Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carrier Pre-Commissioning Unit John F. Kennedy (CVN-79), laid down in July 2015, launched in October 2019, and scheduled to enter service in March 2027, after missing the delivery date July 2025. (Wikipedia)
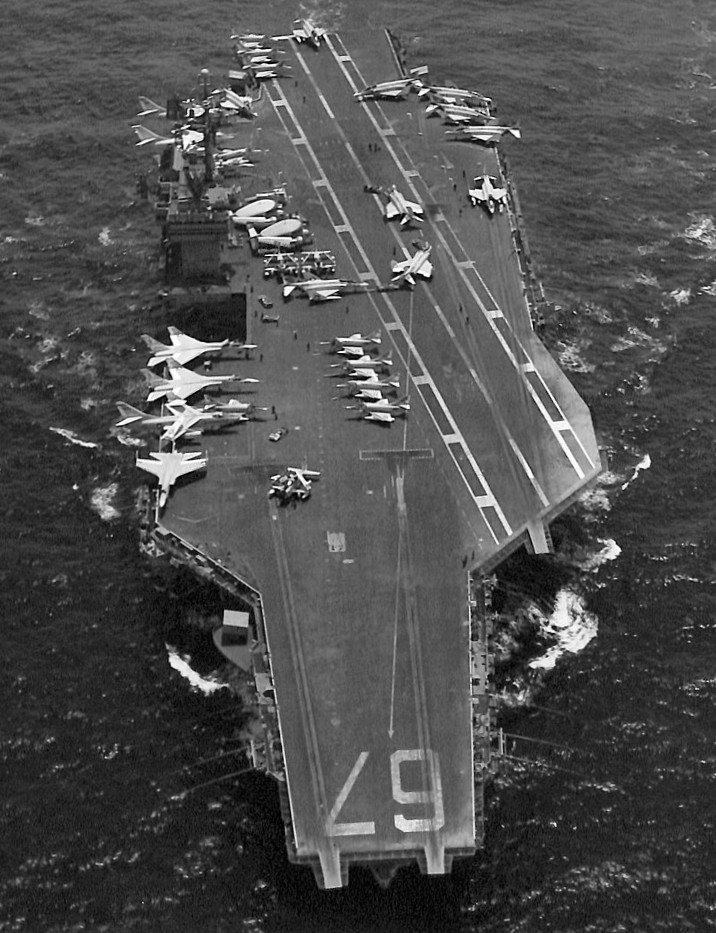

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CVA-67) underway in the Mediterranean Sea, in November 1969.
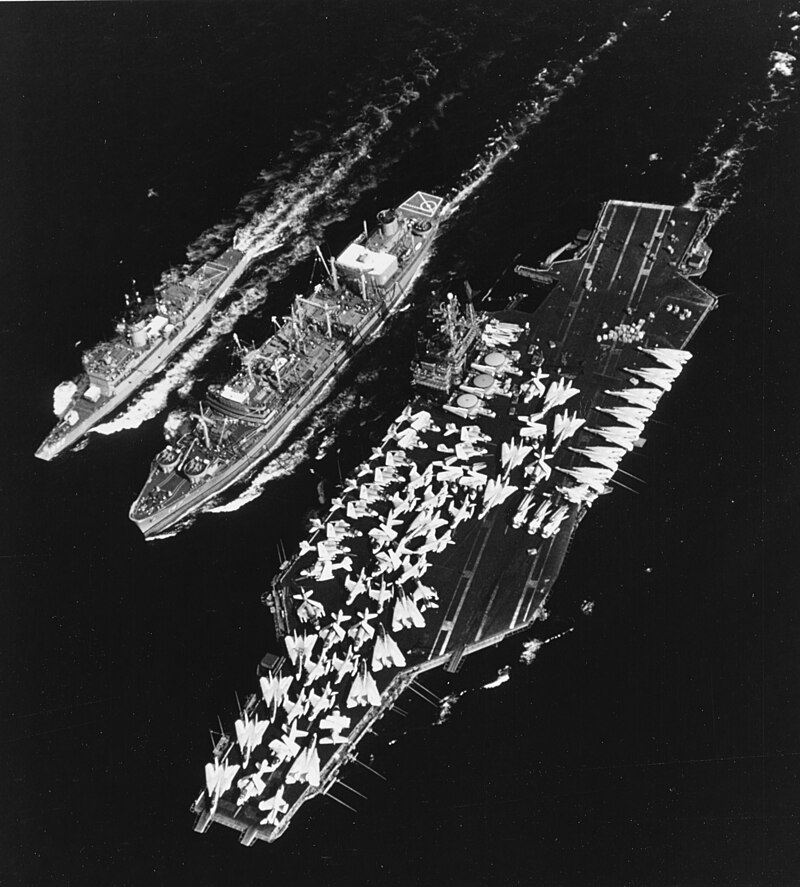
(USN Photo)
The U.S. Navy fleet oiler USS Truckee (AO-147) refuels the aircraft carrier USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67) and the frigate USS Thomas C. Hart (FF-1092) on 14 August 1975, while operating with Task Force 60. John F. Kennedy, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1), was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea from 28 June 1975 to 27 January 1976.
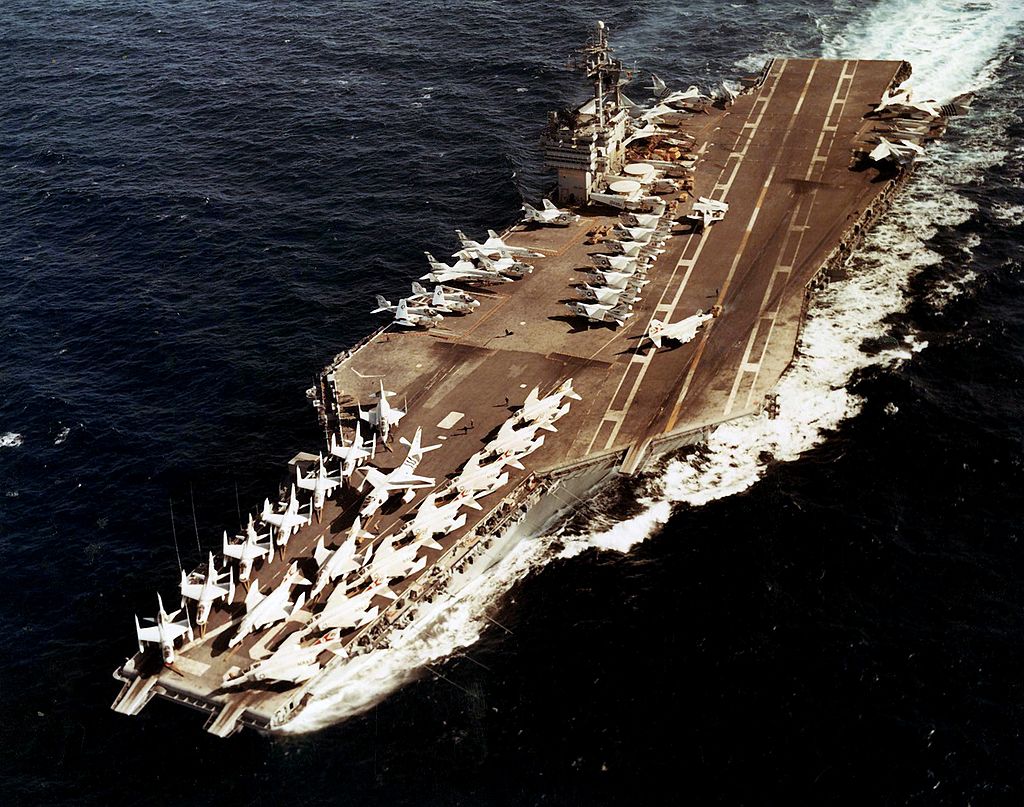

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CVA-67) underway c1970.
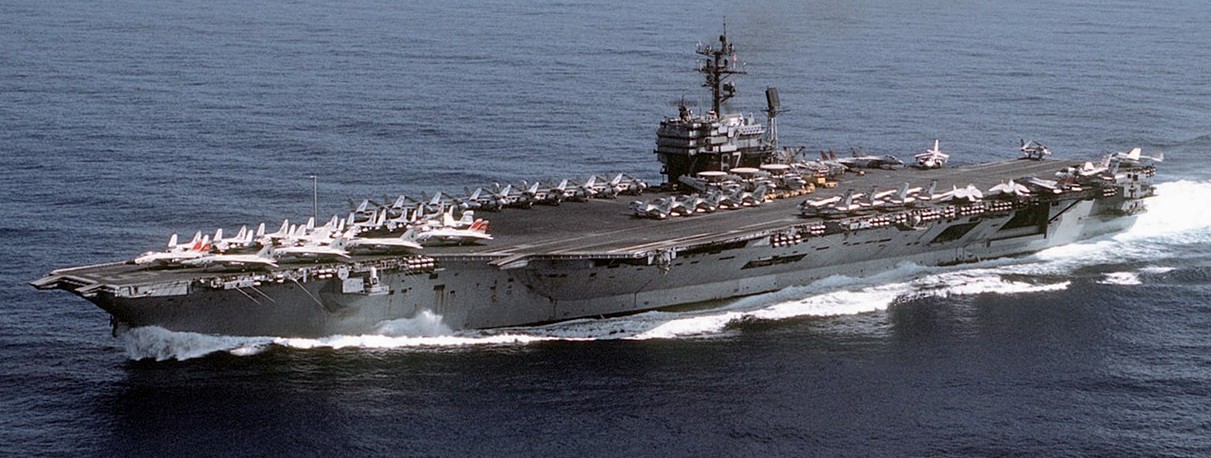

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67) underway. The JFK, with assigned Carrier Air Wing 3 (CVW-3), was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean from 4 January to 14 July 1982.

(USN Photo)
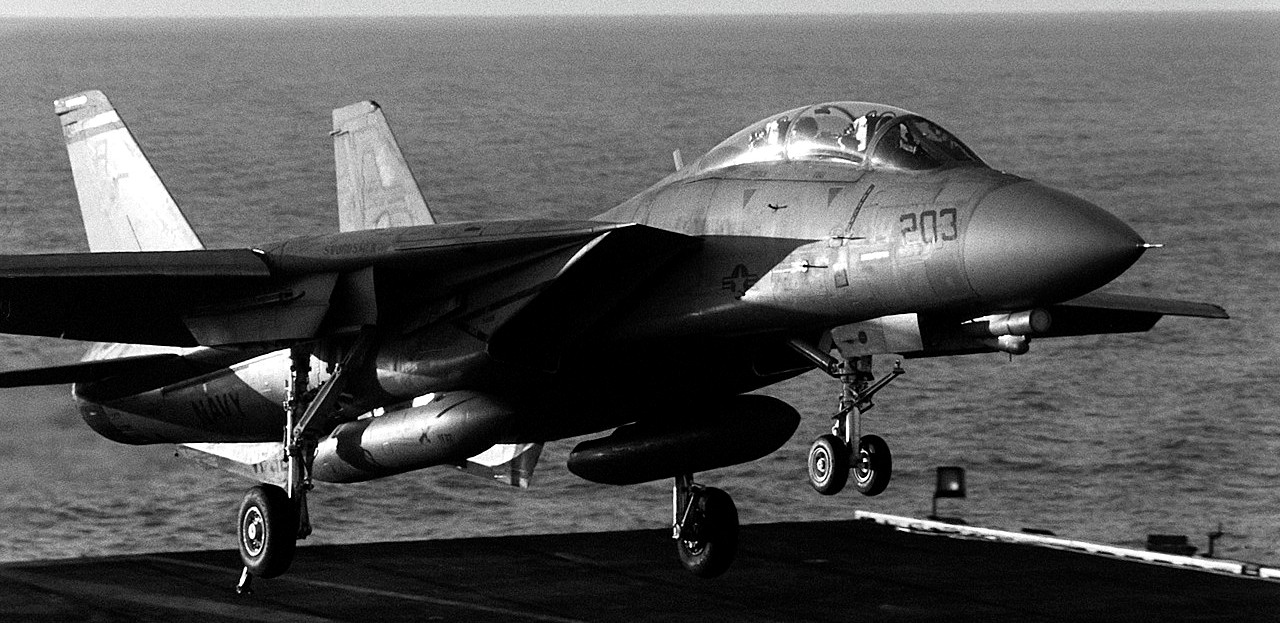
Grumman F-14A Tomcat, Fighter Squadron 32 (VF-32) landing on the flight deck of the USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67) during Fleet Ex 1-90, 1 January 1990.

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CVA-67) underway in the Caribbean Sea, 26 July 1992.

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CV 67) 23 February 2002, passing the “Rock” of Gibraltar, a British owned territory at the extreme southern end of Spain. Escorted by HH-60H “Seahawk” helicopters assigned to the “Nightdippers” of Helicopter Anti-Submarine Squadron Five (HS-5), Kennedy and its embarked Carrier Air Wing (CVW) transited the Atlantic Ocean marking the start of a scheduled deployment, and is expected to relieve USS Theodore Roosevelt (CN 71), to conduct missions in support of Operation Enduring Freedom.

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CV 67) underway, 12 March 1986.

(USN Photo)
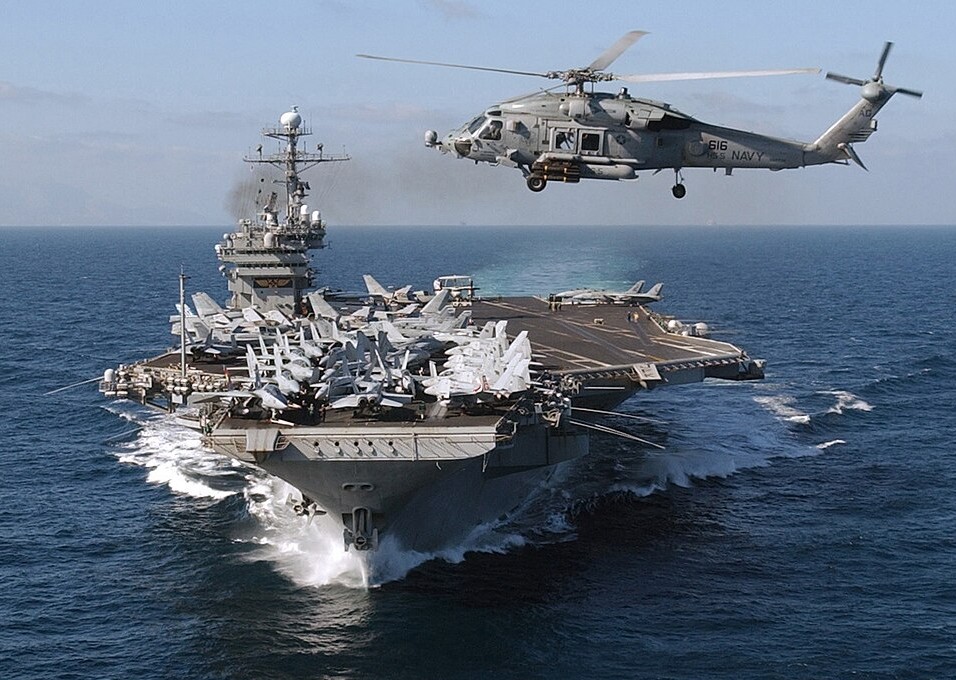
A Bell HH-60H Seahawk helicopter assigned to the “Nightdippers” of Helicopter Anti-Submarine Squadron Five (HS-5) crosses the bow of USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67), as the carrier Battle Group (BG) arrives in the Mediterranean Sea. 23 February 2002.

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CVA-67) underway in the Atlantic Ocean, 12 March 2005.

(USN Photo)
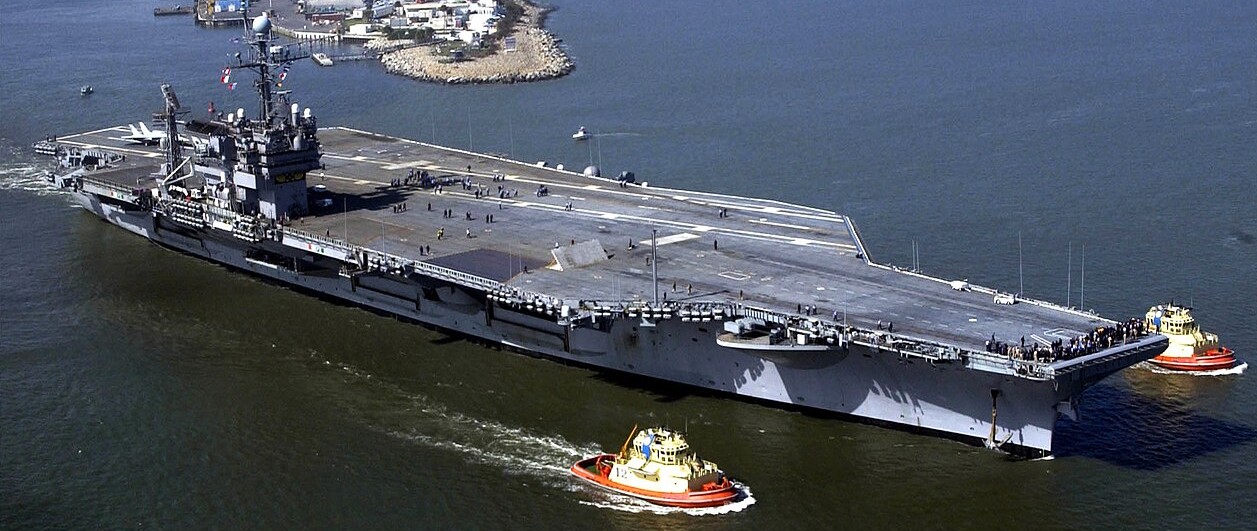
USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67) departs Naval Station Mayport under her own power following a ten month Extended Service Repair Availability (ESRA). During a short at sea period the ship tested numerous systems installed or upgraded while in port. The $300 million maintenance period included renovation of berthing compartments, and new navigational radar system. 11 November 2003.

(USN Photo)
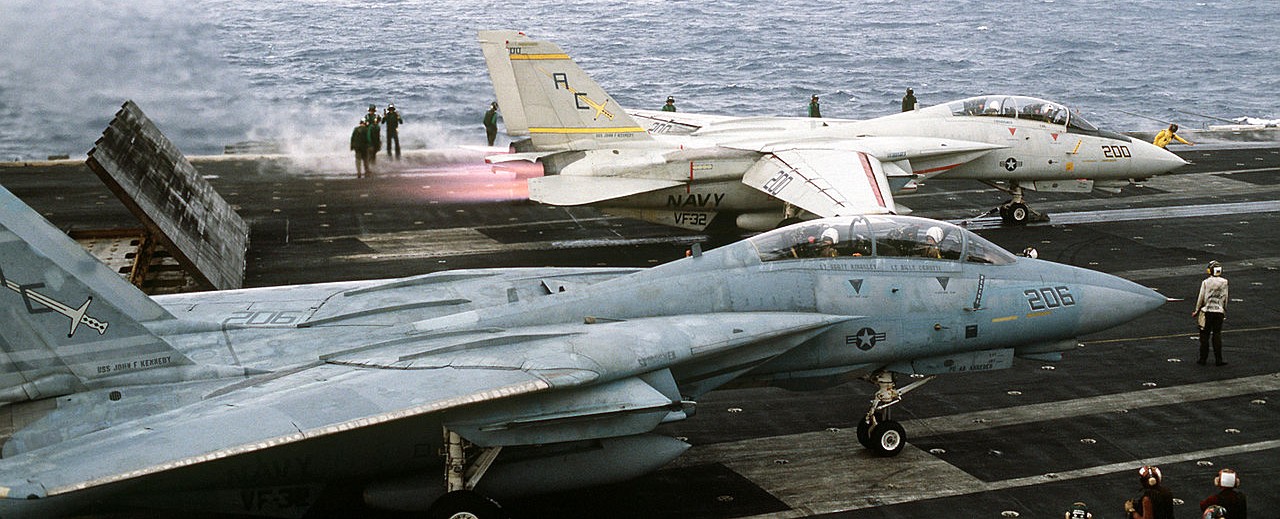
Fighter Squadron 32 (VF-32) F-14A Tomcat aircraft fires its afterburner in preparation for launch from the aircraft carrier USS JOHN F. KENNEDY (CV-67). The ship is participating in NATO Exercise Display Determination ’86.

(USN Photo)
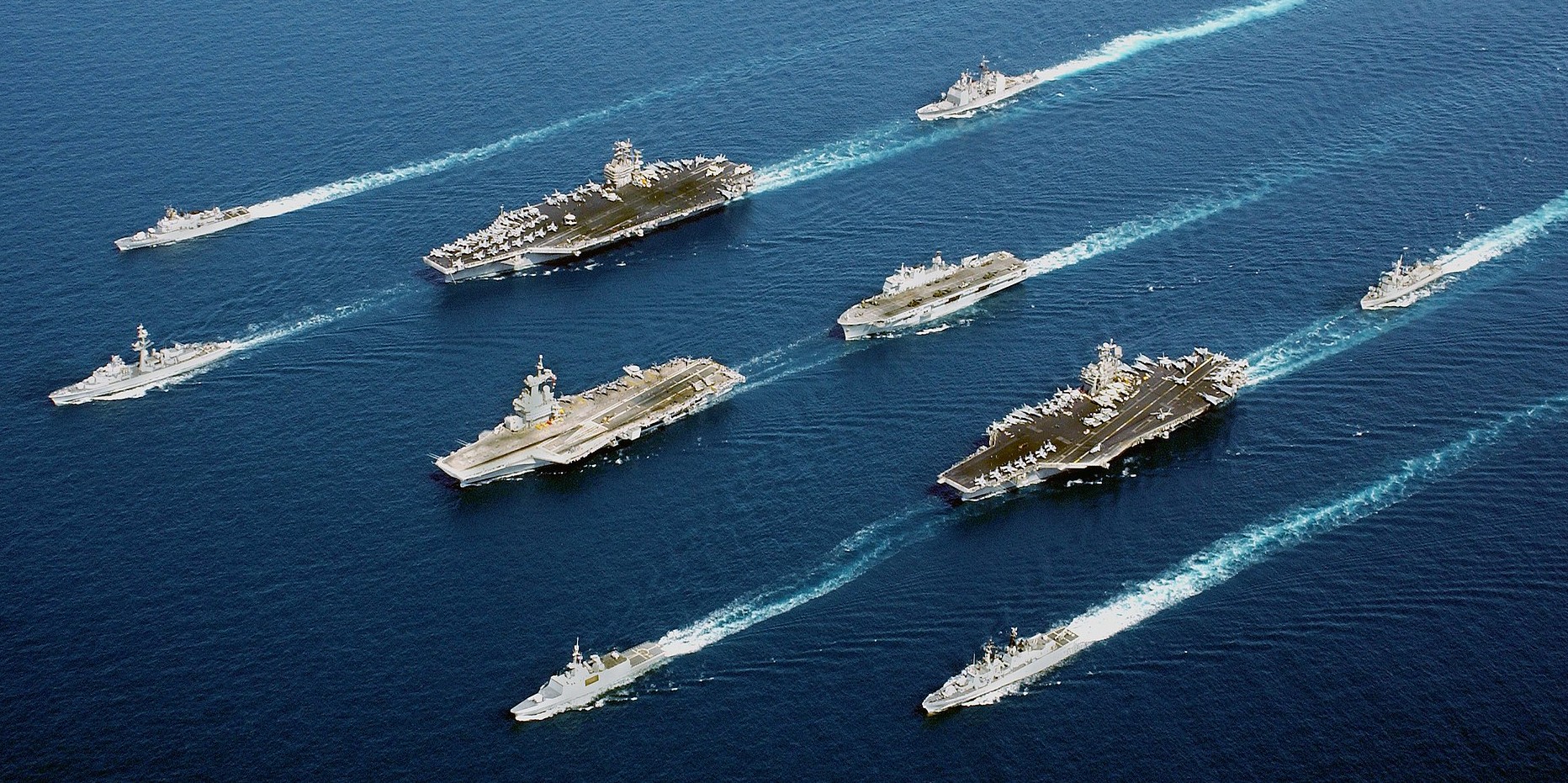
Naval vessels from five nations move in parade formation for a rare photographic opportunity at sea. In four descending columns, from left to right: ITS Maestrale (F 570), De Grasse (D 612); USS John C. Stennis (CVN-74), Charles de Gaulle (R91), Surcouf (F 711); USS Port Royal (CG-73), HMS Ocean (L12), USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67), ITS Luigi Durand de la Penne (D560); and HNLMS Van Amstel (F 831). 18 April 2002.

(USN Photo)
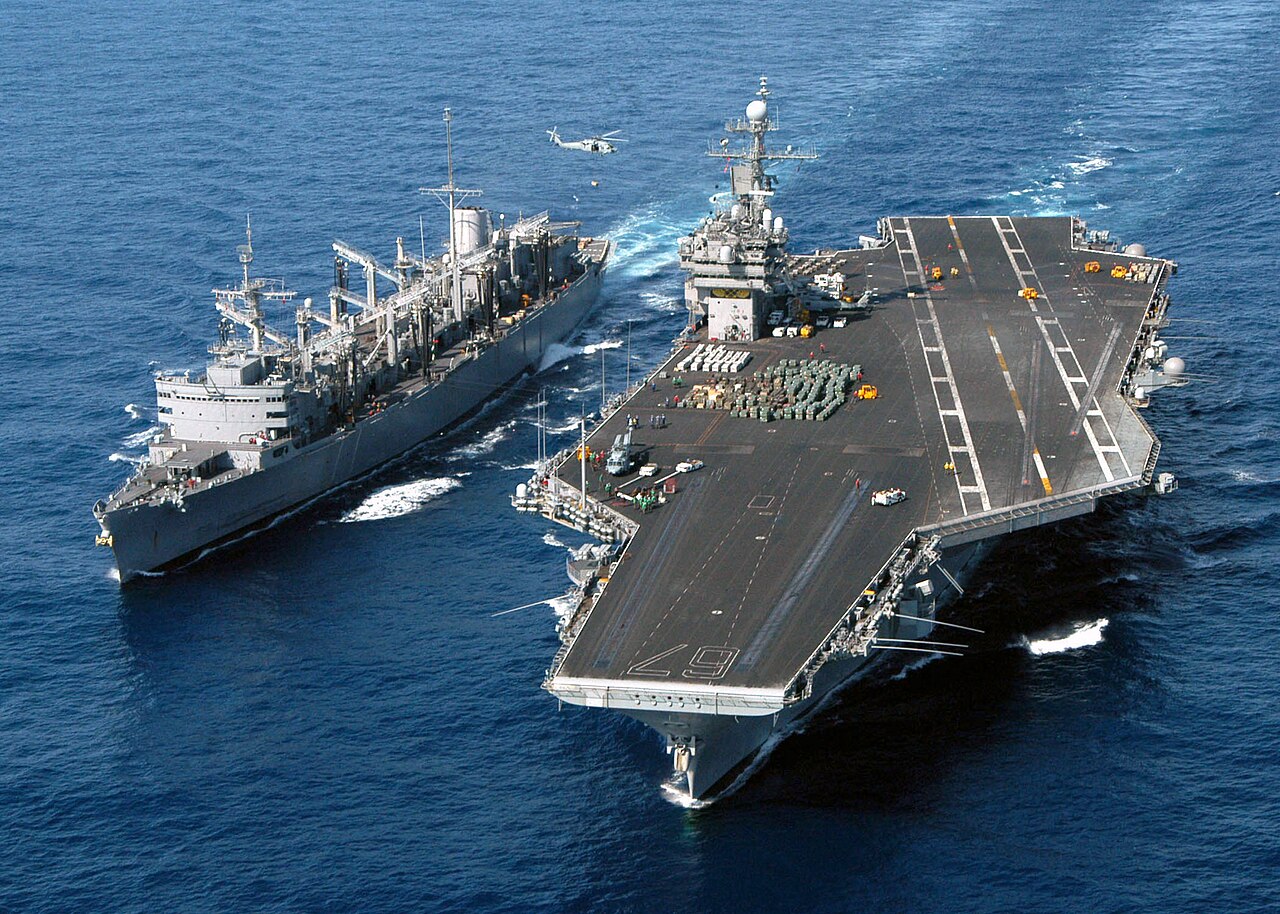
USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67) receives ordnance from the fast combat support ship USS Seattle (AOE-3) during an ammunition onload in the Atlantic Ocean. The conventional powered aircraft carrier conducted an underway replenishment with Seattle and a vertical replenishment with USS Enterprise (CVN-65) in final preparations for a scheduled six-month deployment to the Mediterranean Sea. 23 April 2004.

(USN Photo)
USS John F. Kennedy (CV-67), esorted by an HH-60H Seahawk assigned to the “Nightdippers” of Helicopter Anti-Submarine Squadron Five (HS-5) passes by the Rock of Gibraltar as it leaves the Mediterranean Sea. 8 August 2002.
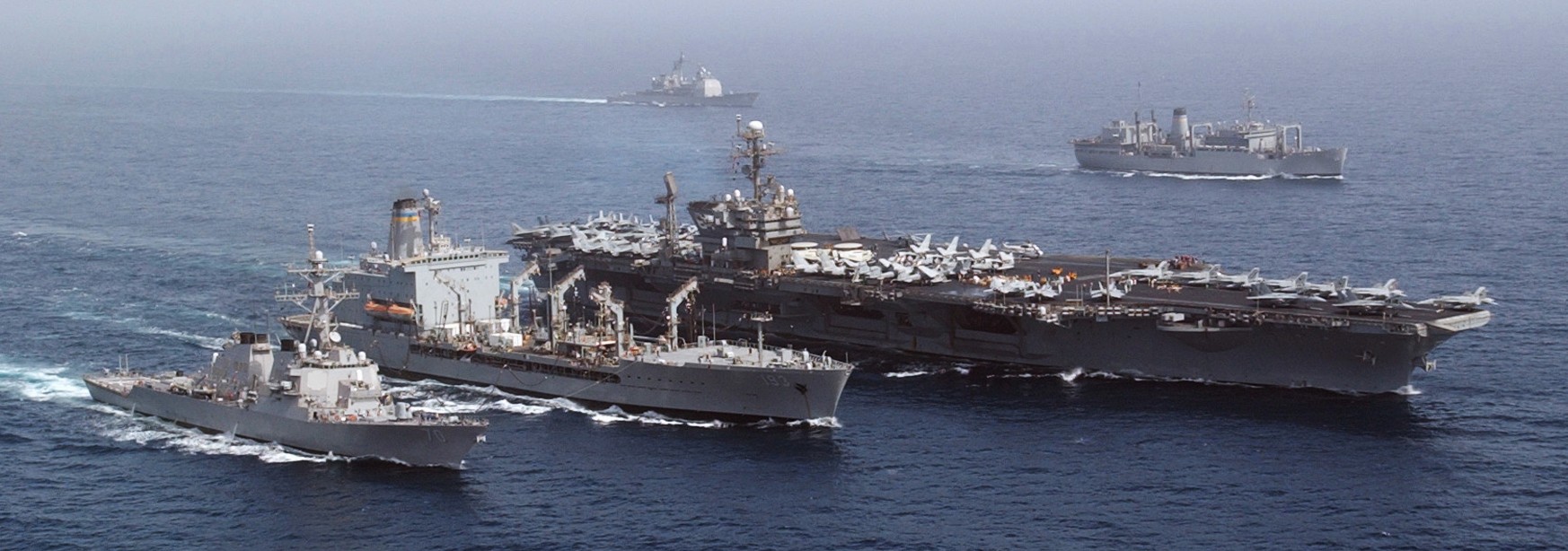

(USN Photo)
The guided-missile destroyer USS Hopper (DDG 70) (left) and the aircraft carrier USS John F. Kennedy (CV 67) (right) conduct a simultaneous replenishment at sea (RAS) with the auxiliary fleet oiler USNS Walter S. Diehl (TAO 193) (center). 19 July 2002
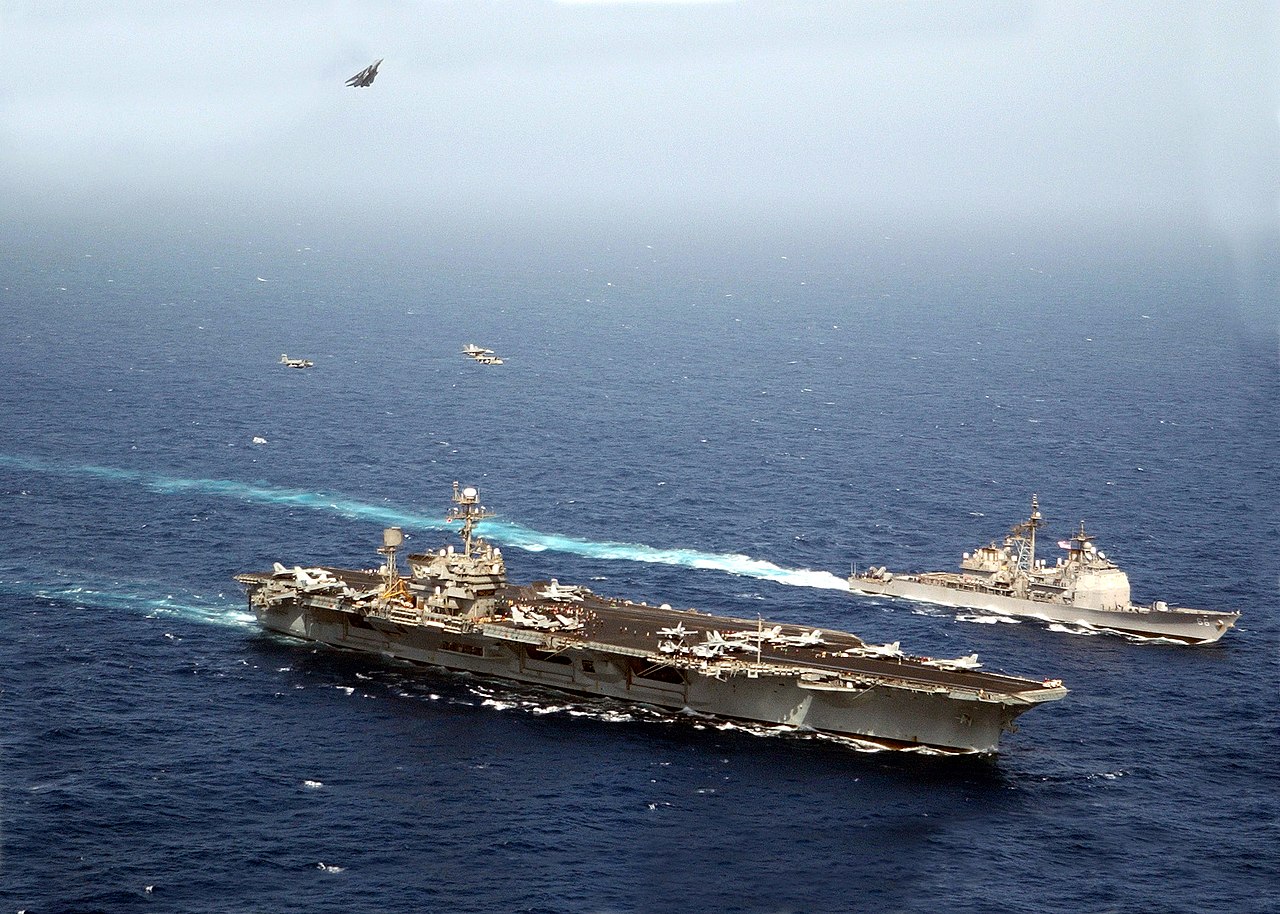

(USN Photo)
Aircraft assigned to Carrier Air Wing Seven (CVW-7) fly between USS John F. Kennedy and USS Hue City (CG 66) on Memorial Day. An F-14B “Tomcat” breaks up and out to form a “Missing Man Formation” in honor of those who gave their lives to preserve freedom. Kennedy is deployed conducting combat missions in support of Operation Enduring Freedom.
