Marine nationale aircraft carrier Béarn and seaplane tender Commandant Teste
Between the World Wars, the Marine nationale modernized and expanded significantly, even in the face of limitations set by the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty. New additions included the heavy and fast Fantasque class “super-destroyers”, the Richelieu class battleships, and the submarine Surcouf which was the largest and most powerful of its day. From the start of the Second World War, the Navy was involved in a number of operations, participating in the Battle of the Atlantic, the Norwegian Campaign, the Dunkirk evacuation and, briefly, the Battle of the Mediterranean. However, after the fall of France in June 1940, the Navy was obligated to remain neutral under the terms of the armistice that created the truncated state of Vichy France.
Worldwide, some 100 naval vessels and their crews heeded General Charles de Gaulle’s call to join forces with the British, but the bulk of the fleet, including all its capital ships, transferred loyalty to Vichy (Marine de Vichy). Concerned that the German Navy might somehow gain control of the ships, the British mounted an attack on Mers-el-Kébir, the Algerian city where many of them were harboured. The incident poisoned Anglo-French relations, leading to Vichy reprisals and a full-scale naval battle at Casablanca in 1942 when the Allies invaded French North Africa. But the confrontations were set aside once the Germans occupied Vichy France. The capital ships were a primary goal of the occupation, but before they could be seized they were scuttled by their own crews. A few small ships and submarines managed to escape in time, and these joined de Gaulle’s Free French Naval Forces, an arm of Free France that fought as an adjunct of the Royal Navy until the end of the war. In the Pacific theatre as well, Free French vessels operated until the Japanese capitulation; Richelieu was present at the Japanese Instrument of Surrender. (Wikipedia)
Marine nationale classes of the Second World War include ship classes used by the French Third Republic, Vichy France, and Free France. The abbreviation FTR beside a class shows it was in service with the Third French Republic, VF indicates it was in service with Vichy France, and FF shows it was in service with Free French forces.
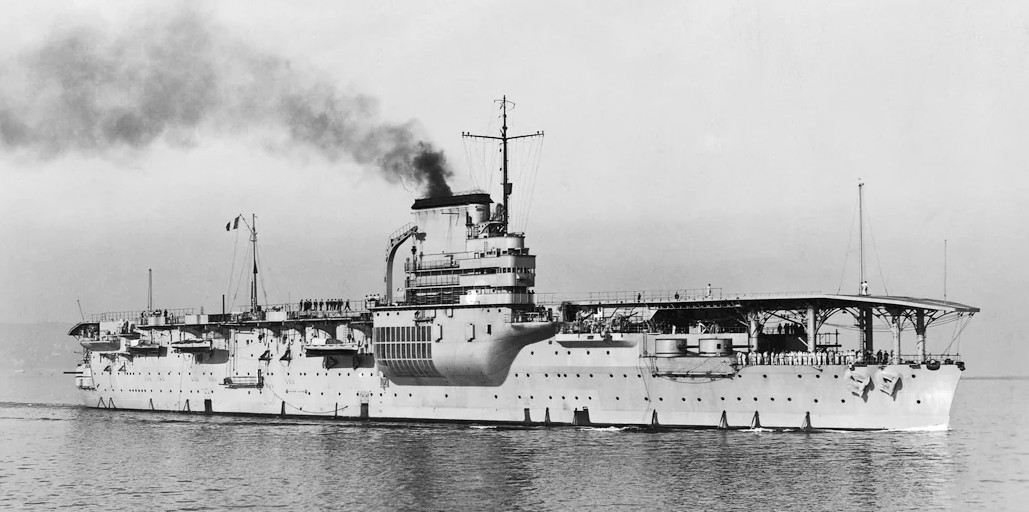
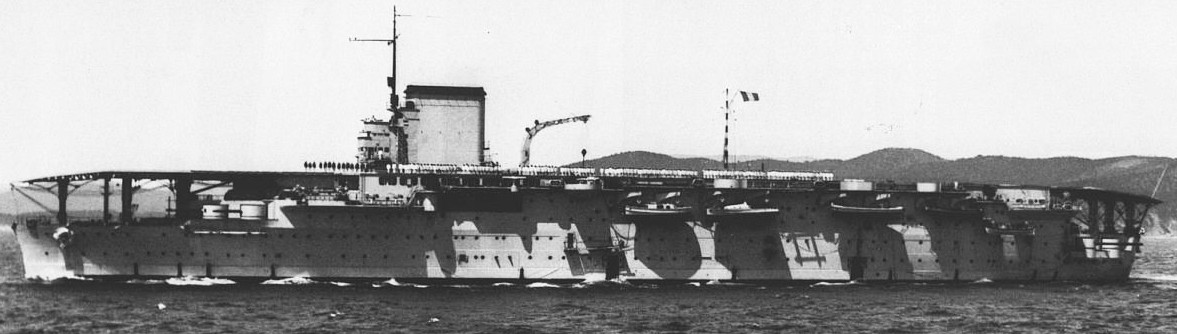
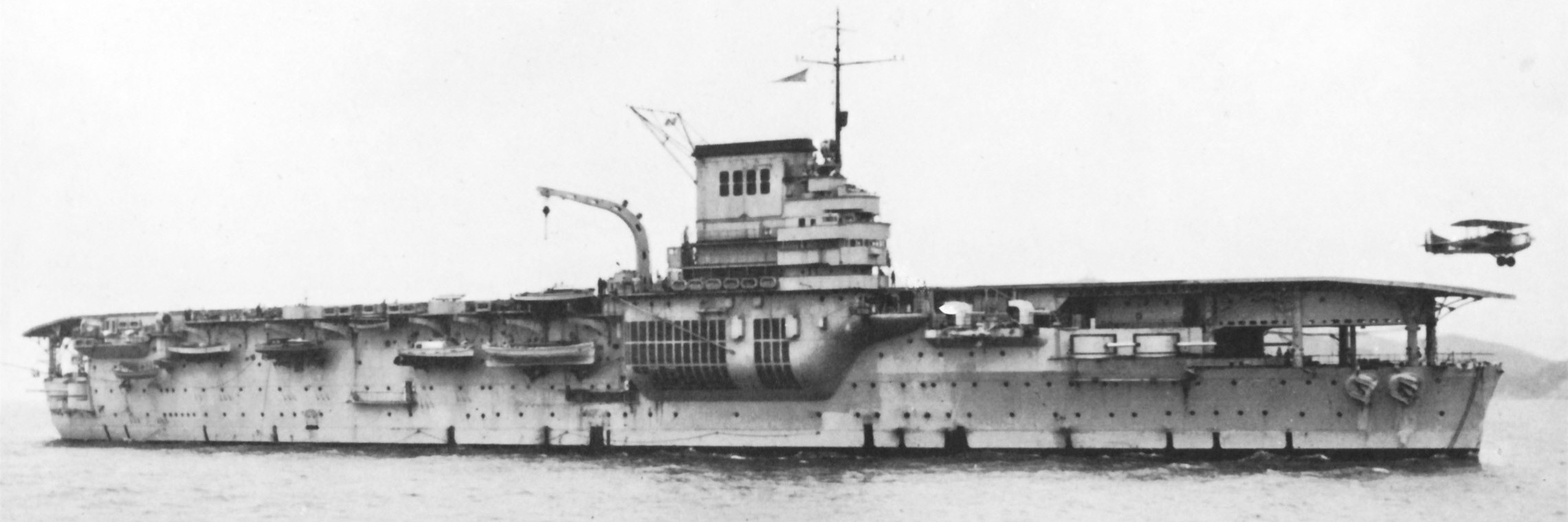
Marine nationale aircraft carrier Béarn
Béarn was an aircraft carrier converted from an incomplete Normandie-class battleship for the Marine nationale (French Navy) during the 1920s. Entering service in 1928, the navy intended to use her to develop tactics and techniques for carrier aviation. The only aircraft carrier France produced until after the Second World War, the ship played a minor role in early stages of the war, training in home waters and conducting pilot training.In late May 1940 Béarn ferried gold to purchase aircraft from the United States, but she was diverted to Martinique in the French West Indies when the French armistice with Germany was signed in June. Under pressure from the United States, which was worried about the Germans taking control of her if she returned to France, the carrier remained there for the next four years. To placate the Americans, the local commander agreed to have her immobilized in mid-1942. The Vichy French government ordered him to sabotage the ship in May 1943 and he ultimately complied by having Béarn run aground.
She was towed to Puerto Rico after the islands joined the Free French later that year for preliminary repairs that would allow her to steam under her own power to New Orleans, Louisiana, to be converted into an aircraft ferry. The conversion was completed in early 1945; on her first trip with a load of aircraft she collided with another ship and had to divert to French Morocco for emergency repairs. Full repairs took almost six months and she then transported personnel and equipment between Metropolitan France and French North Africa for several months.In October the ship sailed for French Indochina with aircraft, material and supplies as the French planned to reassert control over their Japanese-occupied colony. Béarn remained there for a year before returning home where she was immediately placed in reserve. Two years later, the ship was reactivated as the flagship of the Marine nationale’s submarine and anti-submarine group and also served as a submarine tender. In 1960 Béarn was hulked and served as a barracks ship until she became so uneconomical that a replacement vessel was constructed in 1966. She was sold for scrap the following year. (Wikipedia)
(Marine nationale Photo)
Marine nationale aircraft carrier Béarn.
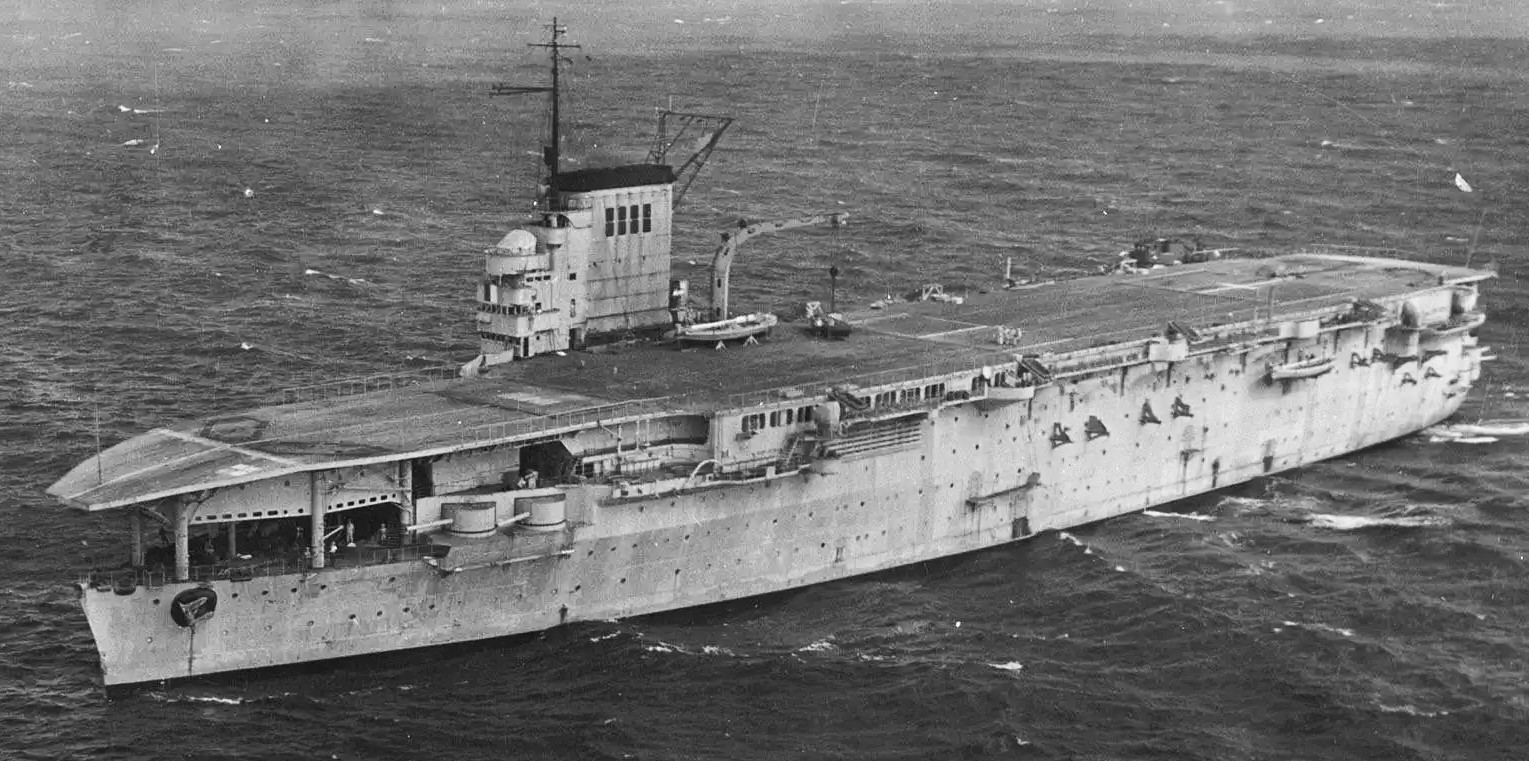

(Marine nationale Photo)
Marine nationale aircraft carrier Béarn. She was in service from 1927 to 1940. From 1944 to 1948 she was used to transport aircraft, then she became a stationary hulk at Toulon, France, until being scrapped in 1967.
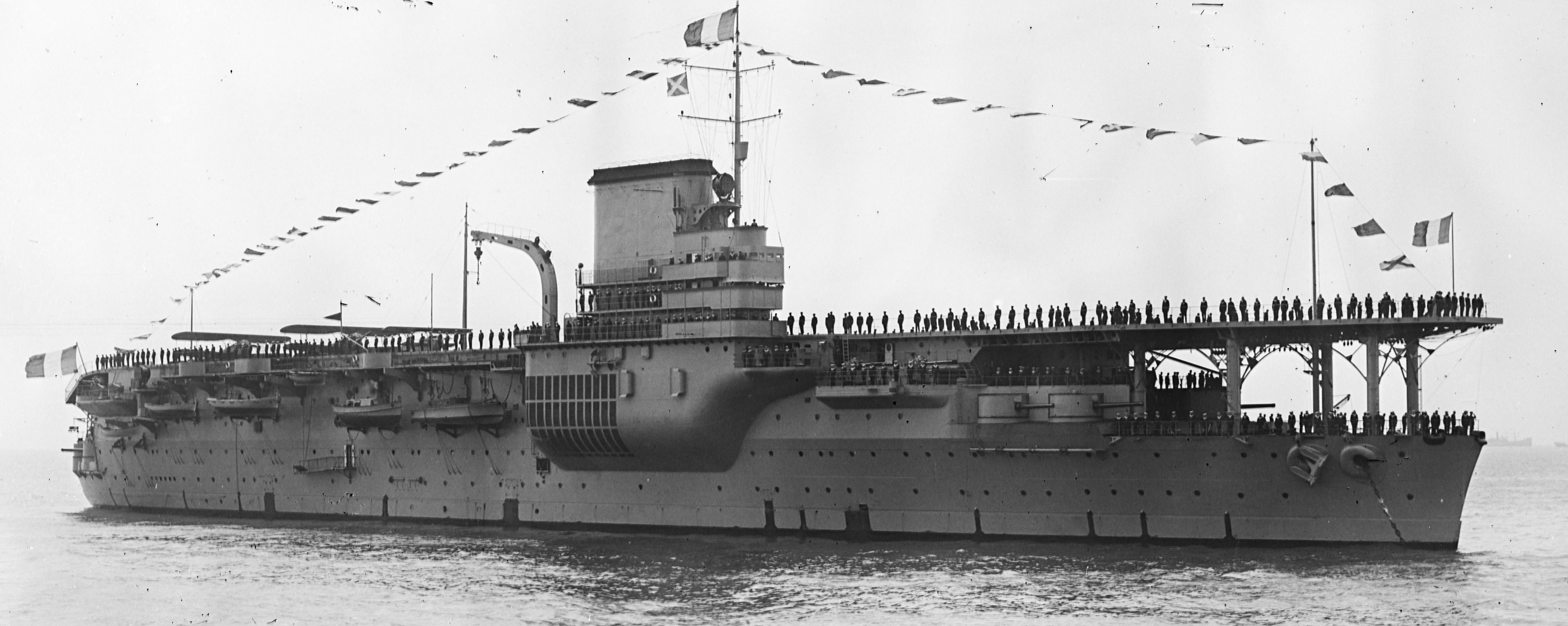

(Marine nationale Photo)
Marine nationale aircraft carrier Béarn.
![1024x599] Aerial view of the French aircraft carrier Béarn and battleship Lorraine at Toulon, after WWII : r/WarshipPorn](https://silverhawkauthor.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/68462a8357157a3f129913bb_86ffkj9ozvu61.jpg)
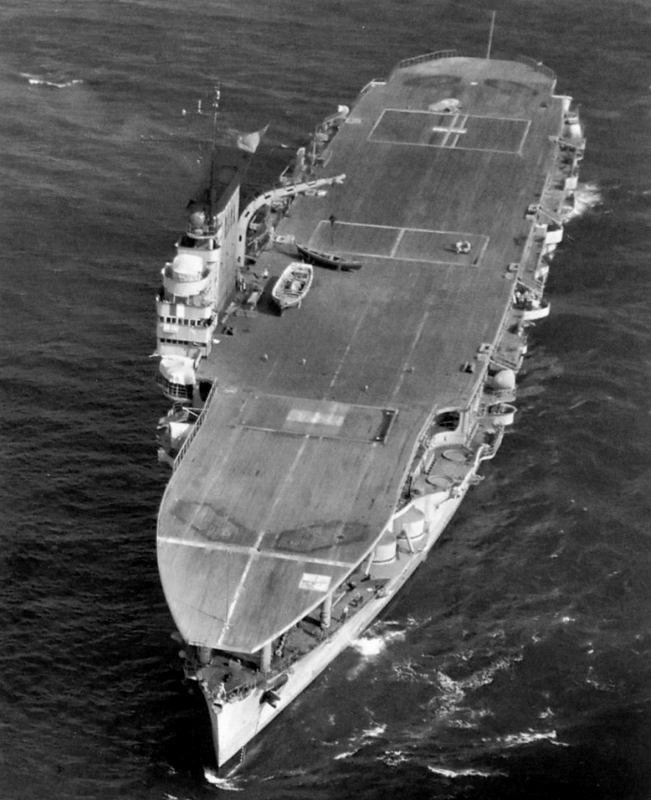

(Marine nationale Photos)
Aerial view of the Marine nationale aircraft carrier Béarn and battleship Lorraine at Toulon, post war.
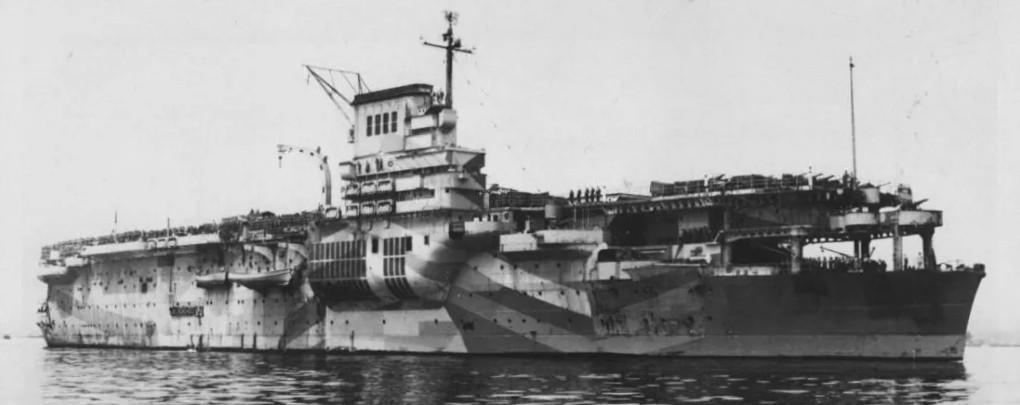

(Marine nationale Photos)
Marine national aircraft carrier Béarn.
Marine nationale seaplane tender Commandant Teste
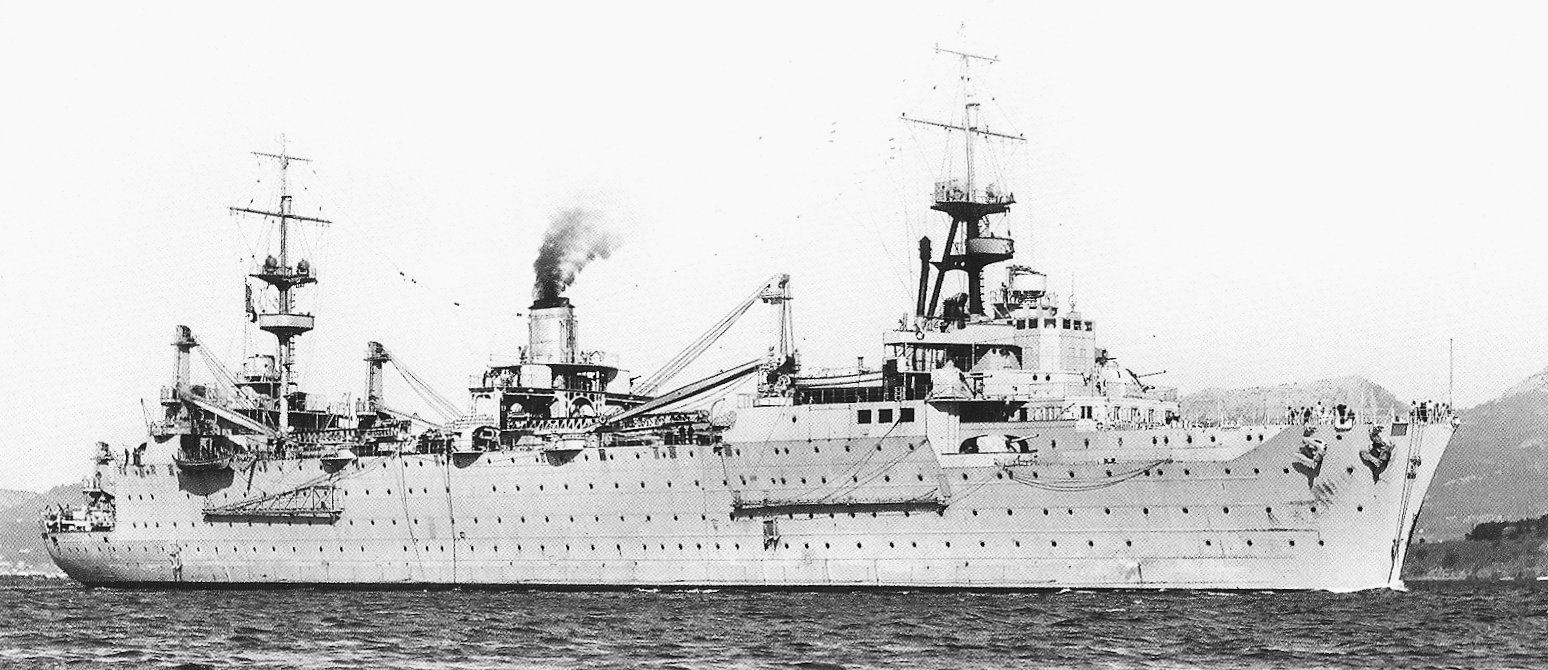

(Marine nationale Photo)
Marine nationale seaplane tender Commandant Teste was a large seaplane tender built before the Second World War. She was designed to be as large as possible without counting against the Washington Treaty limits. During the Spanish Civil War, she protected neutral merchant shipping and played a limited role during the Second World War as she spent the early part of the war in North African waters or acting as an aviation transport between France and North Africa. She was slightly damaged during the British bombardment of the French Fleet at Mers-el-Kébir in July 1940. Commandant Teste was scuttled at Toulon when the Germans invaded Vichy France in November 1942, but was refloated after the war and considered for conversion to an escort or training carrier. Neither proposal was accepted and she was sold for scrap in 1950. (Wikipedia)
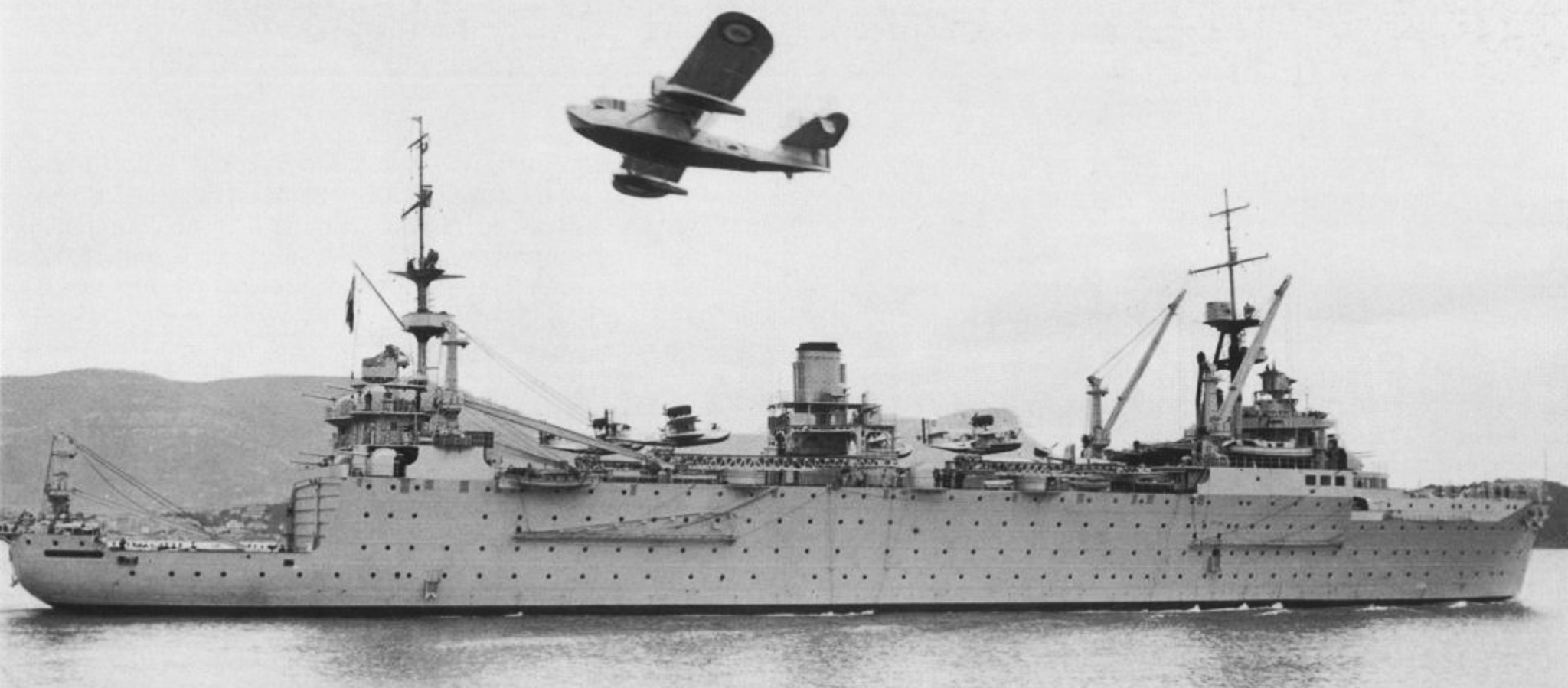

(Marine Nationale Photo)
Marine nationale seaplane tender Commandant Teste underway in 1938 with a Loire 130 seaplane overhead.
