Handley Page Halifax

(IWM Photo, HI 92986)
Handley Page Halifax Mk. II Series 1A, (Serial No. HR928), coded TL-L, of No. 35 Squadron RAF based at Graveley, Huntingdonshire, being flown by Squadron Leader A P Cranswick, an outstanding Pathfinder pilot of No. 5 Group, Bomber Command, who was killed on the night of 4/5 July 1944 on his 107th mission. The Cranswick coat-of-arms decorates the nose just below the cockpit.
The Handley Page Halifax is a British Royal Air Force (RAF) four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It was developed by Handley Page to the same specification as the contemporary twin-engine Avro Manchester.The Halifax has its origins in the twin-engine H.P.56 proposal of the late 1930s, produced in response to the British Air Ministry’s Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for “world-wide use.” The H.P.56 was ordered as a backup to the Avro 679, both aircraft being designed to use the Rolls-Royce Vulture engine. The Handley Page design was altered to use four Rolls-Royce Merlin engines while the rival Avro 679 was produced as the twin-engine Avro Manchester which, while regarded as unsuccessful mainly due to the Vulture engine, was a direct predecessor of the Avro Lancaster. Both the Lancaster and the Halifax emerged as capable four-engine strategic bombers, thousands of which were used during the War.
The Halifax performed its first flight on 25 October 1939, and entered service with the RAF on 13 November 1940. It quickly became a major component of Bomber Command, performing strategic bombing missions against the Axis Powers, primarily at night. Arthur Harris, the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of Bomber Command, described the Halifax as inferior to the rival Lancaster (in part due to its smaller payload) though this opinion was not shared by many of the crews that flew it.[2] Nevertheless, production of the Halifax continued until April 1945. During their service with Bomber Command, Halifaxes flew 82,773 operations and dropped 224,207 long tons (227,805 t) of bombs, while 1,833 aircraft were lost. The Halifax was also flown in large numbers by other Allied and Commonwealth nations, such as the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), and Free French Air Force.
Various improved versions of the Halifax were introduced, incorporating more powerful engines, a revised defensive turret layout and increased payload. It remained in service with Bomber Command until the end of the war, performing a variety of duties in addition to bombing. Specialised versions of the Halifax were developed for troop transport and paradrop operations. After the Second World War, the RAF quickly retired the Halifax, the type being succeeded as a strategic bomber by the Avro Lincoln, an advanced derivative of the Lancaster. During the post-war years, the Halifax was operated by the Royal Egyptian Air Force, the French Air Force and the Royal Pakistan Air Force. The type also entered commercial service for a number of years, used mainly as a freighter. A dedicated civil transport variant, the Handley Page Halton, was also developed and entered airline service; 41 civil Halifax freighters were used during the Berlin Airlift. In 1961, the last remaining Halifax bombers were retired from operational use. (Wikipedia)
H.P.57
Handley Page Halifax Mk. I (Serial No. L7244) H.P.57, was the first Halifax prototype with four Merlin 10 engines and no armament.
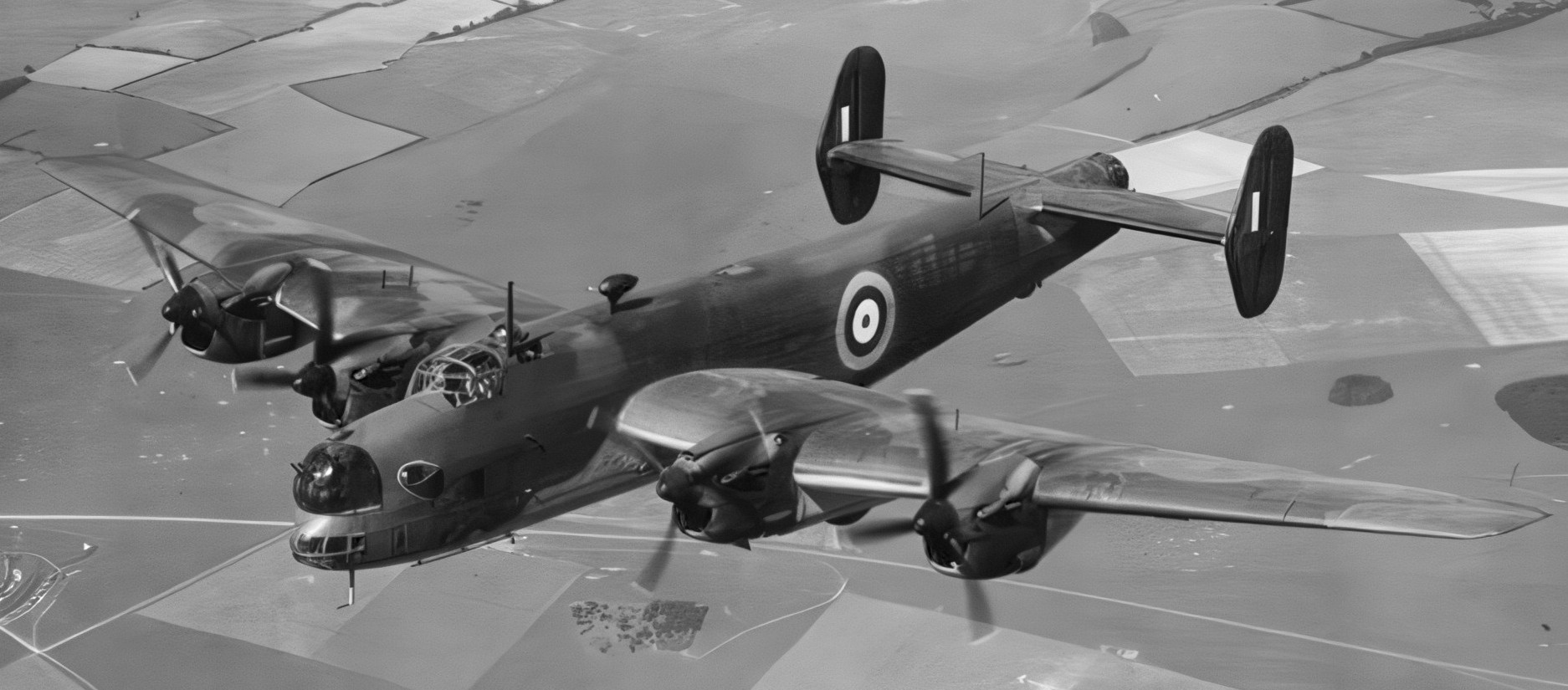

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax Mk. I (Serial No. L7245). H.P.57. Second prototype first flew from Radlett on 17 August 1940 and was more representative of the production configuration including armament.
“This was the second of two Halifax prototypes, which were followed by 6,177 production aircraft. It was the first to be complete with full armament and operationally-representative equipment, including a twin-gun nose turret and a four-gun tail turret, both made by Boulton Paul. (Serial No. L7245) was first flown by Chief Test Pilot James ‘Jim’ L.B.H. Cordes from Handley Page’s factory at Radlett, Hertfordshire, England on 17 August 1940. After manufacturer’s test flights it was transferred on 11 September to the A&AEE at Boscombe Down, Wiltshire, for service testing. A month later,on 13 October 1940, the starboard landing gear failed to retract fully after take off and further attempts to lock it up caused the adjacent hydraulic accumulator to burst, through the level of liquid being too high; the landing gear was then lowered by hand pump, followed by a safe emergency landing. On 24 October 1941, after another year of intensive testing, the aircraft sustained Category B damage. It was returned to Handley Page for repairs, servicing and modifications on 5 November. Fitted with dual controls the aircraft returned to service as a crew trainer with 28 Conversion Flight at RAF Leconfield on 7 December 1941. Only three weeks later, on 27 December, it received Category A damage in a flying accident. It is uncertain the aircraft was repaired, but on 24 February 1942, it was struck off charge. With an alternate (Serial No. 3474M), the prototype became a ground instructional airframe on 24 December 1942. Its ultimate fate is unknown.” (Johan Visschedijk)

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax Mk. I (Serial No. L7245) in day bomber camouflage with yellow undersides.
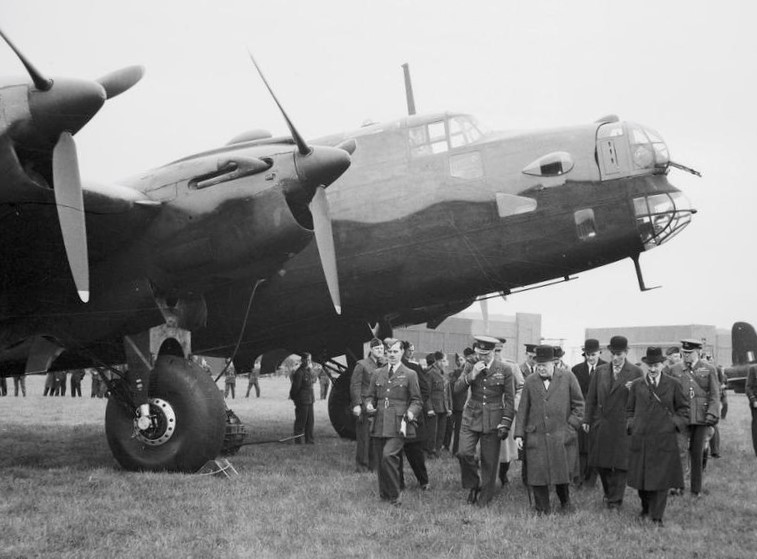

(IWM Photo, H 10310)
Winston Churchill inspecting a Handley Page Halifax B.I, during a visit to an RAF bomber station, 6 June 1941.
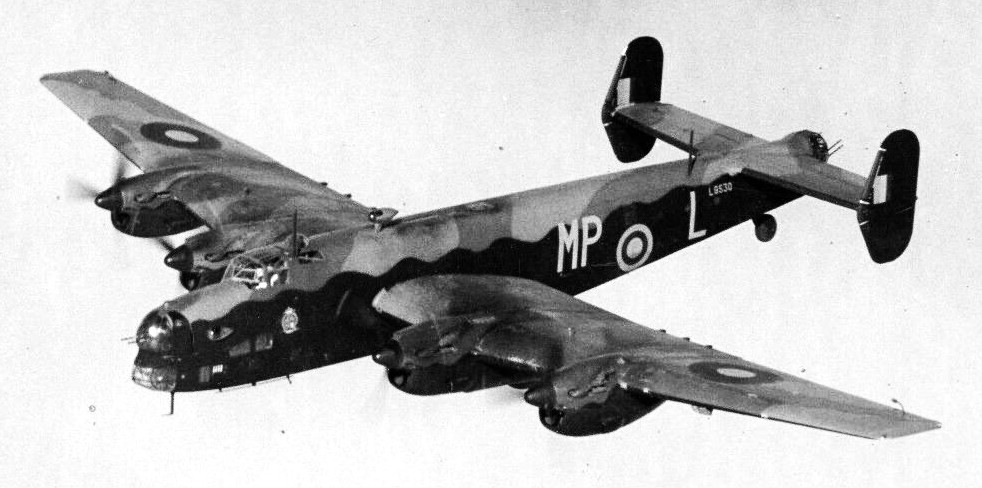

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax B.I Series 1, (Serial No. L9530), coded MP-L, No 76 Squadron RAF.
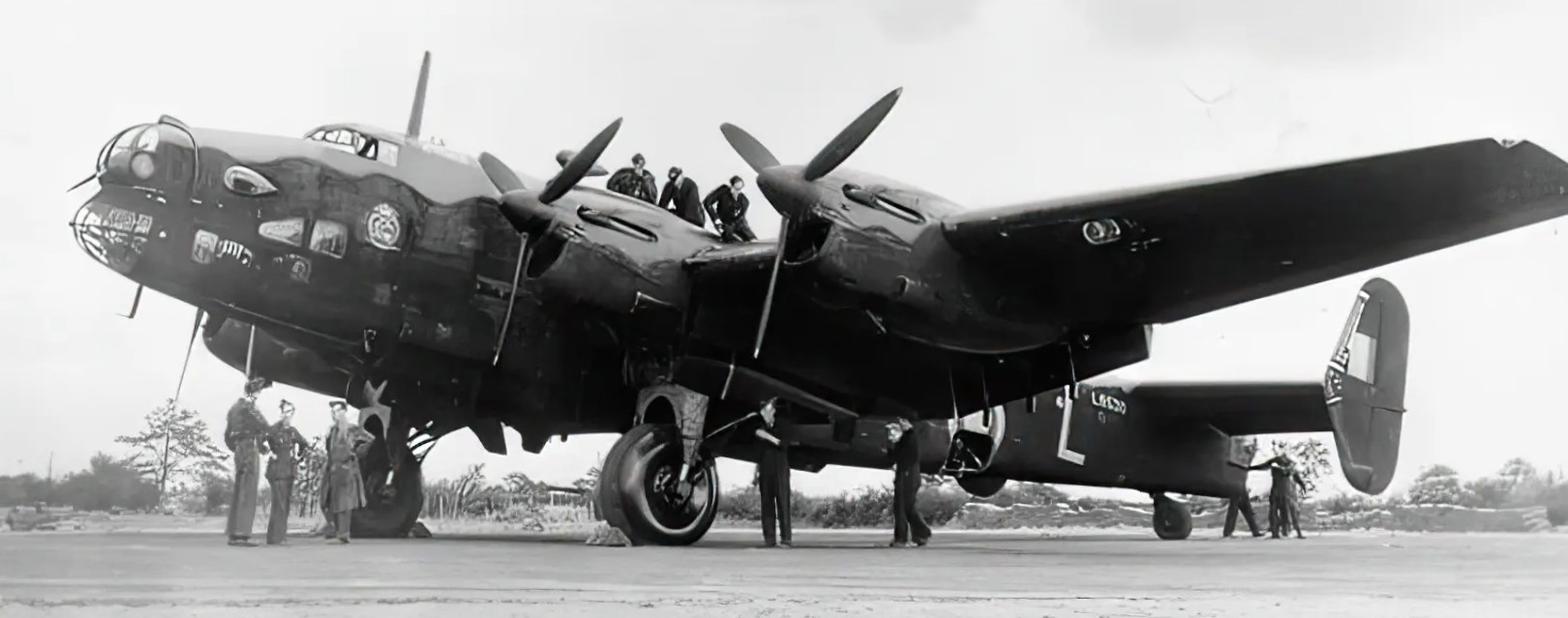

(IWM Photo, CH 3393)
Handley Page Halifax B.I Series 1, (Serial No. L9530), No 76 Squadron RAF, undergoing maintenance at Middleton St George, County Durham. L9530 was shot down while attacking Magdeburg on 15 August 1941.
Halifax B.I Series I was a four-engined long-range heavy-bomber aircraft powered by Rolls-Royce Merlin X engines; the first production version. Armament consisted of nose turret with two guns, tail turret with four guns and two beam guns. Recognizable from large deep radiator intakes containing circular Gallay radiators and oil cooler. 50 produced.
Halifax B.I Series II. Stressed for operating at a higher gross weight. 25 produced.
Halifax B.I Series III. Re-engined with Merlin XX engines with slimmer coolers, introduced new twin-gun Boulton Paul type C upper turret in place of beam guns, with revised undercarriage and additional centre-section fuel tanks. 9 produced.
H.P.59
Halifax Mk.II
New variant with increased takeoff weight, fuel and weapons carriage.
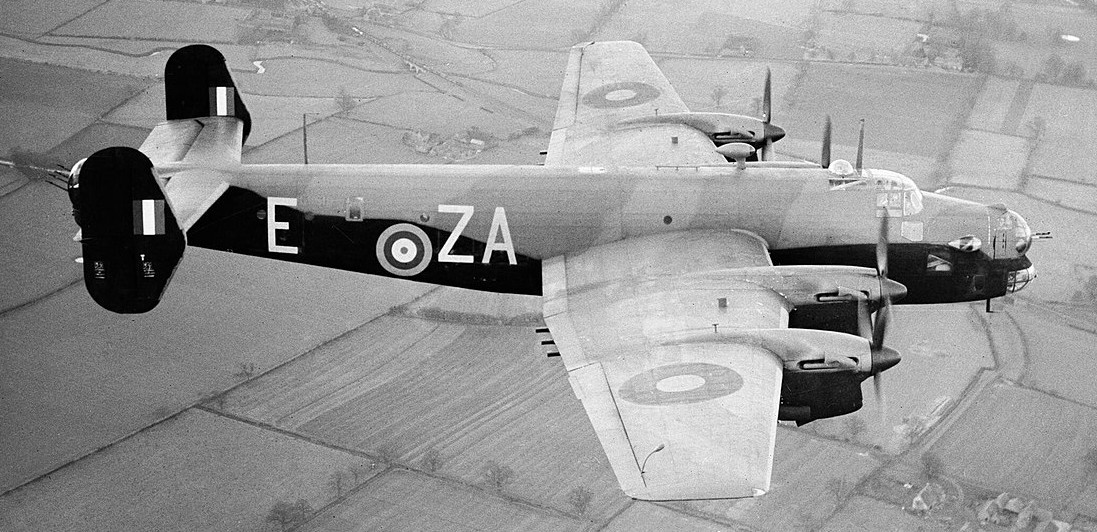

(IWM Photo, CH 4435)
Handley Page Halifax B.II Series 1, (Serial No. L9619), coded ZA-E, of No. 10 Squadron RAF based at Leeming, Yorkshire, in flight. This aircraft is an early production machine fitted with beam gun hatches amidships instead of a mid-upper turret.
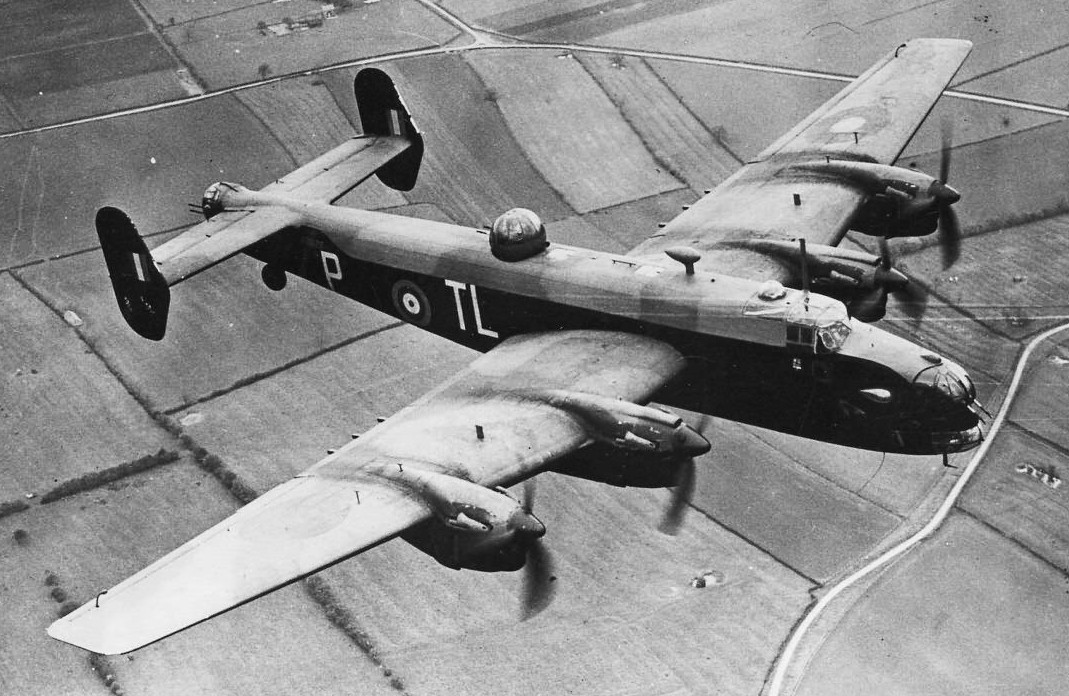

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax B.II Series I (Serial No. W7676), coded TL-P, No. 35 Squadron RAF.Handley Page Halifax Mk. II (Serial No. BB324), coded ZA-X of of No. 77 Squadron RAF. BB324 failed to return from a raid on Mulheim, Germany on 23 June 1943. The loss included two RCAF aircrew, Flight Sergeant James Franklin Carl Crowe, and Flight Sergeant Timothy Leo Macaskill, both KIA.
Halifax B.II Series I
First series of the bomber variant; from March 1942 onwards, these were fitted with TR 1335 navigationaids.
Halifax B.II Series I (Special), SOE
Special version for Special Operations Executive (SOE used to drop supplies over Europe. Nosearmament and dorsal turret removed, the nose being faired over, as well aschanges to the fuel vent pipes and exhaust shrouds.
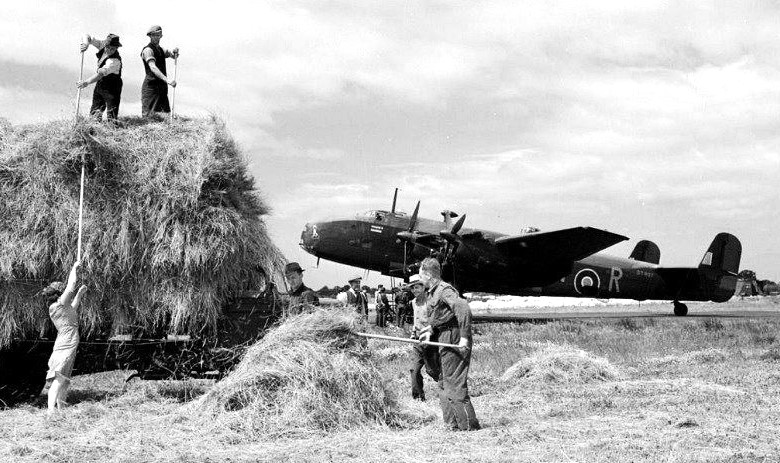

(RAF Photo)
Gathering hay during the Second World War in and around RAF Elvington, Yorkshire. In the background is Handley Page Halifax B.II Series I Special, (Serial No. DT807), coded KN-R, “Rita“, of No. 77 Squadron RAF.
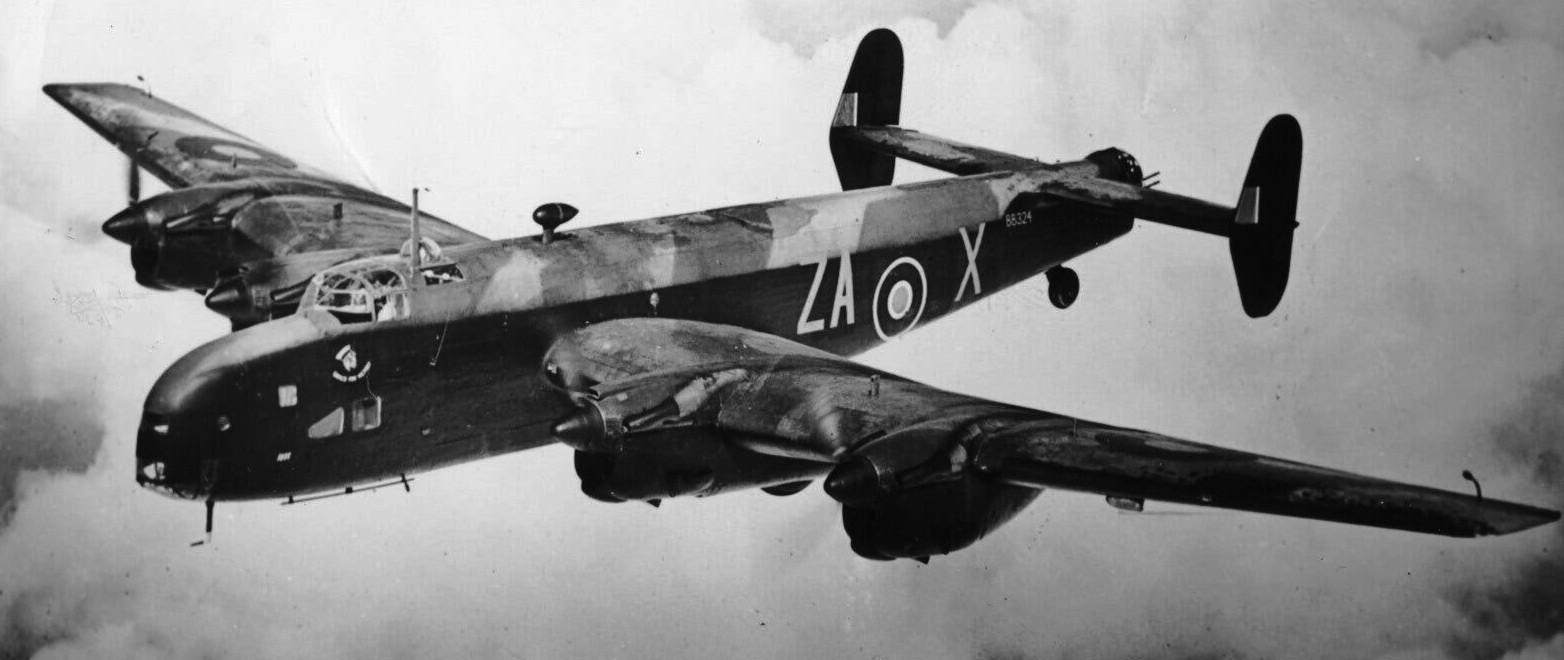

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax B.II Series 1 (Special) (Serial No. BB324), coded ZA-X of of No. 77 Squadron RAF.
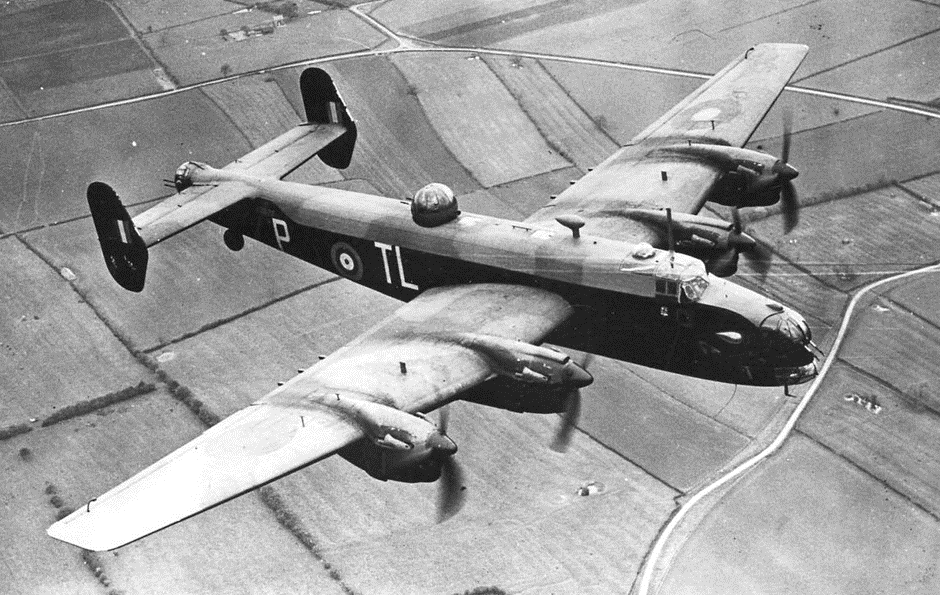
(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax B.II.
Halifax B.II Series I (Special)
Generally similar to the aircraft used by the SOE, these were employed in the bombing role. These aircraft were more varied in appearance, especially concerning the fitting of dorsal armament with some aircraft retaining the standard Boulton Paul “Type C” turret in different mounts with others mounting a “Type A” turret. There were also examples with no dorsal turret, similar to the SOE-aircraft
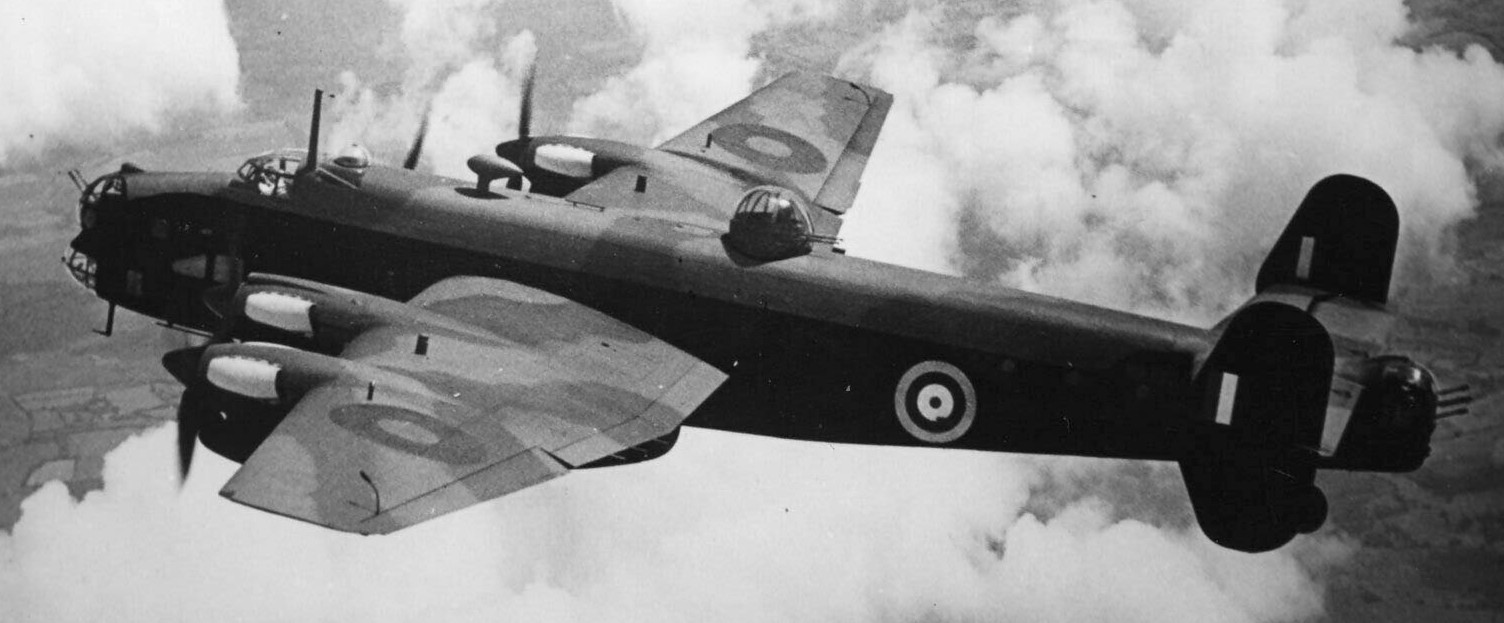

(RAF Photo)
A Halifax B Mk. II Series 1 (Serial No. W7773).

(RAF Photo)
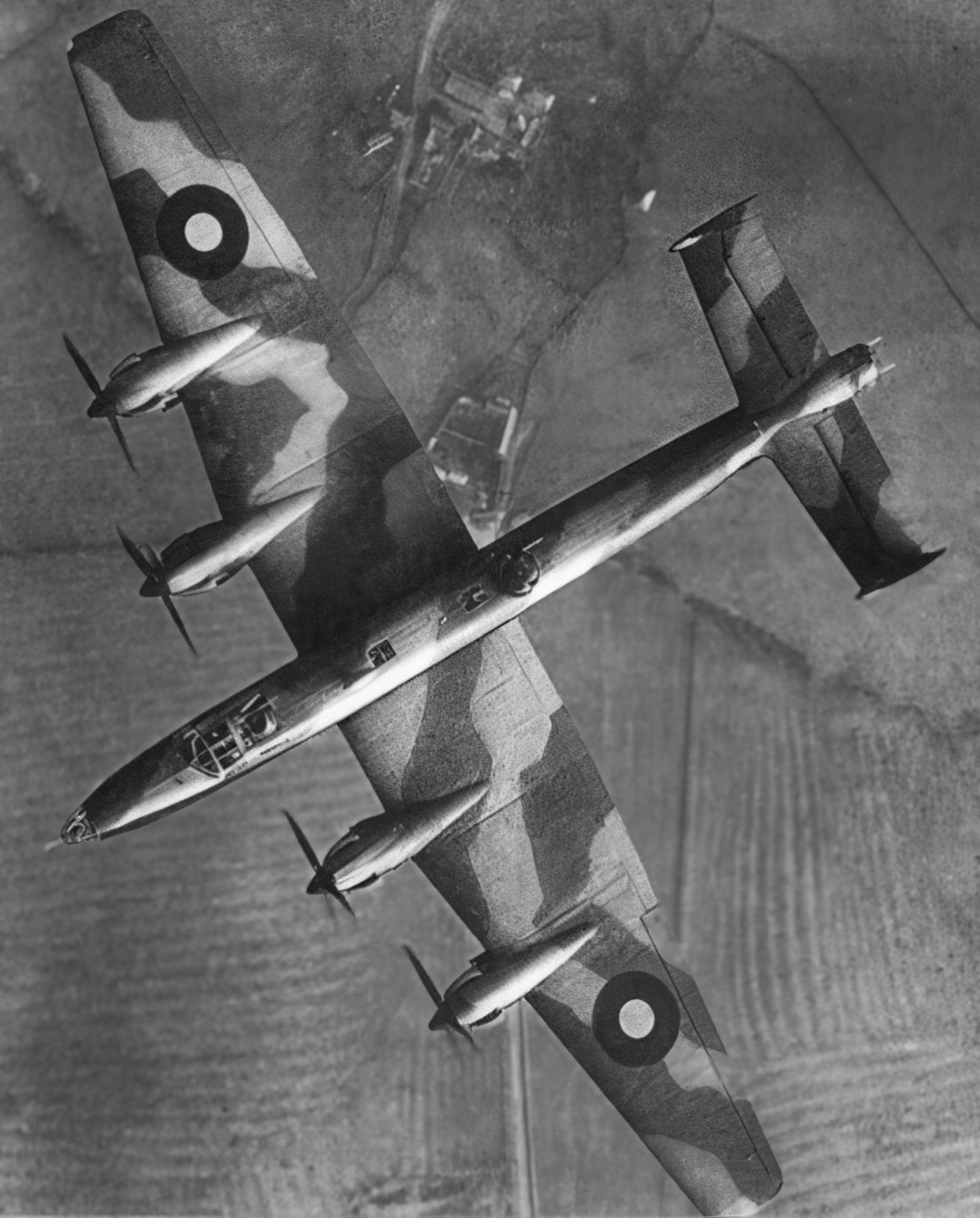
Handley Page Halifax B.II Series IA, overhead view, 1943.

(IWM Photo, CH 11328)
A Halifax B Mk. II Series 1A (Serial No. LW235), coded EY-B of No. 78 Squadron RAF based at RAF Breighton, Yorkshire (UK), in flight with triangular tail fins initially fitted to this version.
âHalifax B.II Series IA
Modified with new glazed nose section, Merlin XX or 22 engines, new square Morris radiators and new “D” fin and rudder. The dorsal turret was changed to a four-gun Boulton Paul Type A Mk.VIII, and there were improvements to the bomb bay doorsealing. Some aircraft were fitted with the H2S radar.
Handley Page Halifax B Mk. II (Serial No. W1048), “S for Sugar” of No. 35 Squadron RAF. On the night of the 27/28 April 1942, W1048 was taking part in a raid on the German battleship Tirpitz – its first operational flight. It was hit by anti-aircraft fire after releasing the four 1,000-pound (450 kg) mines it carried and the pilot made a successful belly landing on the frozen surface of Lake Hoklingen. The crew escaped to Sweden with the help of the Norwegian resistance, except for the Flight Engineer who remained behind because of a broken ankle and was taken prisoner. Within hours, the aircraft sank through the ice into 27 metres (89 ft) of water. In the summer of 1973, it was recovered from the lake by a team of divers from the RAF and a Norwegian diving club, and was transported to the UK on a British Army Landing craft tank. It is displayed in its “as recovered” condition in the Bomber Command display at the Royal Air Force Museum London, Hendon, apart from the nose turret which had already been restored.
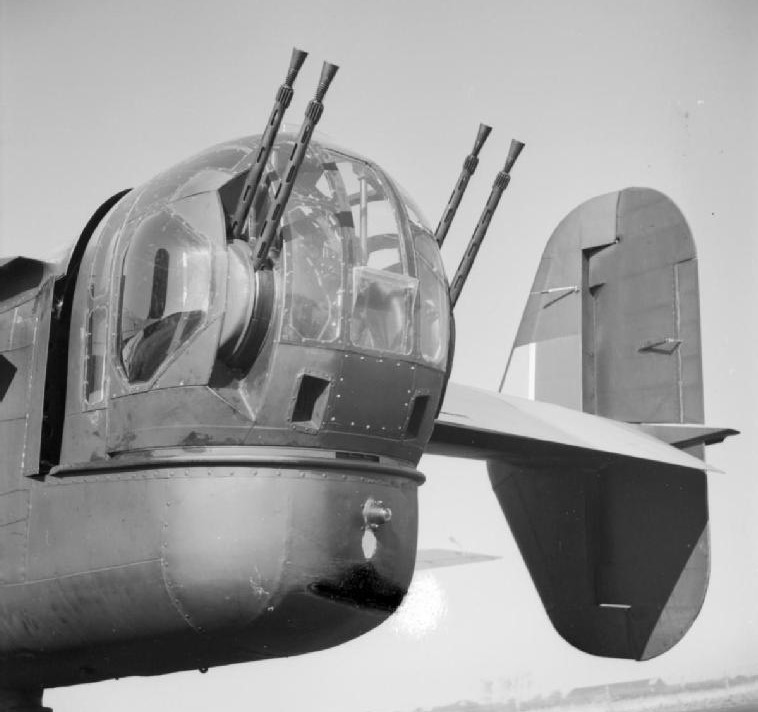

(IWM Photo, CH 11320)
Close-up of the Boulton Paul Type ‘E’ tail gun-turret, mounting four .303 machine guns, on a Handley Page Halifax B.II of No. 78 Squadron RAF at Breighton, UK.
Halifax B.II Series I, Freighter
A few Mk. IIs were employed in the transport role in Great Britain (unmodified SOE-aircraft) and in the Middle East (simple modifications to allow carriage of engines or Spitfire fuselages).
Halifax GR.II
Coastal Command variant of the Halifax B.II.
Halifax GR.II Series I
A handful of aircraft converted from Series I or Special to GR.II standard, having differences in dorsal armament. The main difference was the fitting of a ASV.Mk 3 radarin an H2S type fairing. Sometimes, a .50 in (12.7 mm) machine gun was fitted in the faired nose.
Halifax GR.II Series IA
Definitive Coastal Command variant of the GR.II with glazed nose mounting .50 in(12.7 mm) machine gun, Merlin XX or 22 engines, B-P A-type dorsal turret and extra long-range fuel tanks in fuselage. A ventral turret with a single .50 in (12.7 mm) machine gun was mounted on most aircraft although some employed the ASV.Mk 3 radar in its place.
H.P.61
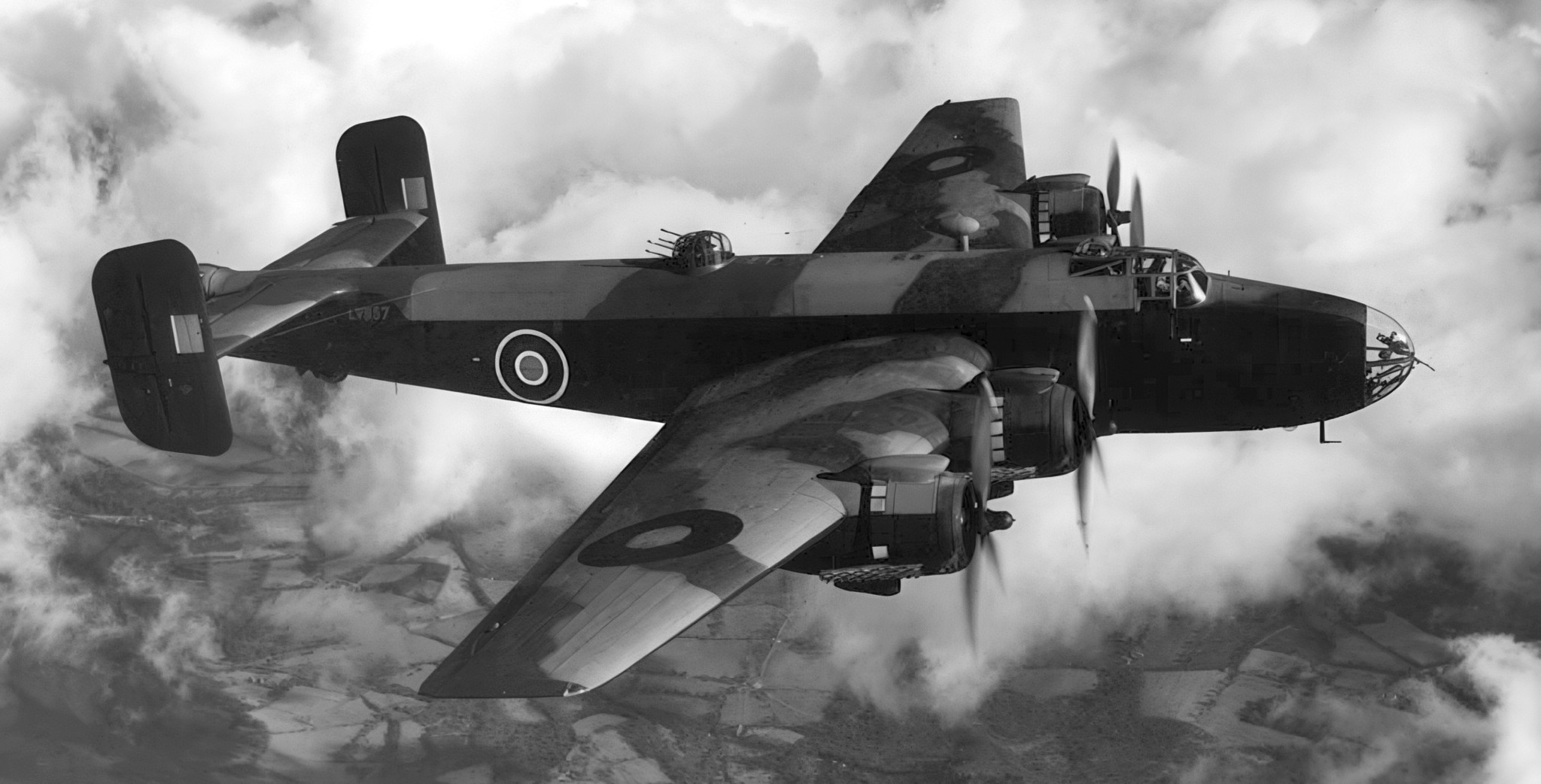

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax B. III. Main production variant, fitted with Bristol Hercules engines. B.III bombers were fitted with transparent nose dome with single machine gun, Boulton Paul dorsal turret with four guns and tail turret with four guns. All but first few had longer wing with rounded wingtips that increased wingspan to 104 ft 2 in (31.75 m).
Halifax B.III
Main production variant, fitted with Bristol Hercules engines. B.III bombers were fitted with transparent nose dome with single machine gun, Boulton Paul dorsal turret with four guns and tail turret with four guns. All but the first few had a longer wing with rounded wingtips that increased the wingspan to 104 ft 2 in (31.75m). 2,091 produced.
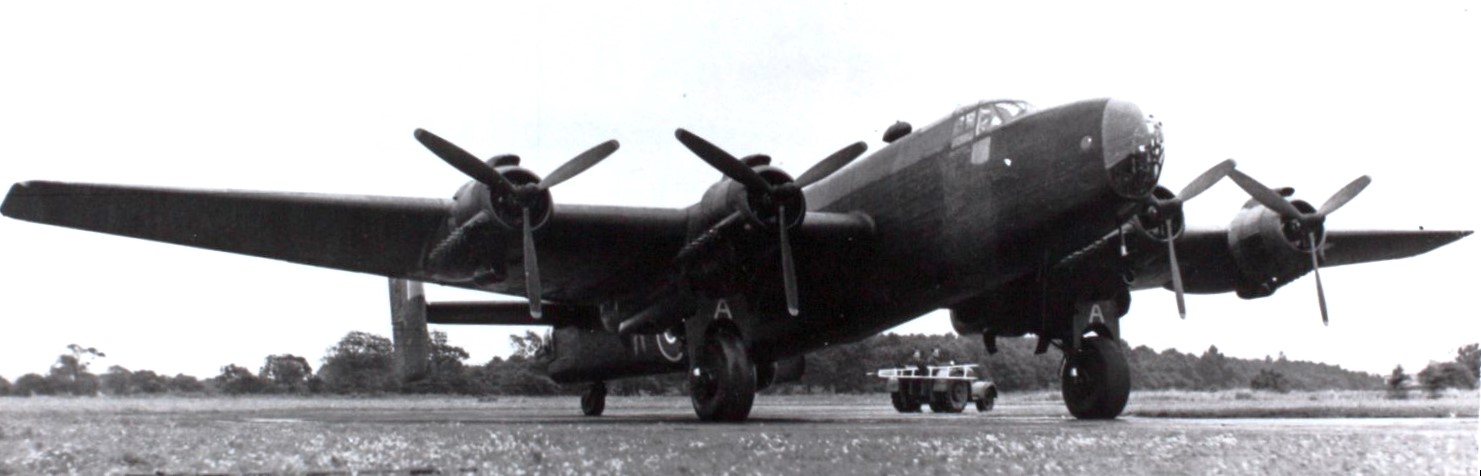

(SDASM Photo)
Handley Page Halifax B.III four-engined long-range heavy-bomber, powered by four 1,615 hp (1,204 kW) Bristol Hercules XVI radial engines.
Halifax A.III

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax A.III (Serial No. RT796), glider tug aircraft.
Halifax B.III bombers converted into glider tug and paratroop transport aircraft.
Halifax C.III
Halifax B.III bombers converted into military transport aircraft.
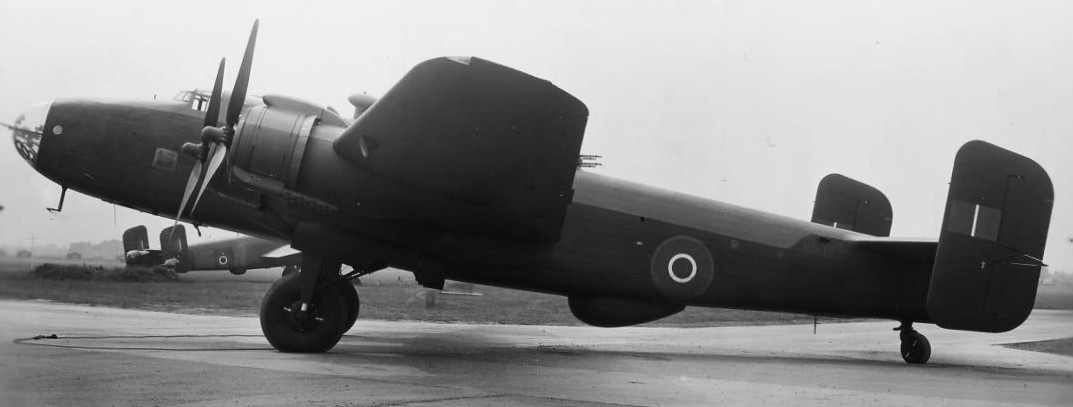

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax G.R. III (Serial No. NR187), May 1945.
H.P.63
Halifax B.V
Four-enginedlong-range heavy-bomber, powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlin XX engines with square empennage and wingtips. Armament as B.III. 904 produced.
Halifax B.V Series I (Special)
Halifax A.V
Halifax B.V bombers converted into glider tugs and paratroop transport aircraft.
Halifax GR.V
Coastal Command variant. Halifax B.V bombers converted into maritime reconnaissance aircraft.
Halifax B.VI
Four-engined long-range heavy-bomber, powered by four 1,615 hp (1,204 kW) BristolHercules XVI radial engines with H2S. No dorsal turret. Square empennage, round wing tips. 643 produced.

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax C.VI (Serial No. PP216), transport, March 1945.
Halifax C.VI
Halifax B.VI bombers converted into military transport aircraft.
Halifax GR.VI
Coastal Command variant. Halifax B.VI bombers converted into maritime reconnaissance aircraft.
Halifax B.VII
Halifax A.VII

(Library and Archives Canada Photo, MIKAN No. 3226555)
Handley Page Halifax A.VII’s from No. 644 Squadron based at RAF Station Tarrant Rushton, Dorset, preparing to tow General Aircraft Hamilcar gliders of the 6th Airborne Division to Germany, 22 March 1945.
Halifax B.VIIs converted into paratroop transport and glider tug aircraft.
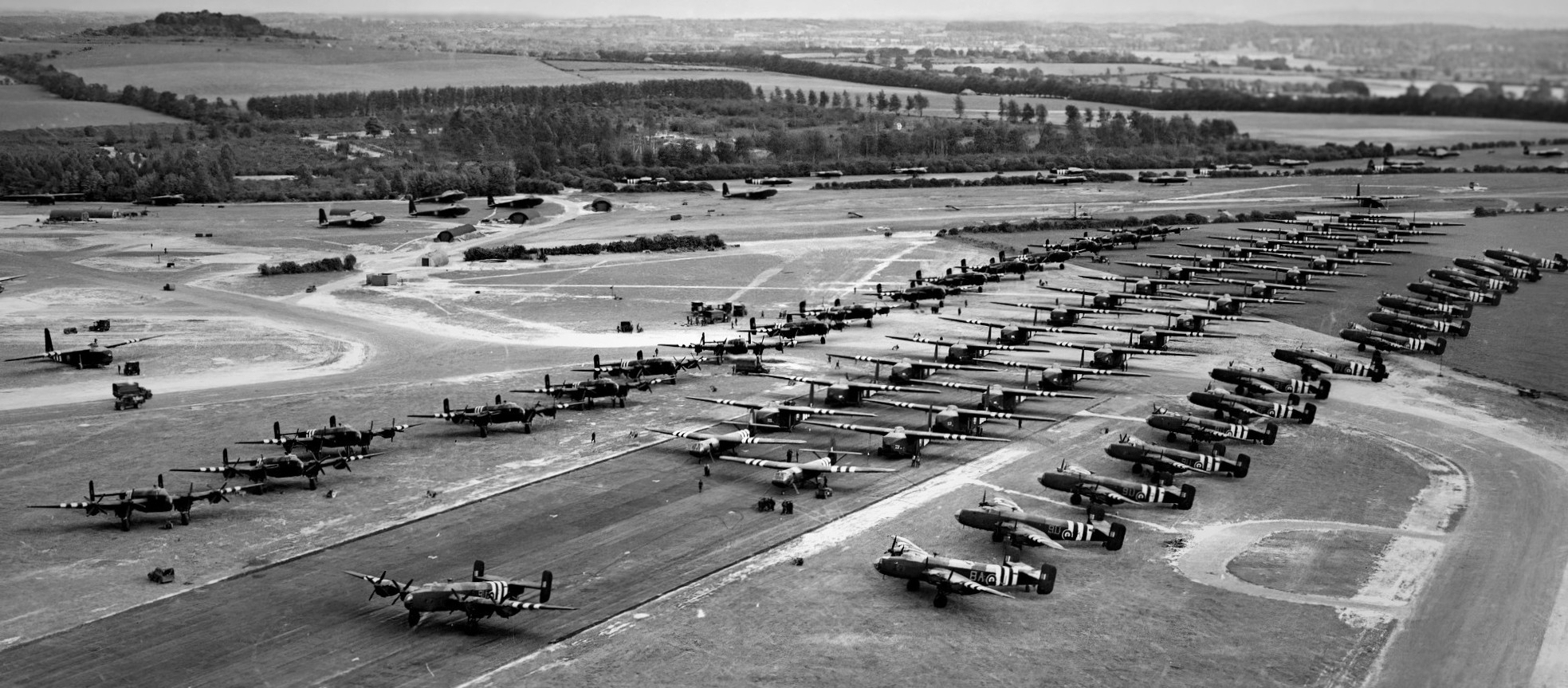

(RAF Photo)
On the evening of 5 June 1944, elements of the 6th Airlanding Brigade, 6th Airborne Division, awaited departure from RAF Tarrant Rushton. The runway featured Hamilcar heavy gliders, with two Horsa troop-carrying gliders in front of them. Flanking the gliders were Handley Page Halifax glider-tugs from Nos. 298 and 644 Squadrons RAF. Fifty-eight Halifax bombers and their gliders took off from Tarrant Rushton on D-Day.
â
Halifax C.VII
Halifax B.VIIs bombers converted into military transport aircraft.
H.P.70

(RAF Photo)
Handley Page Halifax C Mk. VIII (Serial No. PP225).
Halifax C.VIII
Cargo and passenger transport aircraft.
H.P.71
Halifax A.IX
Paratroop transport,glider tug aircraft.
H.P.70 Halton
Halton I
Interim civil transport version. Postwar, a number of Halifax bombers were converted into civilian transport aircraft.
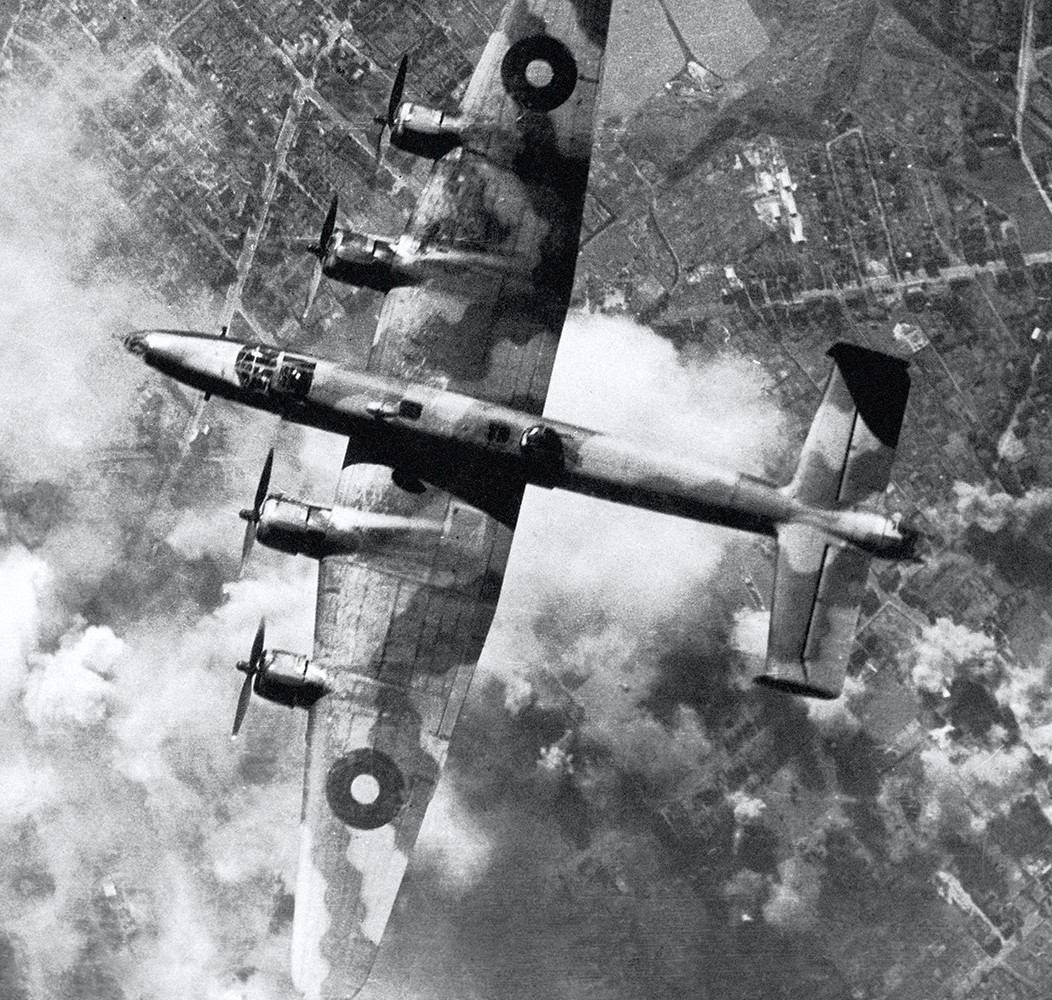

(IWM Photo, C 4713)
Handley Page Halifax of No 6 Group flies over the smoke-obscured target during a daylight raid on the oil refinery at Wanne-Eickel in the Ruhr, 12 Oct 1944. 111 Halifaxes of 6 Group and 26 Avro Lancasters of No. 8 Group took part in the raid which destroyed a chemical factory but only inflicted minor damage on the refinery itself.
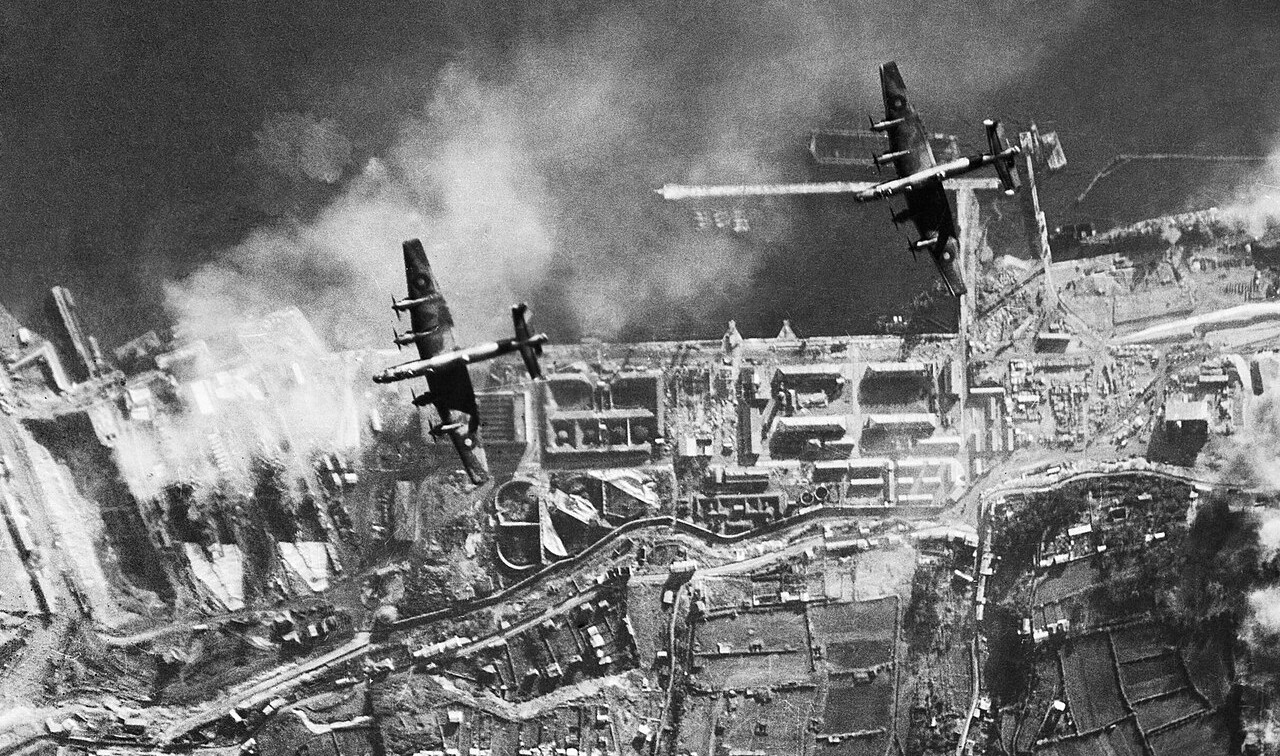

(IWM Photo, C 4109)
Daylight attack on German warships docked at Brest, France. Two Handley Page Halifaxes of No. 35 Squadron RAF fly towards the dry docks in which the battlecruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau are berthed (right), and over which a smoke screen is rapidly spreading. Prinz Eugen is morred at the right, 18 Dec 1941.
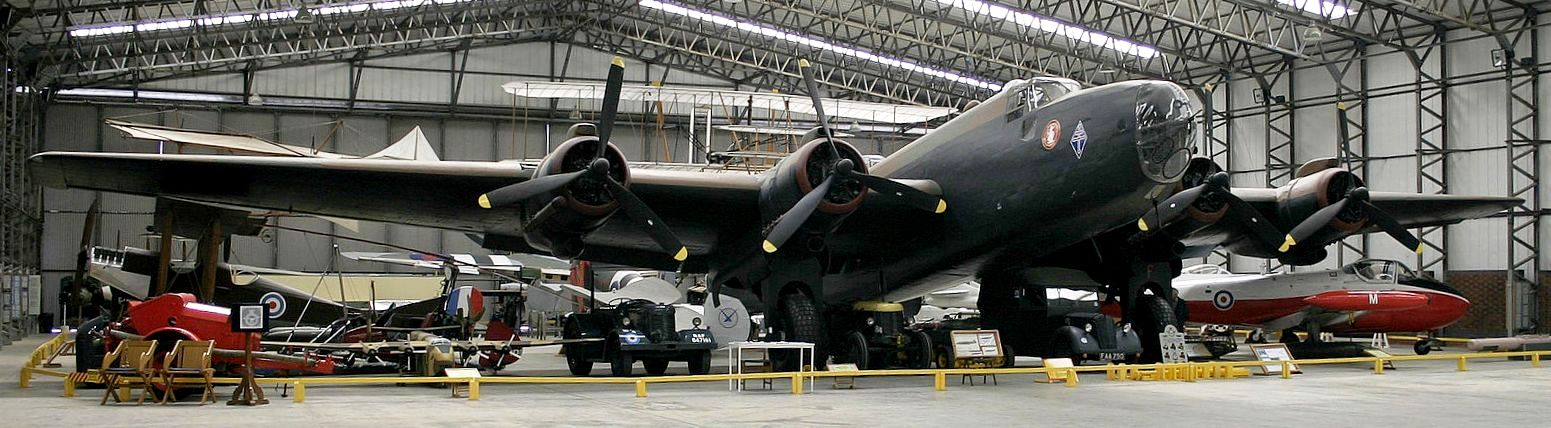

(Alan Zomerfeld Photo)

(Rachel Semlyen Photo)
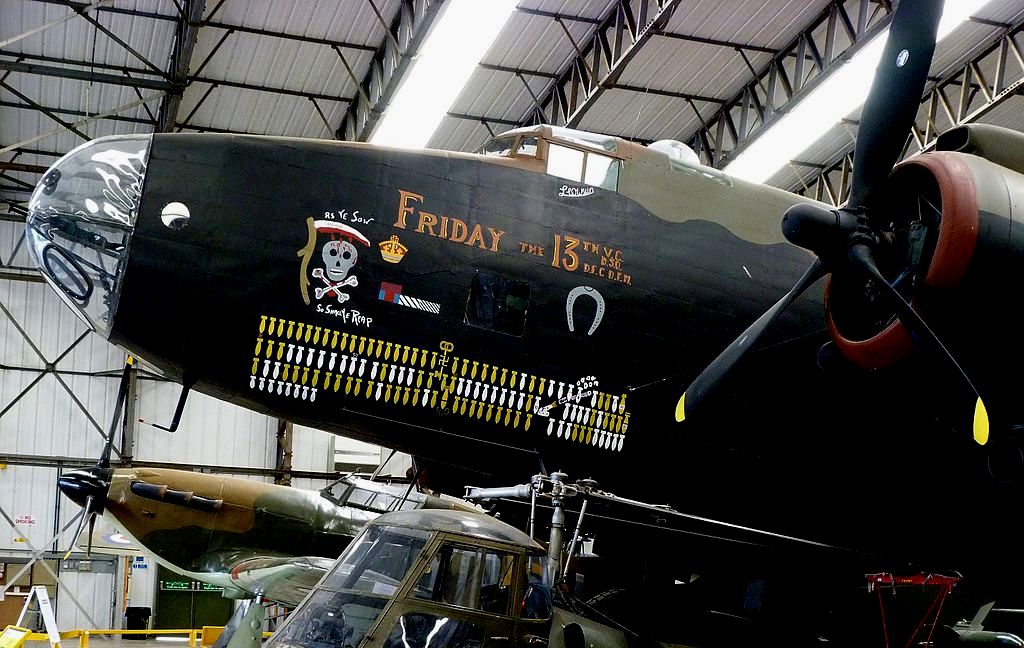


(Craig Sunter Photos)
Handley Page Halifax B Mk. II (Serial No. HR792). The Yorkshire Air Museum, Elvington, Yorkshire, on the site of the Second World War airfield, RAF Elvington, has a fully restored aircraft re-constructed from a fuselage section of HR792 and parts from other aircraft including the wings from an RAF Hastings. It is painted to represent Halifax (Serial No. LV907), “Friday the 13th” from No. 158 Squadron RAF on the port side and “N – Novembre” of 347 “Guyenne” Squadron, Free French Air Force, (NP763), on the starboard side (RAF Elvington was the home of the only two French heavy bomber squadrons in Bomber Command).
Handley Page Halifax B Mk. VII (Serial No. PN323), front fuselage. Imperial War Museum, London.
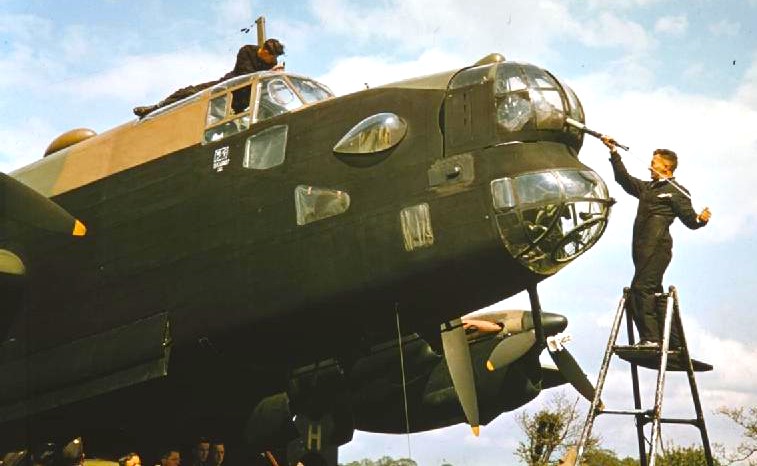

(IWM Photo, TR 4)
A rigger cleans the cockpit perspex while an armourer rods the barrels of the front turrets of a recently received Handley Page Halifax B.I at Linton-on-Ouse.

(RAF Photo)
The Halifax B.II (Serial No. JP201) pictured here was later lost while operating with No. 1666 Heavy Conversion Unit (HCU) from RAF Wombleton, in a collision with a Halifax Mk. V (Serial No. LL137) of No 1664 HCU from RAF Dishforth, over Morchard Bishop, Devon, on the evening of the 15 November 1944. Note the Bristol Beaufighter on the right.
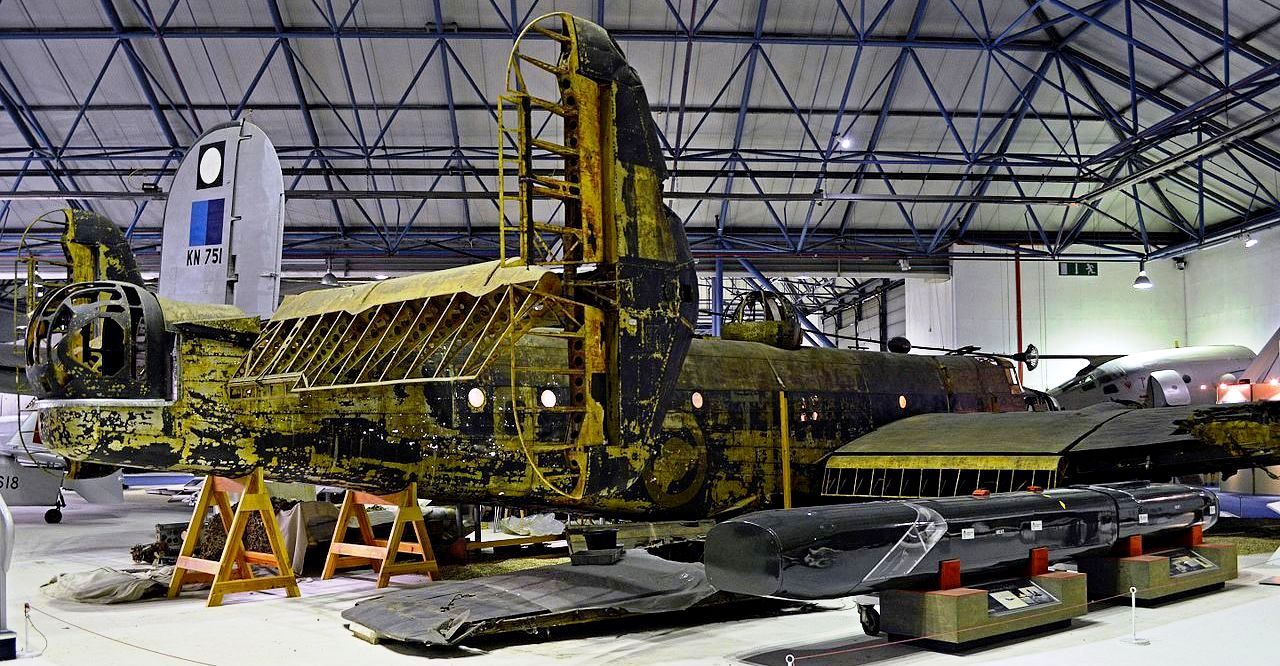
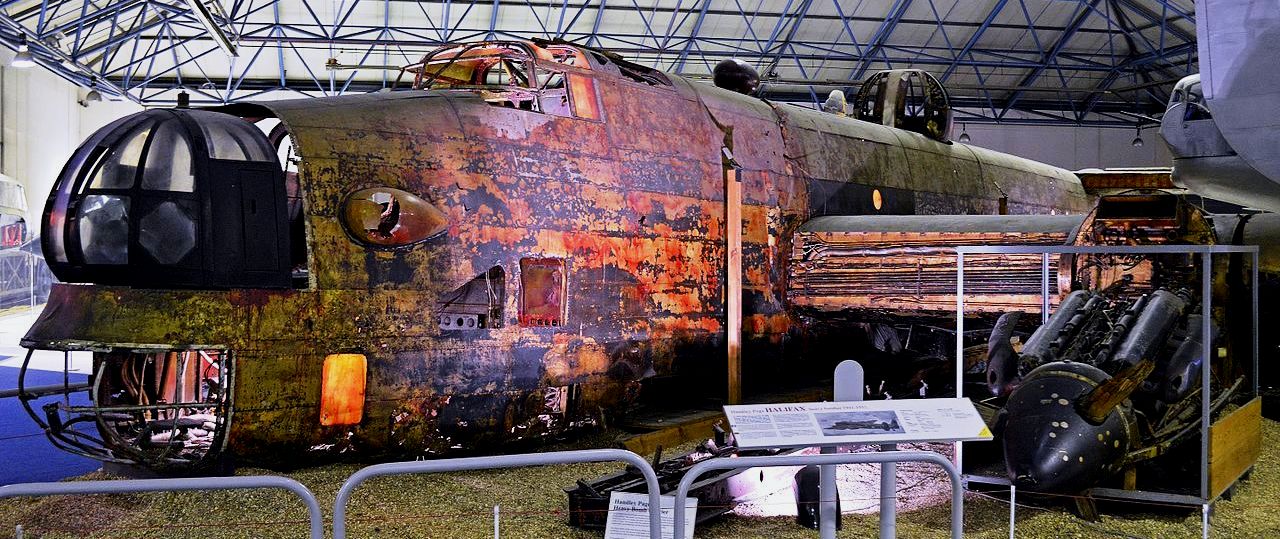


(Alan Wilson Photos)
Handley Page Halifax B Mk. II (Serial No. W1048), “S for Sugar” of No. 35 Squadron RAF. On the night of the 27/28 April 1942, W1048 was taking part in a raid on the German battleship Tirpitz – its first operational flight. It was hit by anti-aircraft fire after releasing the four 1,000-pound (450 kg) mines it carried and the pilot made a successful belly landing on the frozen surface of Lake Hoklingen. The crew escaped to Sweden with the help of the Norwegian resistance, except for the Flight Engineer who remained behind because of a broken ankle and was taken prisoner. Within hours, the aircraft sank through the ice into 27 metres (89 ft) of water. In the summer of 1973, it was recovered from the lake by a team of divers from the RAF and a Norwegian diving club, and was transported to the UK on a British Army Landing craft tank. It is displayed in its “as recovered” condition in the Bomber Command display at the Royal Air Force Museum London, Hendon, apart from the nose turret which had already been restored.
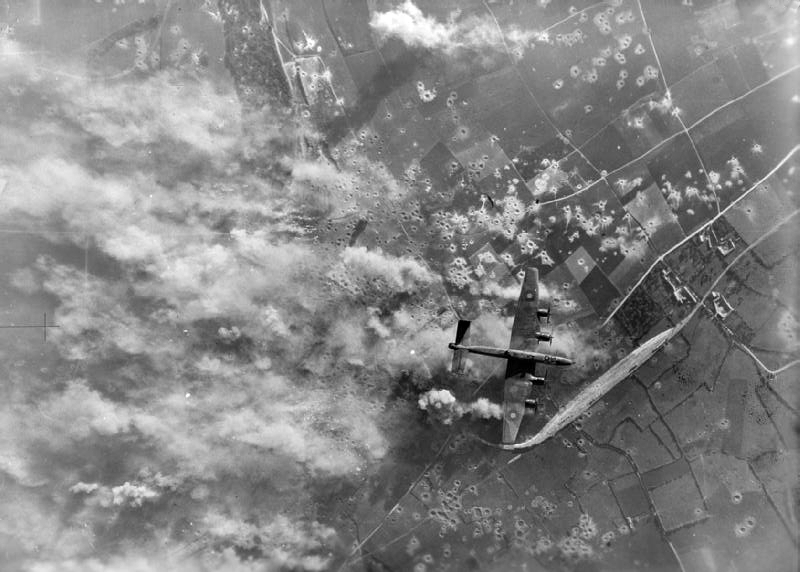

(IWM Photo, C4458)
Handley Page Halifax bombing a target over Mimoyecques, near Marquise, France, 5 July 1944.
