Yokosuka D4Y Suisei
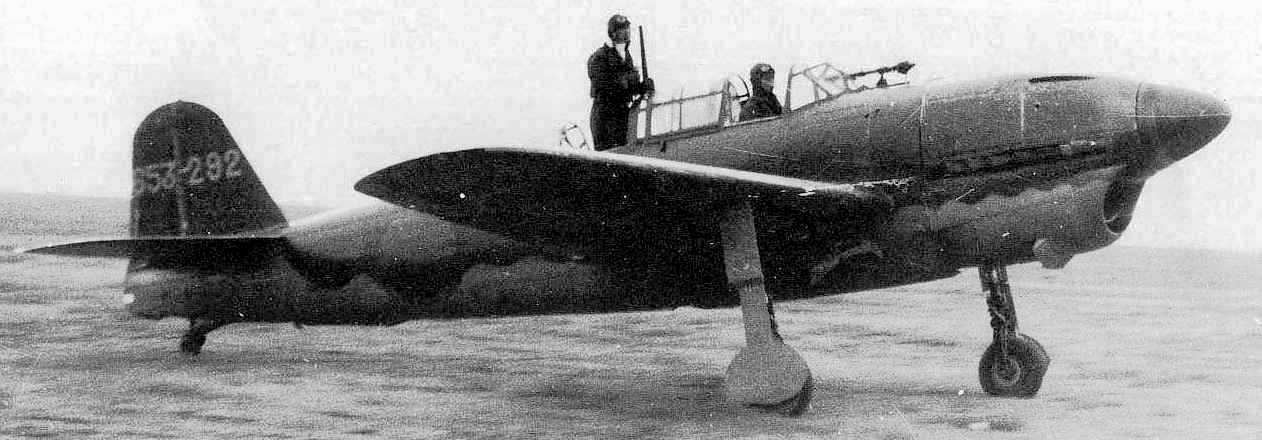

Yokosuka/Kugisho D4Y2 Susei (Comet) Navy Type 2 Carrier Reconnaissance Plane Model 33 (Judy).
The Yokosuka D4Y Suisei (彗星, Suisei, “Comet”; Allied reporting name “Judy”) is a two-seat carrier-based dive bomber developed by the Yokosuka Naval Air Technical Arsenal and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy from 1942 to 1945 during the Second World War. Development of the aircraft began in 1938. The first D4Y1 was complete in November 1940 and made its maiden flight at Yokosuka the following month.
While the aircraft was originally conceived as a dive bomber, the D4Y was used in other roles including reconnaissance, night fighter and special attack (kamikaze). It made its combat debut as a reconnaissance aircraft when two pre-production D4Y1-Cs embarked aboard the Sōryū to take part in the Battle of Midway in 1942. It was not until March 1943 that it was accepted for use as a dive bomber. The early D4Y1 and D4Y2 featured the liquid-cooled Aichi Atsuta engine, a licensed version of the German Daimler-Benz DB 601, while the later D4Y3 and D4Y4 featured the Mitsubishi MK8P Kinsei radial engine.Like many other Japanese aircraft of the time, the D4Y lacked armour and self-sealing fuel tanks and it was not until the final variant, the D4Y4, that the aircraft was given bulletproof glass and armor protection for the crew and fuel tanks.
The D4Y was one of the fastest dive bombers of the war, particularly the D4Y4. Max Gadney said was the “fastest dive-bomber of the Second World War” and that it was “faster than the Zero”. Only the delays in its development hindered its service while its predecessor, the slower fixed-gear Aichi D3A, remained in service much longer than intended. In October 1944, an attack by a lone D4Y resulted in the sinking of light carrier USS Princeton in the Battle of Leyte Gulf. Similarly in March 1945, a single D4Y managed to hit the carrier USS Franklin with two bombs, nearly sinking Franklin and resulting in the loss of almost 800 of her crew. A D4Y was used in one of the final kamikaze attacks in 1945, hours after the surrender of Japan, with Vice Admiral Matome Ugaki in the rear cockpit. (Wikipedia)
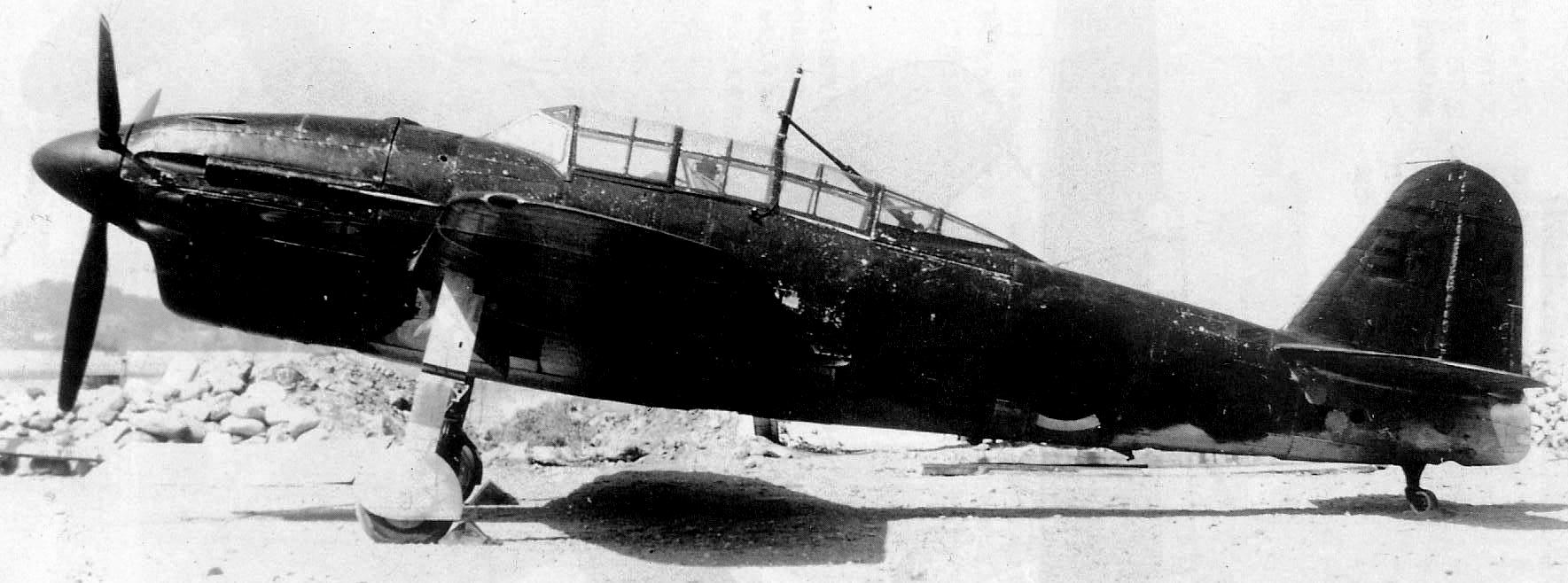
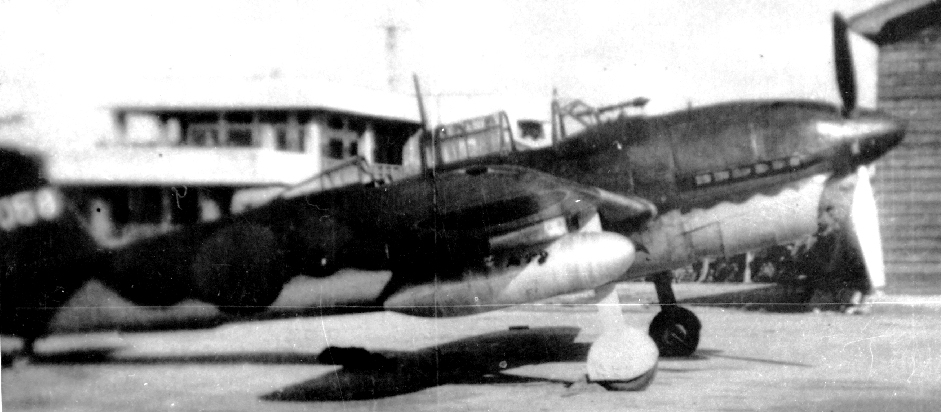



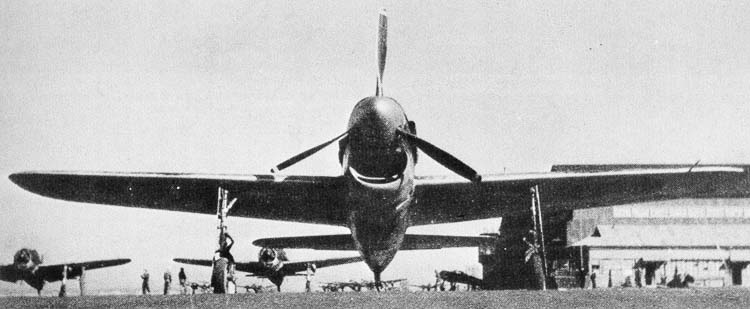


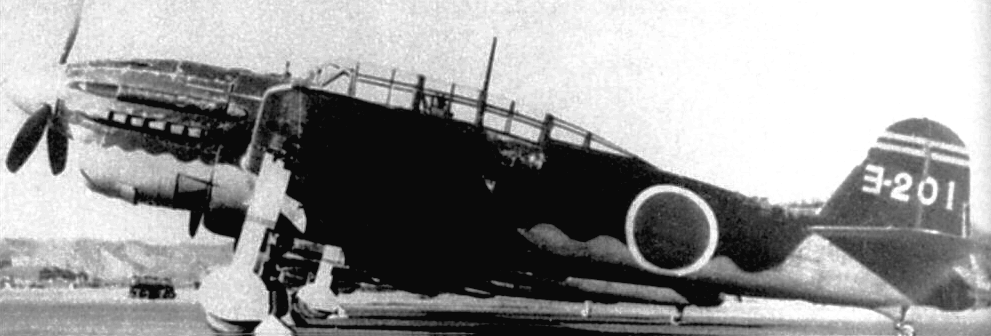




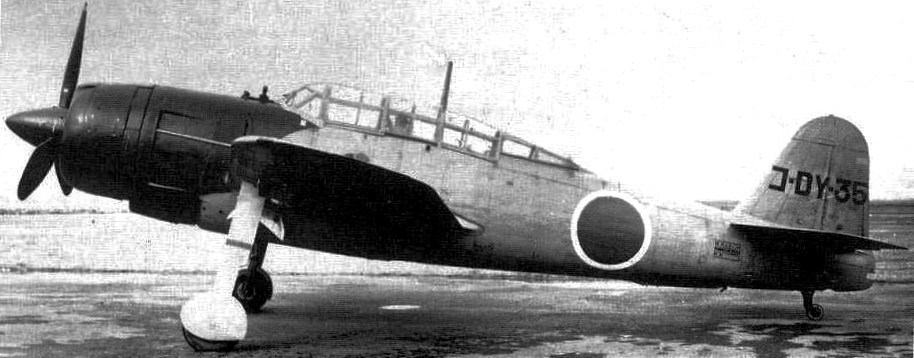


(IJAAF Photos)
Yokosuka/Kugisho D4Y2 Susei (Comet) Navy Type 2 Carrier Reconnaissance Plane Model 33 (Judy).

(USN Photo)
Yokosuka/Kugisho D4Y2 Susei (Comet) Navy Type 2 Carrier Reconnaissance Plane Model 33, codenamed Judy, in USAAF markings.

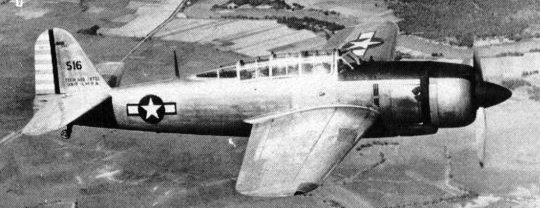
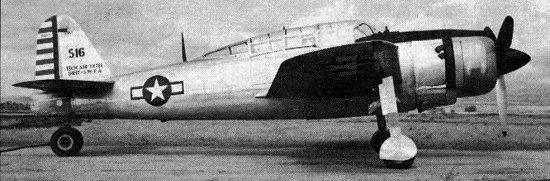

Yokosuka/Kugisho D4Y2 Susei (Comet) Navy Type 2 Carrier Reconnaissance Plane Model 33, codenamed Judy, (Serial No. 3957), captured at Clark Field in the Philippines, in TAIC-SWPA S16, USAAF markings.. It was flight tested at NAS Anticosti post war. (USN Photos)


Yokosuka D4Y4 Susei (Serial No. unknown), one of two Kugisho-built D4Y4s shipped to the USA. This aircraft was designated USAAF FE-1201. It was scrapped at Middletown, Pennsylvania. It was one of two Kugisho-built D4Y4s shipped to the USA. This aircraft was designated USAAF FE-1203. It was scrapped at Park Ridge ca. 1950. (USAAF Photos)
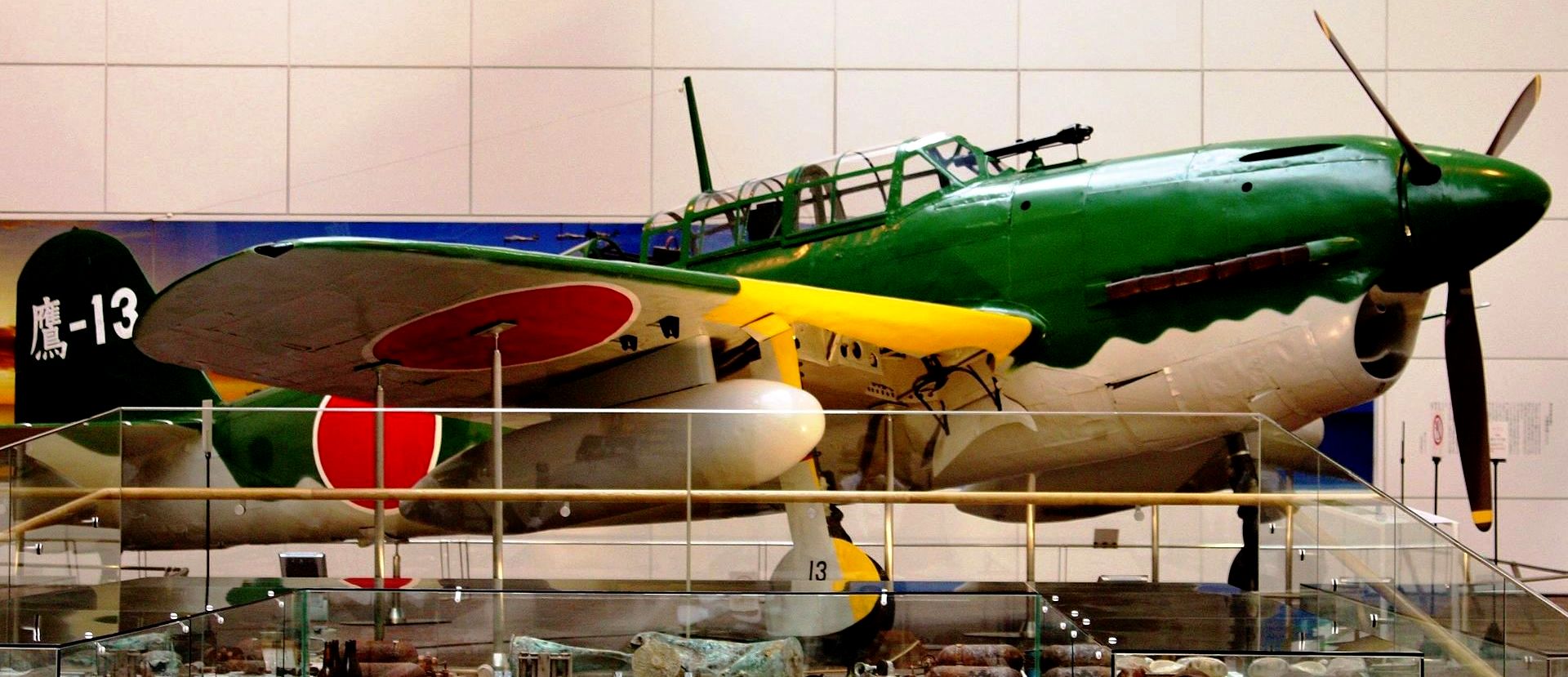
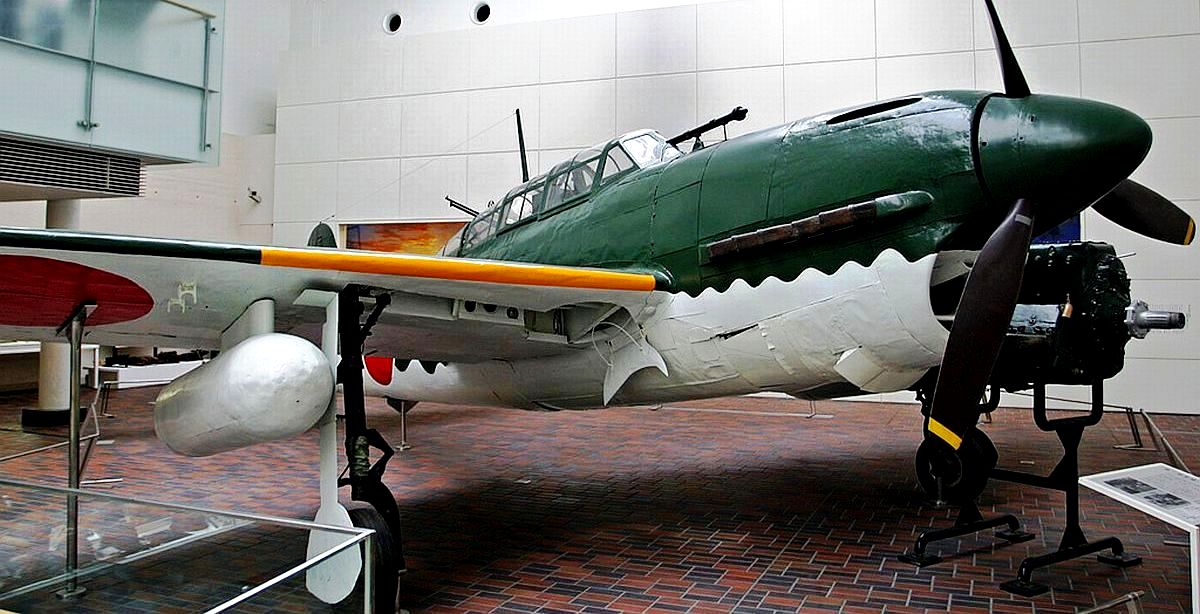
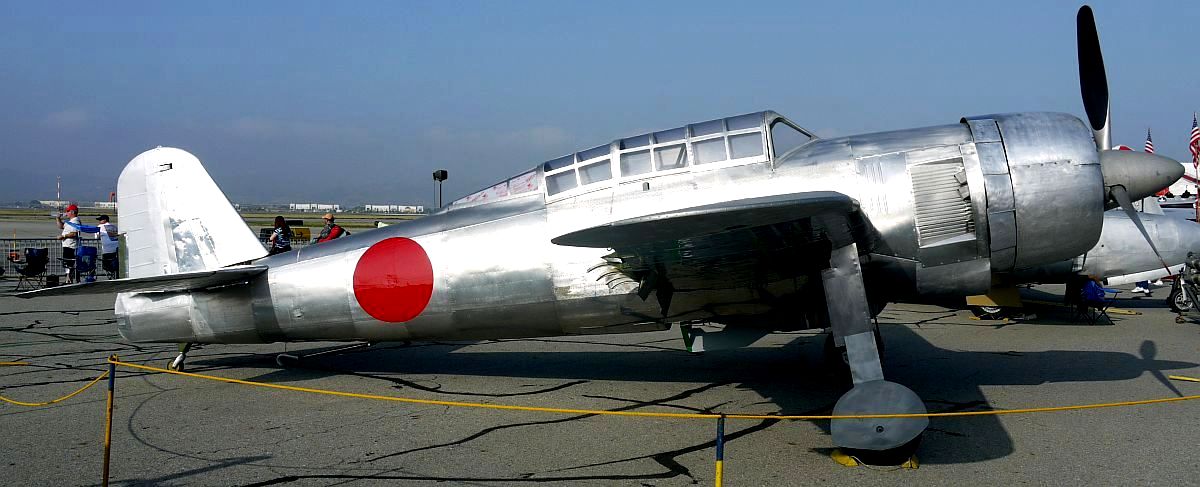
The Yokosuka D4Y Suisei (Comet) Navy Carrier Dive bomber codenamed “Judy” was operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. The D4Y was one of the fastest dive-bombers of the war. A surviving restored D4Y1 (Serial No. 4316) is located at the Yasukuni Jinja Yushukan shrine in Tokyo. A second example, an engineless D4Y1 (Serial No. 7483) was recovered from Babo Airfield, Indonesia in 1991 and as of 2012 has been restored/rebuilt by the Planes of Fame Air Museum in Chino, California to non-flying (but taxiable) condition as a D4Y3. The installed radial engine is American.

(Chirokostage Photo)

(YJY Photo)
Yokosuka D4Y1 Susei (Serial No. 4316) on display in the Yasukuni Jinja Yushikan shrine in Tokyo.

(PoF Photo)
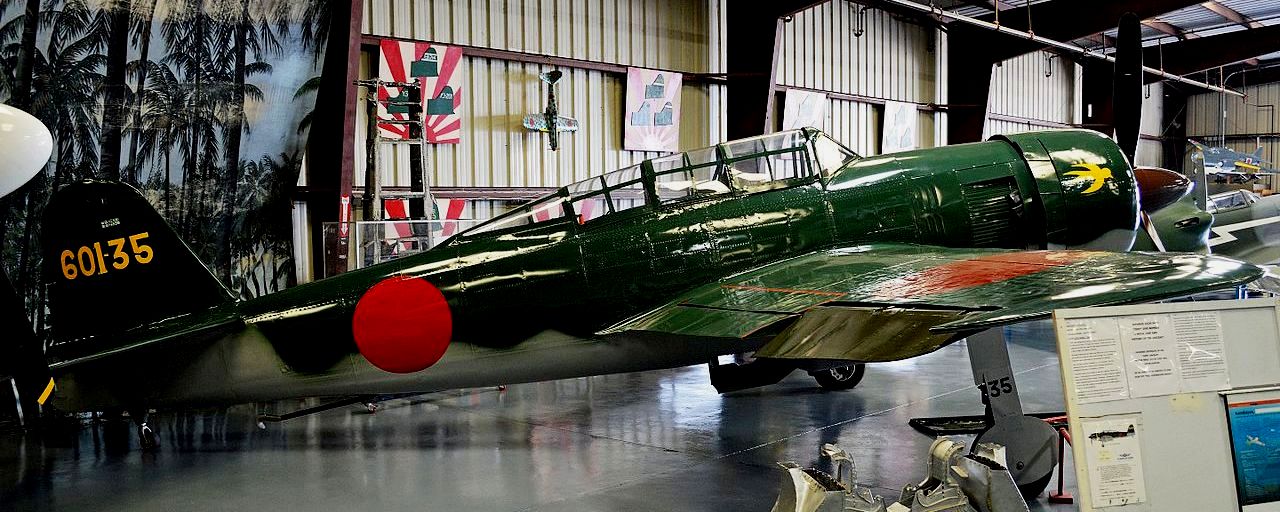

(Alan Wilson Photo)
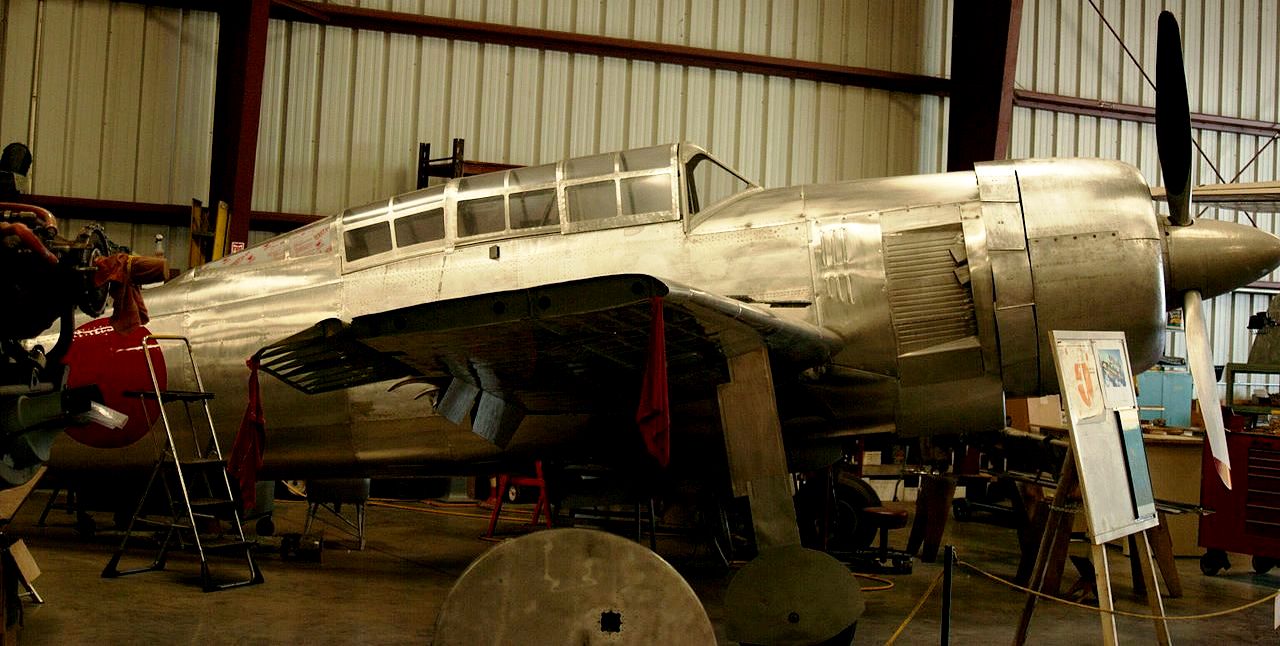

(Dustin May Photo)
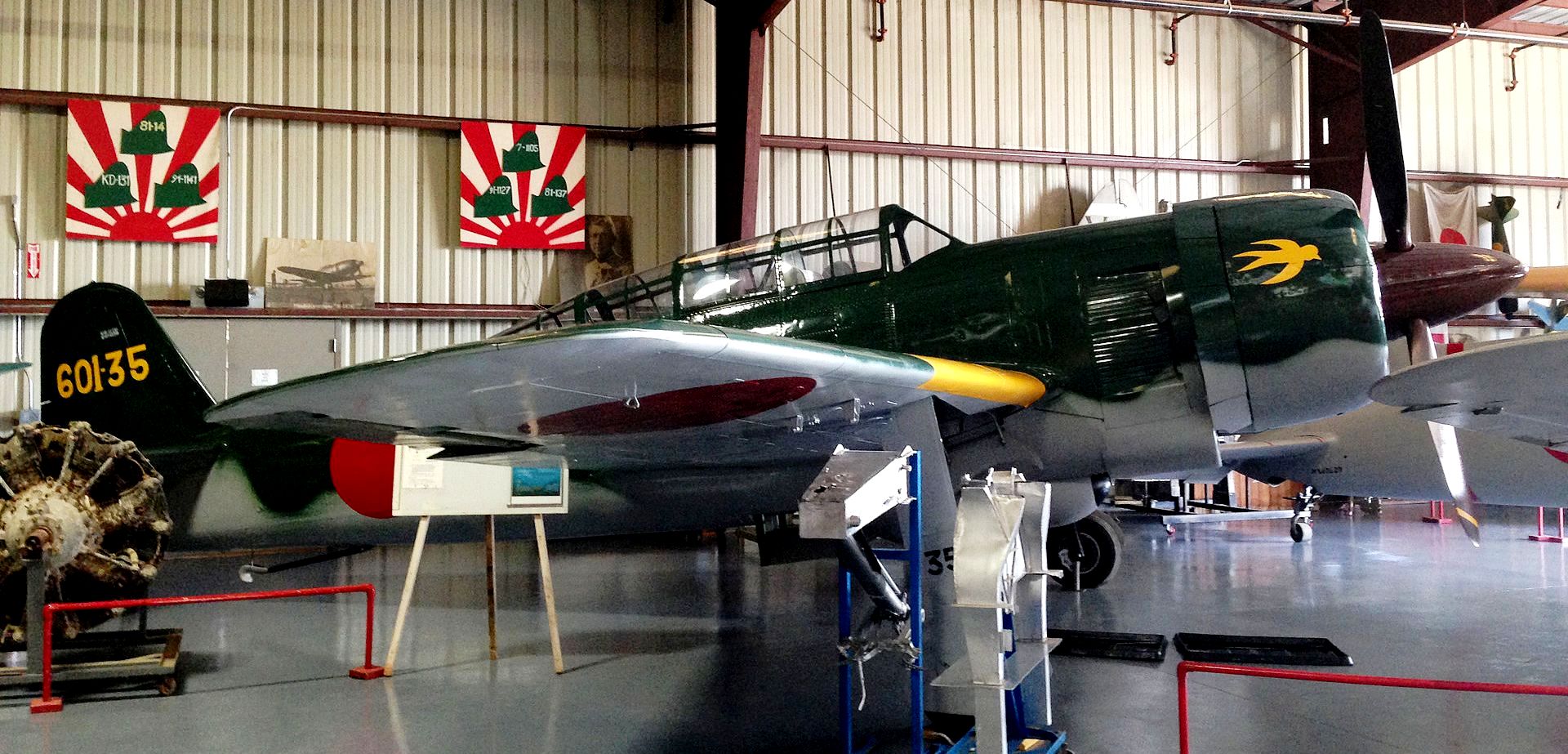

(Howard Shen Photo)
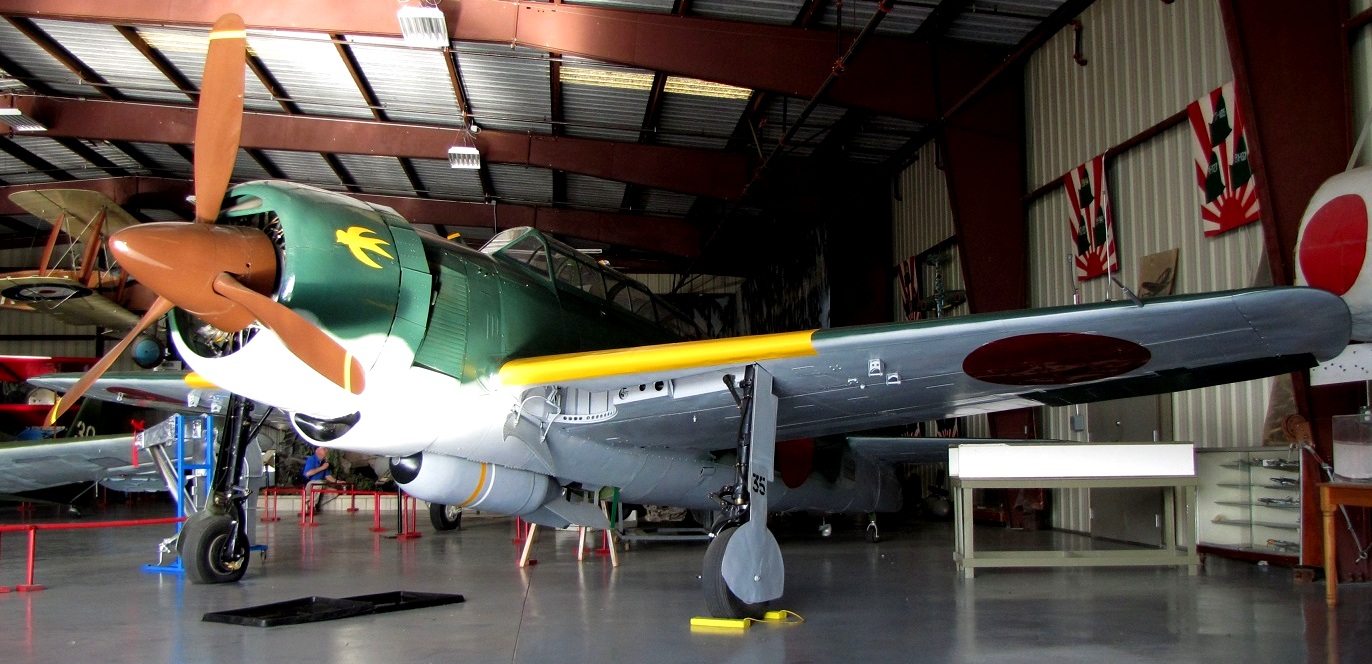

(Goshimini Photo)
Yokosuka D4Y Suisei (Serial No. 7483) Navy Carrier Dive bomber, Planes of Fame Museum, Chino, California.
